Account Configuration interface guide
The Account Configuration interface is where administrators, superadmins, and supervisors can configure and administer an Unblu account. (Supervisors can only administer their teams and the agents in their teams.)
Users with the necessary rights to access the Account Configuration interface have an Administration section in their Agent Desk user menu. The section contains a link labeled Account settings which opens the Account Configuration interface.
This guide discusses each of the sections of the navigation menu in the Account Configuration interface. Which sections a user actually sees depends on what they’re allowed to change. If you can’t see a certain item, it means you aren’t authorized to change it.
A number of the sections in the Account Configuration interface include tabs labeled General, Settings, and Texts, respectively. These tabs have a lot of features in common across the various sections. It therefore makes sense to first discuss what you can do in these tabs, and how to do so.
The configuration tabs General, Settings, and Texts
This section describes what the tabs mentioned in the title have in common across various sections of the Account Configuration interface.
The General tab
The General tab contains general information about the entity it pertains to.
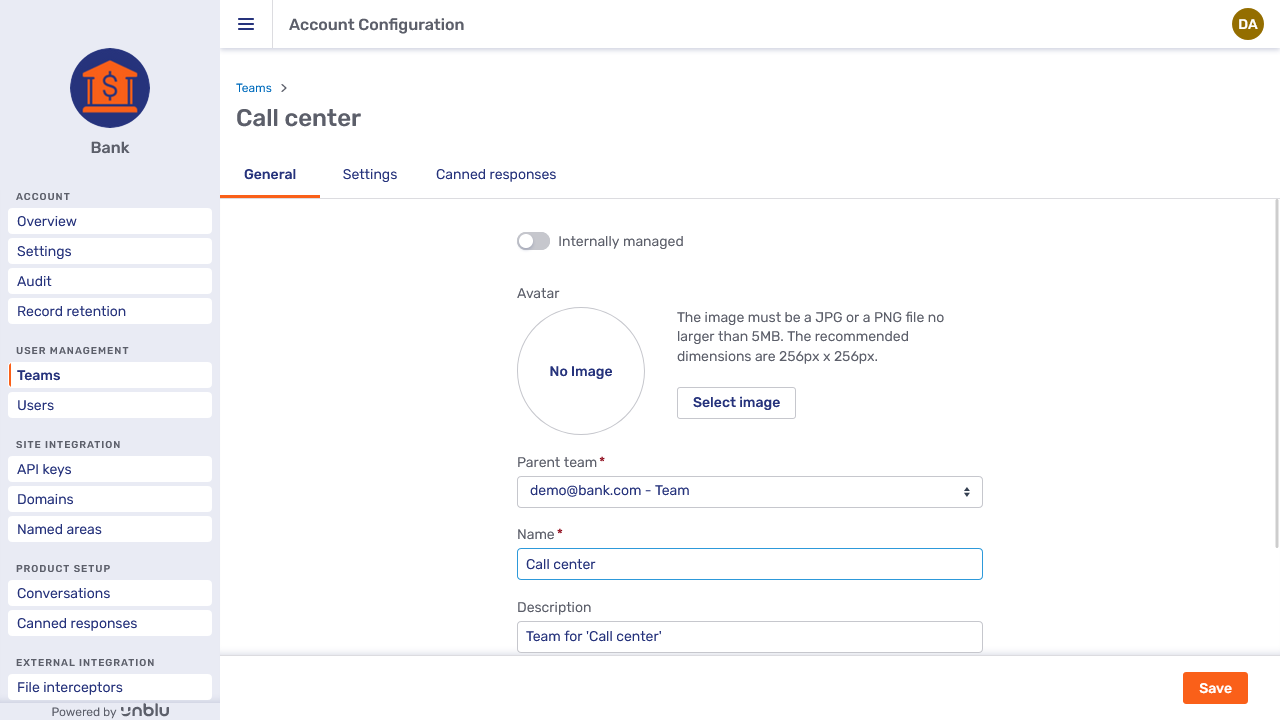
As a rule, you can edit the entity’s name and its description. You can also upload a file to use as the entity’s avatar if it’s meant to have one.
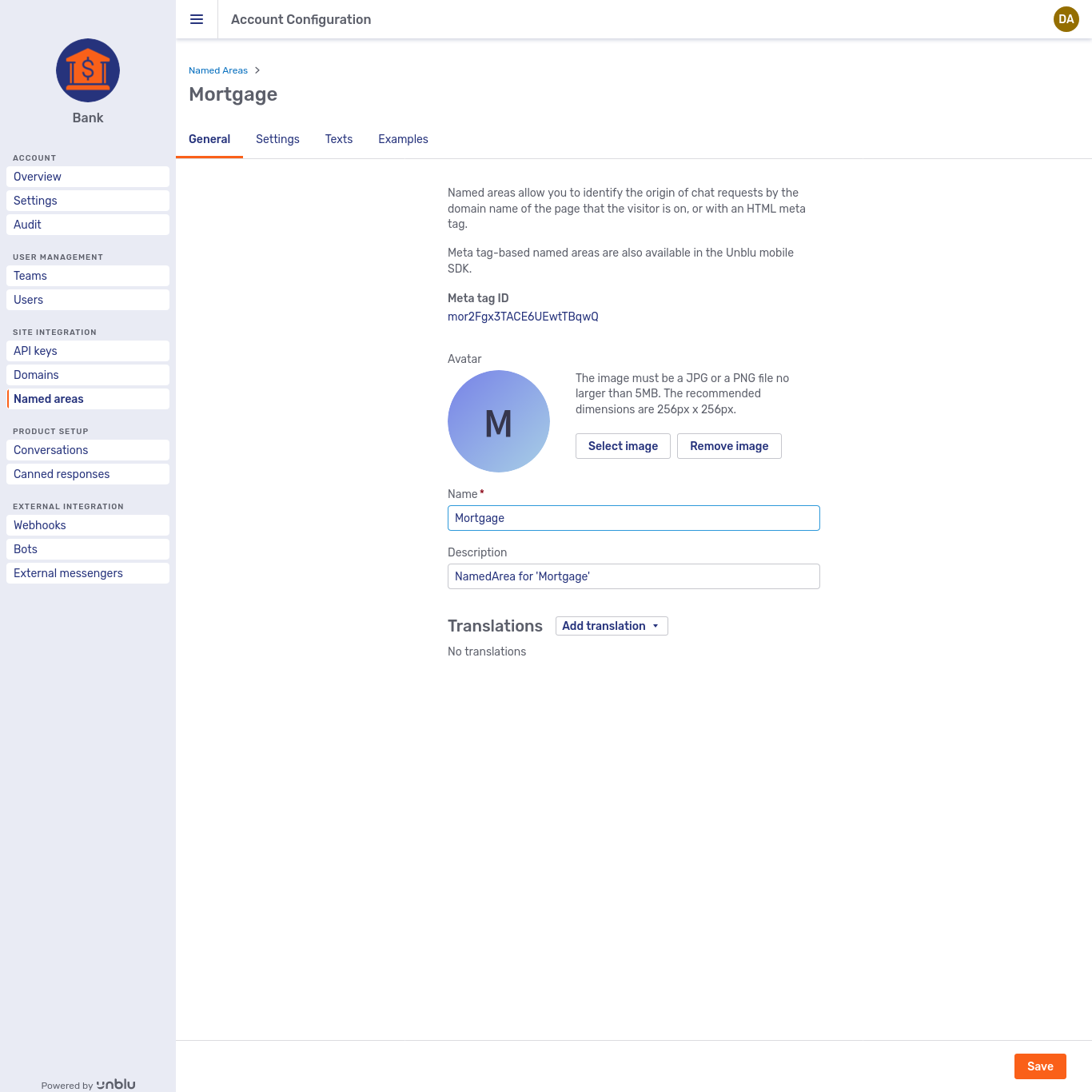
The General tab for some entities offers—or requires—additional information. For example, contrast the tab for the Call center team pictured above with the one for the named area Mortgage below.
Translations
The names and descriptions of some entities appear in UIs accessible to visitors or agents. The General tab for these entities—accounts, conversation templates, named areas, and teams—has a Translations section where you can provide localized versions of the name and description.
To add a translation:
-
Click Add translation and select the language you want to add a translation for.
-
In the form that appears, enter the name of the entity in the language you selected. You can also provide a localized description of the entity.
Adding a German translation to the named area "Mortgage"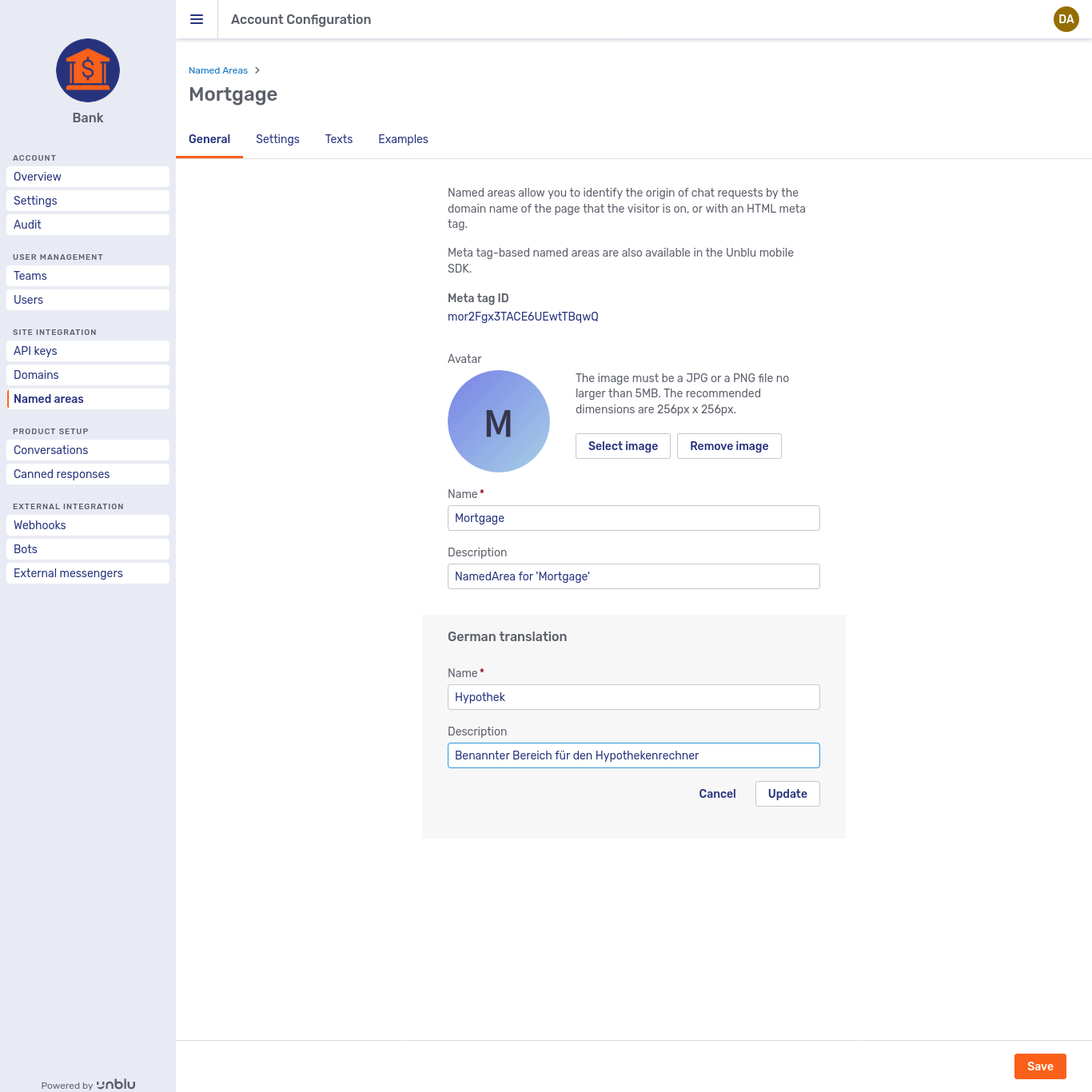
-
Click Update to add the translation to the entity. The translation now appears on the General tab.
The named area "Mortgage" with a German translation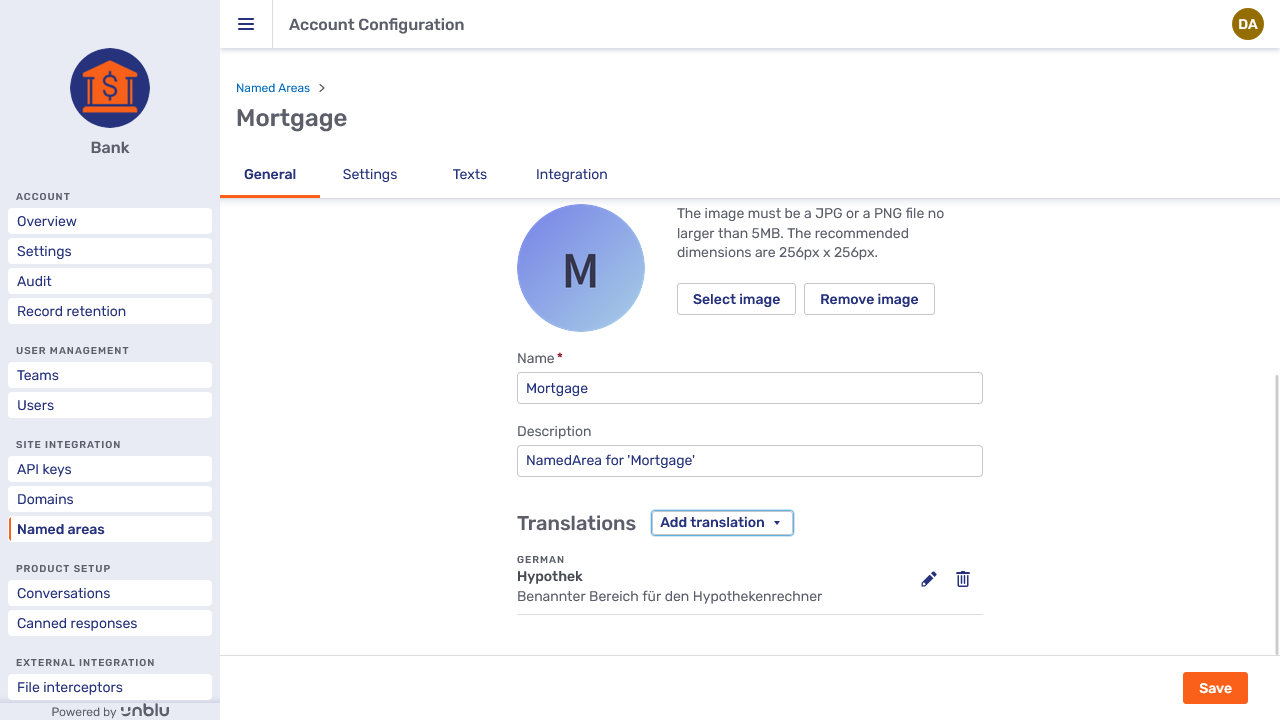
To edit the translation, select the edit button
.
Selecting the delete button
deletes the translation without warning or confirmation.
-
Repeat steps 1—3 for each language you want to add translations for.
| Once you’ve finished adding translations, click Save. They’re deleted if you don’t. |
The languages you’ve added translations for are listed on the overview page for the entity in question.
The Settings tab
The Settings tab lets you change configuration properties for the entity it’s related to.
This is the default view of the Account Settings tab:
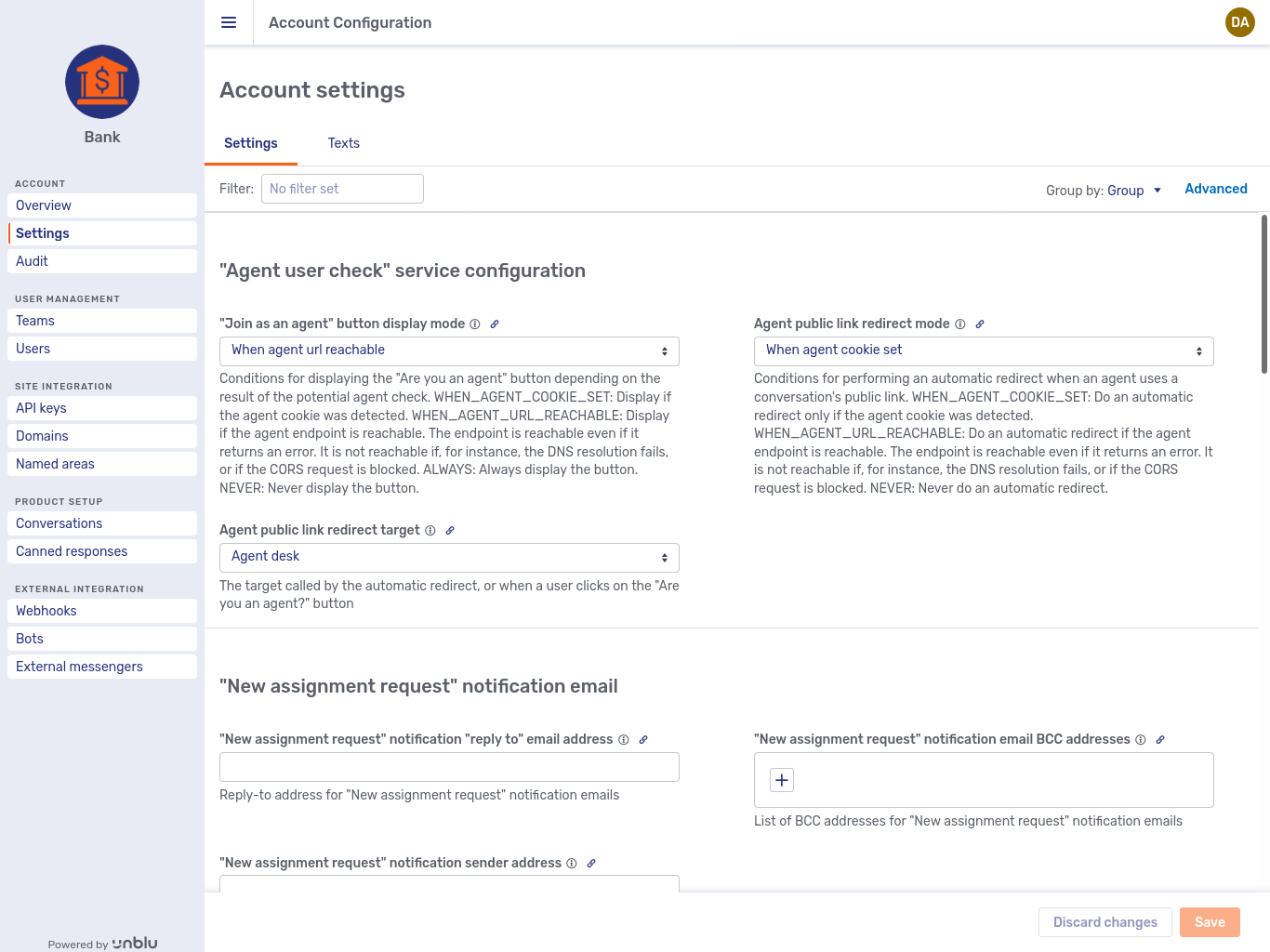
Unlike the General tab, the Settings tab looks the same for all entities, albeit with different settings you can change. The settings you can change here are the configuration properties for which the entity is in scope.
Next to the configuration property’s label, there are usually two icons, the Information icon 

-
Hovering over the information icon displays additional information about the configuration property, such as its full key and its default value.
If you clicked the Advanced button, the information in the hover box includes the cascade of the property’s values.
-
Clicking the link icon opens a modal dialog with a link to the configuration property that you can copy and share with other users.
Beneath the label, you see the full name of the configuration property. The Copy icon 
Some configuration properties depend on other configuration properties. For example, the property Enable push notifications by email (com.unblu.core.push_notification.mail.enableEmailPushNotification) depends on Enable push notifications (com.unblu.core.push_notification.enablePushNotification). If a property has dependencies, the Account Configuration interface tells you beneath its full name whether its dependencies are met or not. Clicking the Dependencies or Unmet dependencies link displays a list of all the configuration properties that the property you’re viewing depends on. Each dependency has a Copy icon next to its full name.
Before you can change a property with unmet dependencies, you must make sure those dependencies are satisfied. You can’t edit properties with unmet dependencies.
If the value of a setting is defined on a particular entity, as opposed to the entity inheriting the value from an entity higher up the configuration cascade,you see a Cross button 
In the picture below, the settings Enable video archiving and Session Type have been changed for this account, thereby overriding the value for the setting defined globally. Note the blue edge of the checkbox and the green edge on the dropdown. Clicking the Cross button, deletes the value of the setting defined for the account. The setting is still visible in the account settings, but now it inherits the value specified at the global level.
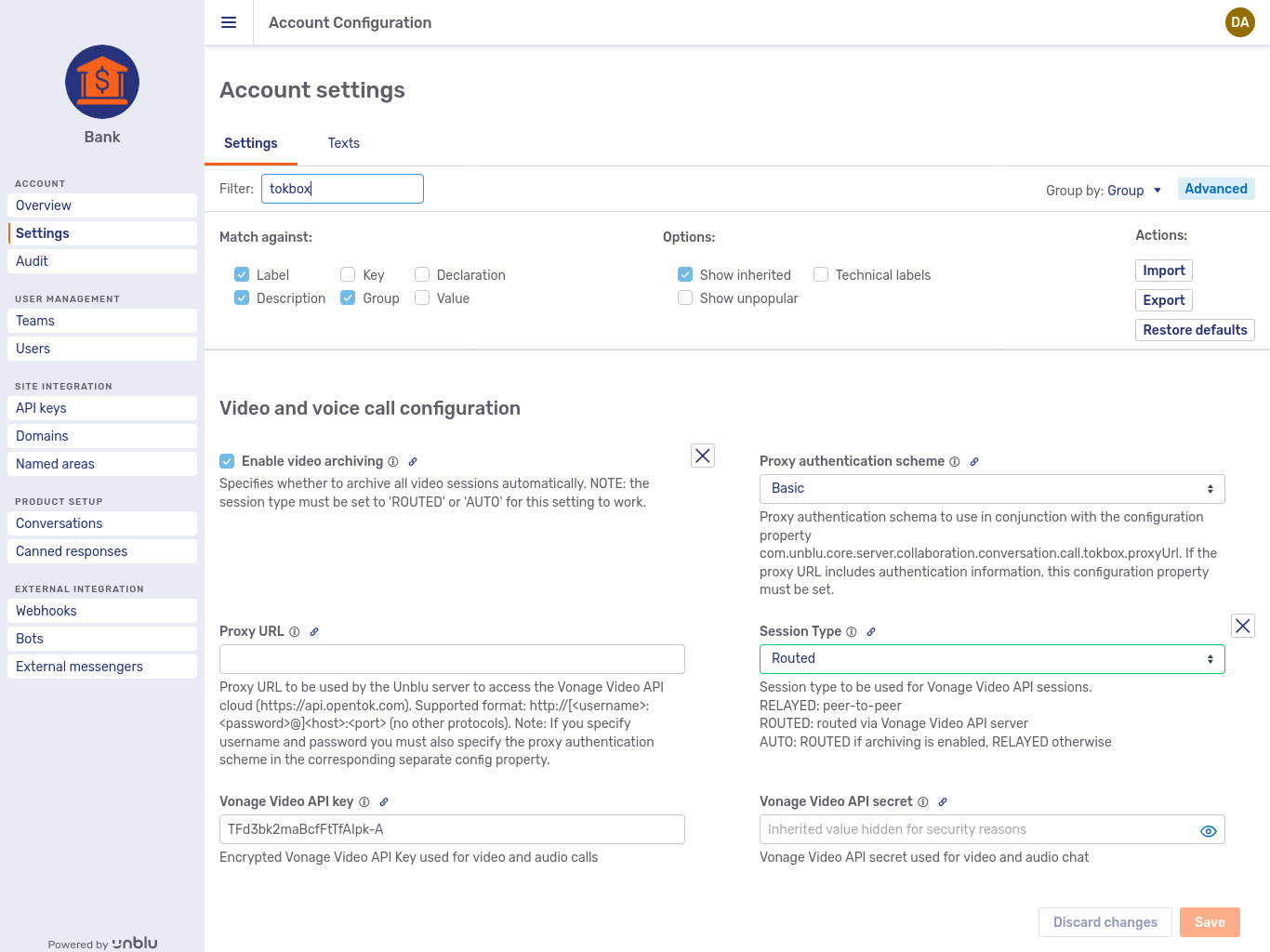
By default, settings are grouped under the same headers as in the configuration properties reference. The groups are listed in alphabetical order, as are the settings within each group. You can change the grouping with the Group by dropdown to the left of the Advanced button above the list of settings.
The Advanced button, in turn, opens an accordion containing two sets of checkboxes and three buttons:
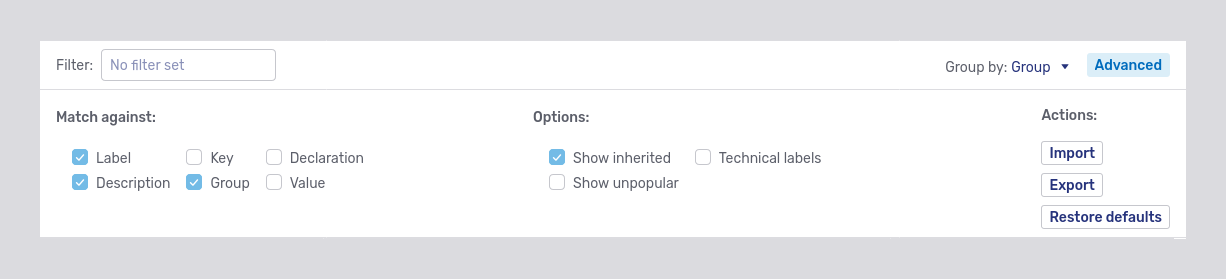
The checkboxes provide additional functionality for the filter. The buttons under the Actions heading are used for bulk operations.
The Settings filter
The filter above the list of settings allows you to reduce the number of the settings displayed on the page. Simply enter a term to limit the list to groups and settings that use that term in their label or description.
To determine more specifically which settings should be shown, use the checkboxes in the Advanced accordion. The checkboxes under the heading Match against define which fields of a setting the filter should be applied to.
Suppose, for example, that you want to experiment with the configuration property com.unblu.queue.ui.autodispatching.autoDispatchedQueueCategories for automatic request dispatching. Searching for "autoDispatchedQueueCategories" won’t return any results with the default filter settings. This is because the term only appears in the property’s key, which the default filter settings don’t taken into consideration. Once you tick the Keys checkbox and search again, it does return a result:
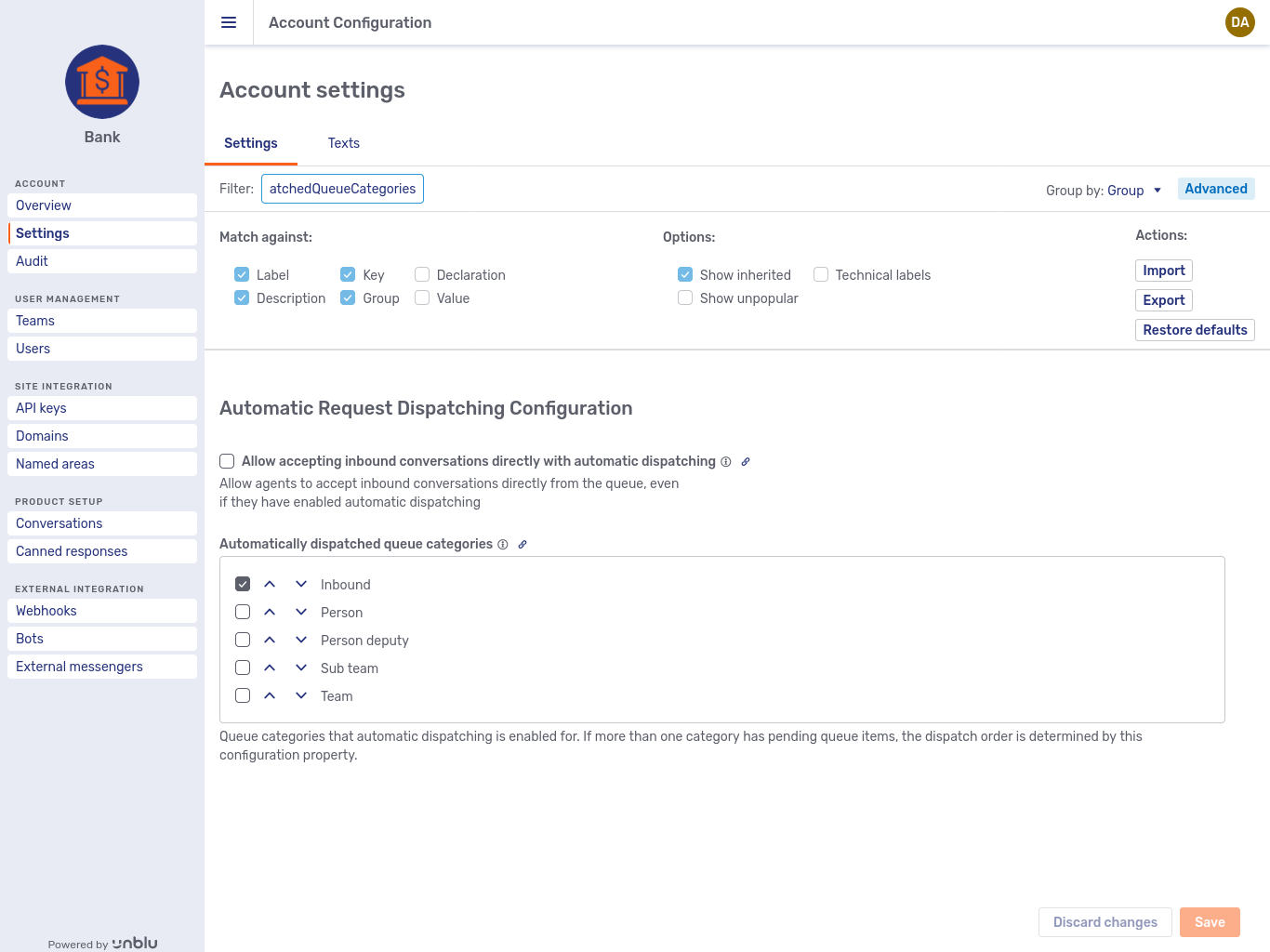
What you enter in the Filter field is treated as a simple string, not as a regular expression or a search expression. If you enter "queue item", say, that is exactly what it will look for; it won’t find "queue of the item".
The options available for filter matching are:
- Declaration
-
The Declaration checkbox is mainly for internal use. It matches the filter against the name of the Java class that a setting is defined in.
- Description
-
This will include settings in the results whose description includes the filter term. Each setting’s description is displayed beneath the setting itself in the Settings tab.
- Group
-
The Group option matches the filter against the header that settings are grouped under. This is useful when the setting labels differ from the term you might expect, or when you want to review all of the settings in a group.
- Key
-
This is the name of the configuration property that corresponds with the setting.
- Label
-
The label is a more human-friendly name for a setting. In the configuration properties reference page, the label is used as the heading beneath which a configuration property is listed.
- Value
-
Tick this checkbox to match the filter to settings' values.
By default, the Description, Group, and Label filters are active.
The checkboxes under the Options heading provide additional ways to influence the settings tab:
- Show inherited
-
With this option ticked, settings inherited by the current scope as part of the configuration cascade will also appear in the settings tab. For example, if you are in a user’s settings tab and Show inherited is ticked, then all settings that apply to that user. The setting may have been set on the user’s team, or it may be the default value specified at, say, the
GLOBALlevel.Compare the two pictures below. In both cases, the filter has been set to agent availability. In the first picture, Show inherited is ticked, and you see four settings, three of which are inherited from the
GLOBALscope.Account settings with Show inherited ticked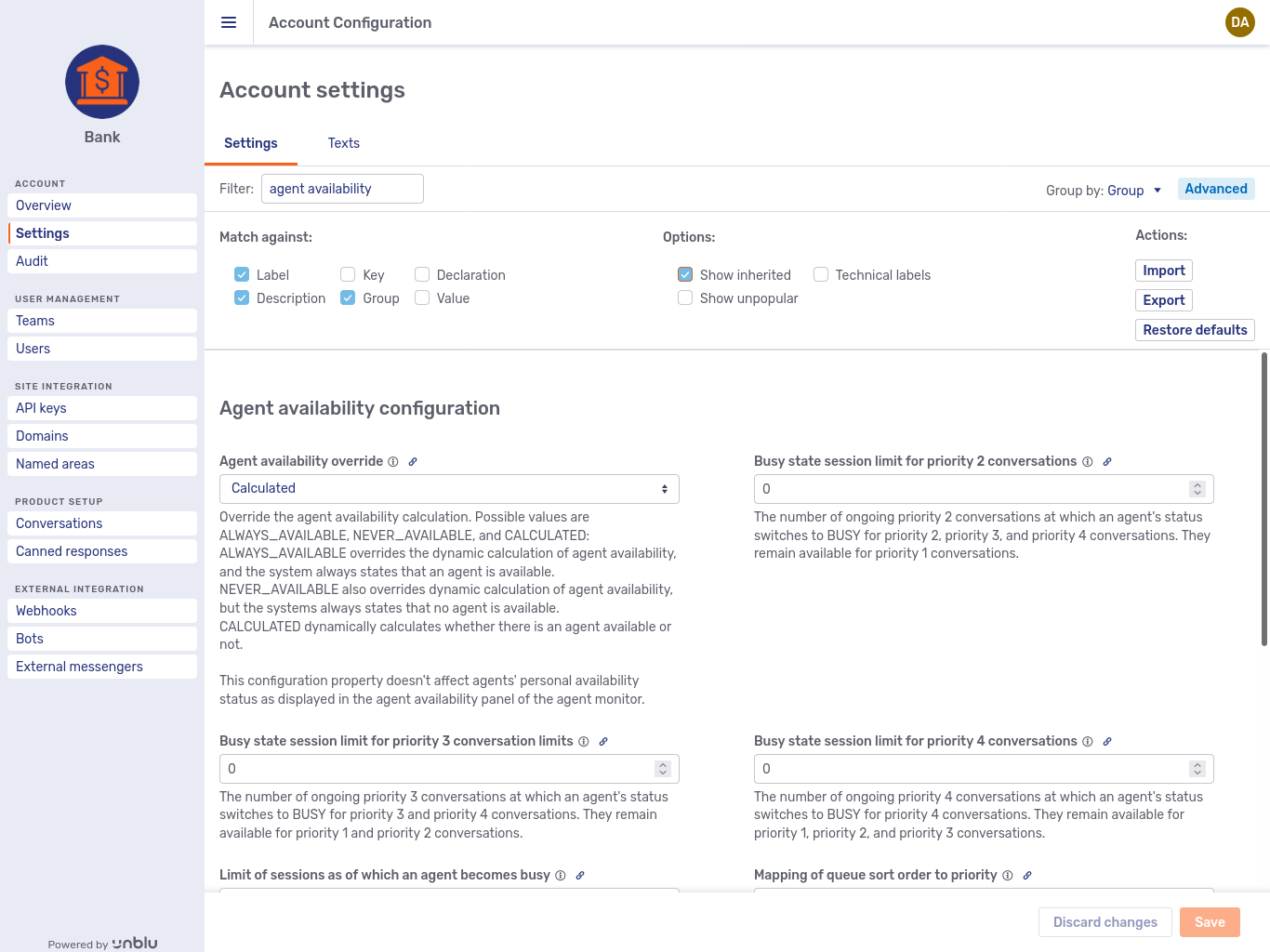
In the second picture, Show inherited is unticked, so you see only the setting defined on the account itself:
Account settings with Show inherited unticked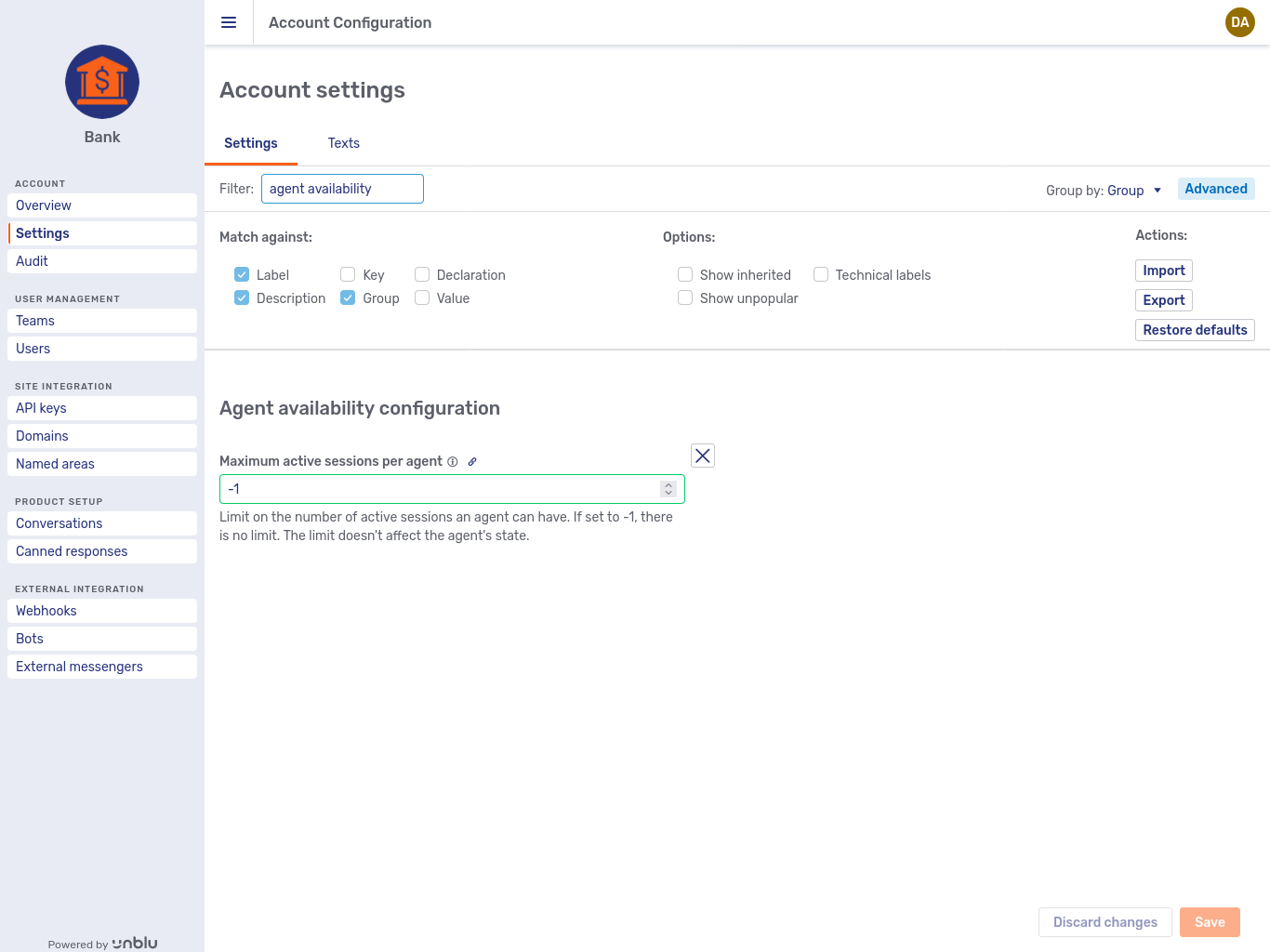
- Show unpopular
-
Tick this box to display settings with a visibility level other than popular.
- Technical labels
-
If you tick this box, the name of the configuration property will be displayed rather than the setting’s label. The
com.unbluat the beginning of every configuration property is omitted from the technical label.
By default, the following checkboxes are ticked:
-
Description
-
Group
-
Label
-
Show inherited
If you aren’t sure what the setting you are looking for is called, we recommend starting off with all of the checkboxes ticked and then narrowing down the number of settings displayed by unticking one box after the next.
Bulk operations
The Advanced accordion contains three buttons for bulk operations:
-
The Import button allows you to change settings in bulk by uploading a JSON file containing the relevant configuration properties. Here is an example file:
Listing 1. JSON file containing configuration properties for an account{ "version": 1, "scope": "ACCOUNT", "type": "CONFIGURATION", "data": { "properties": { "com.unblu.cobrowsing.startwithuniversalcobrowsingoptionenabled": "false", "com.unblu.hbworker.googleviewersupportedmimetypes": "[\"application/msword\",\"application/vnd.ms-excel\",\"application/vnd.ms-powerpoint\",\"application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation\",\"application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet\",\"application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document\",\"text/plain\"]", "com.unblu.core.push_notification.enablepushnotification": "true", "com.unblu.session.inboundconversationreservationtimeout": "100000", "com.unblu.cobrowsing.startwithmobilecobrowsingoptionenabled": "true", "com.unblu.core.server.livetracking.agent.availabilityoverride": "NEVER_AVAILABLE", "com.unblu.conversation.call.tokbox.apiSecret": "d401724a7c1t5a53cr379cb6f71ab188573f5346", "com.unblu.conversation.call.tokbox.enablearchiving": "false", "com.unblu.agent.mobile.ui.showinboxactionbar": "false", "com.unblu.conversation.call.tokbox.apiKey": "NQFg_1t5a53cr37PIqWlUA", "com.unblu.cobrowsing.startwithscreensharingoptionenabled": "true", "com.unblu.mobile.push_notification.firebasedatabasename": "unblu Companion",(1) "com.unblu.visitor.ui.showoverviewactionbarminmaxaction": "true", "com.unblu.conversation.messaging.ui.chatmessageasmarkdownenabled": "true", "com.unblu.visitor.ui.alwaysdisplayrecipientinconversationoverview": "true", "com.unblu.chat.videochat.sessiontype": "ROUTED", "com.unblu.hbworker.localsitesallowed": "false", "com.unblu.queue.ui.autodispatching.autorequestdispatchingenabled": "true", "com.unblu.queue.ui.enablefilterchanges": "true" } } }1 This is the firebase project ID. Unblu doesn’t need a firebase database. -
The Export button generates a JSON file of the settings defined in the scope you are currently viewing. The file doesn’t contain settings inherited from entities further up the configuration cascade.
Export files are formatted as follows:
<ownerType>_<dataType>_<ownerId>_ISO8601Date.json-
ownerType: Global/Account/APIKey/NamedArea/Team/User -
dataType: CONFIGURATION or TEXT -
ownerId: The ID of the entity -
ISO8601Date: Current timestampHere is an example of what the exported JSON filename looks like at the Account level for configuration properties:
Account_CONFIGURATION_wZvcAnbBSpOps9oteH-Oxw_2017-05-12T11-00-44.json
-
If you want to import or export more complex selections of configuration data for multiple entities, see the utransfer utility. |
-
The Restore Defaults button restores the default settings for the entity whose settings you are currently viewing. Any changes you made to the entity’s settings will be deleted.
The Texts tab
The Texts tab contains the text properties relevant to the entity you are viewing.
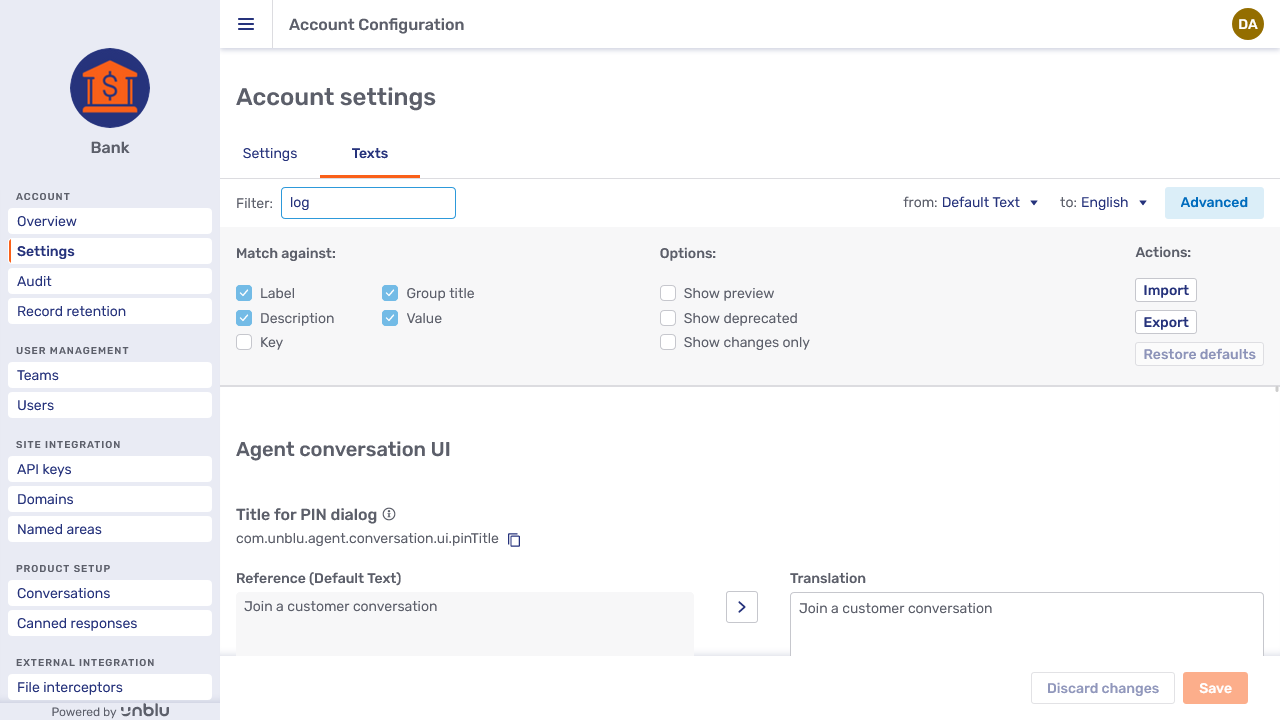
In the picture above, the Advanced accordion is open. It contains the same checkboxes and buttons as on the Settings tab, and the various elements have the same effect. Note also that the Restore Defaults button is not active. This is because the current texts are equivalent to the defaults.
Next to the Group by dropdown there are two further dropdowns to set the language being translated from and to, respectively. The text you are translating from is referred to as the reference language in the list. Texts in the reference language are displayed on the left of the result list.
The language you select from the to dropdown is the target language of your translation, displayed on the right of the result list. We supply a number of pre-translated versions but you can supply your own translations by writing them in the Translation box and saving.
The Fallback Text entry in the language selection dropdowns refers to the text Unblu will use if there is no translation of a text available in the language required. It is always the English text.
The list of text properties
Like settings, texts are grouped under the same headers as they are on the text properties reference page, with groups listed in alphabetical order. Text properties within groups are also listed alphabetically.
Below some Translation text fields, there are terms in orange boxes. These terms are variables that you can use in this particular text. In the screenshot above, the text for Subject of new message notification email provides three variables, conversationId, participantNames, and recipientName. participantNames has already been used in the translation, so its color is paler than that of the other two variables.
To use a variable in a text simply click it. This will add the variable to the translation, surrounded by curly brackets and preceded by a dollar sign, e.g. ${participantNames}. (You can, of course, type the variable reference in the text field yourself.)
The Arrow button 
Text bulk operations
Bulk operations work the same as on the Settings tab.
Here is an example of a JSON file containing text properties as generated by the Export button. Note that the name of the text property has the locale it is to be used in at the end, .en in this case:
{
"version": 1,
"scope": "ACCOUNT",
"type": "TEXT",
"data": {
"supportedLocales": [
"cs",
"de",
"en",
"es",
"fr",
"it",
"pl",
"pt",
"ro",
"ru",
"sk",
"sl",
"sr",
"sv",
"zh-Hans",
"zh-Hant"
],
"properties": {
"com.unblu.conversation.messagelog.mail.logentryformat.en": "At ${serverUtcTime}, ${senderName} wrote: ${messageText}"
}
}
}Account
The Account section provides information on and access to settings that affect the entire account.
Overview
The Overview page displays basic information about the account you are viewing, including information about the licenses for the account:
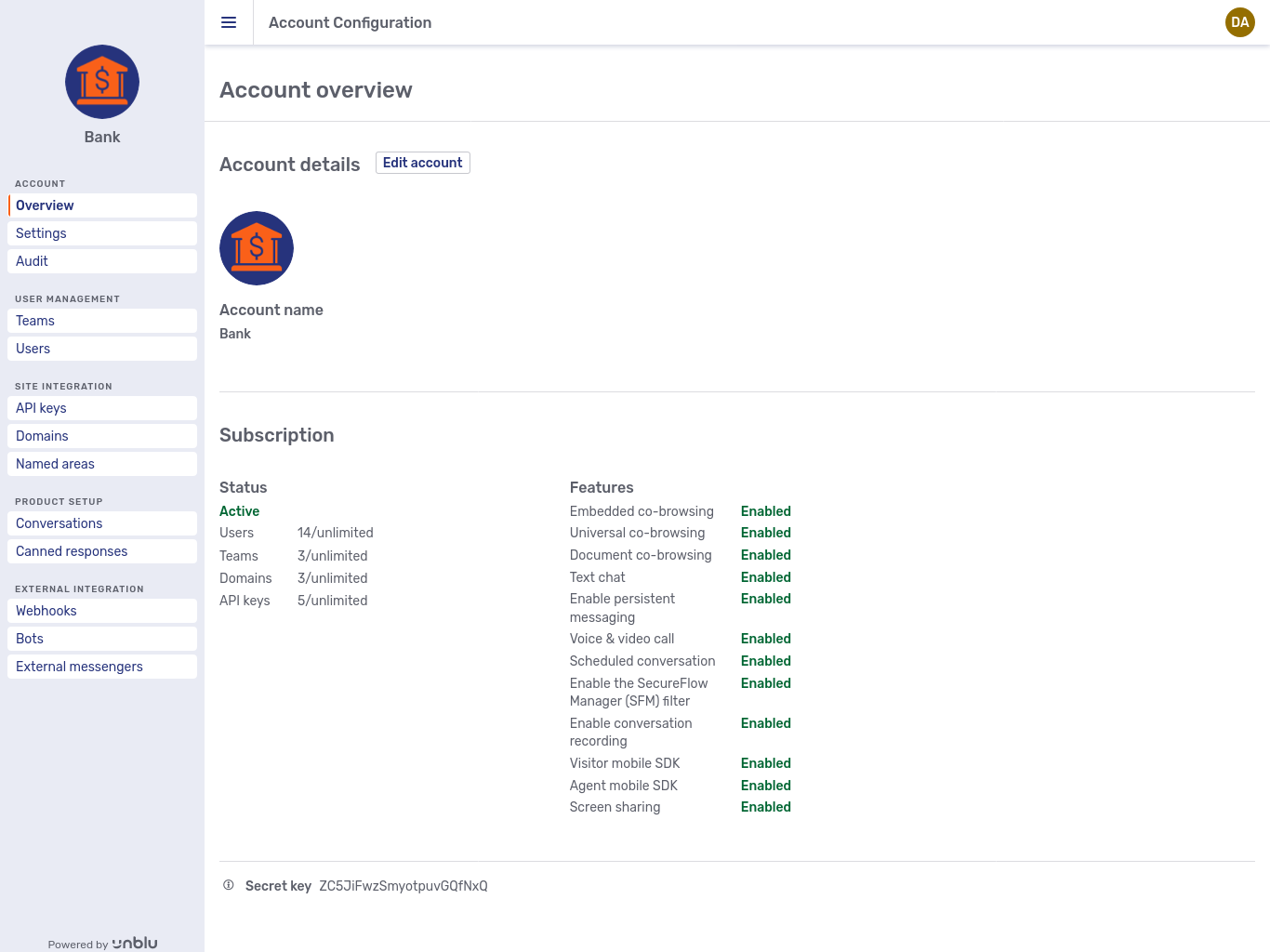
Clicking the Edit account button in the account overview opens the Edit account fly-in page.
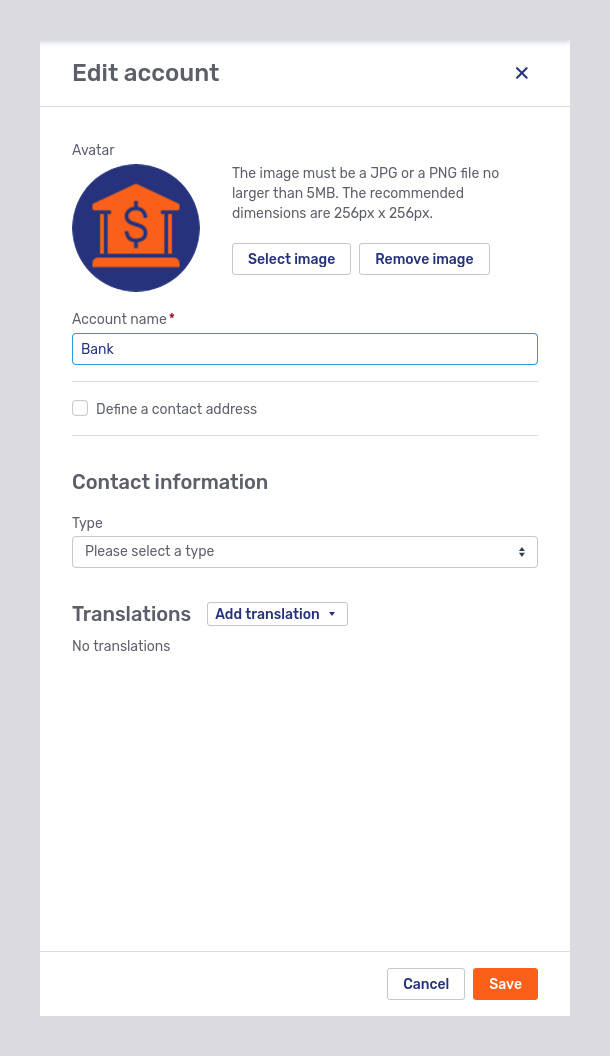
If you tick the Define a contact address box, a form appears where you can enter the contact address. If you want to add a different billing address, tick the Use a separate billing address box to display additional form fields for this purpose.
The Type dropdown in the Contact information section allows you to add a phone number, email address, or website URL of the account. You can add more than one type of contact information.
Settings
The Settings entry in the navigation menu provides access to the account’s Settings and Texts tabs. Changes you make here are inherited by entities below the account in the configuration cascade.
Both tabs work as outlined above.
SECRET and MULTILINE_SECRET configuration properties
The values of configuration properties of the types SECRET and MULTILINE_SECRET aren’t displayed in the Settings tab. The visibility toggle 
Once you refresh the page, the toggle longer works.
Audit
The Audit section gives administrators access to the account’s audit log, which provides a record of users' interactions with Unblu.
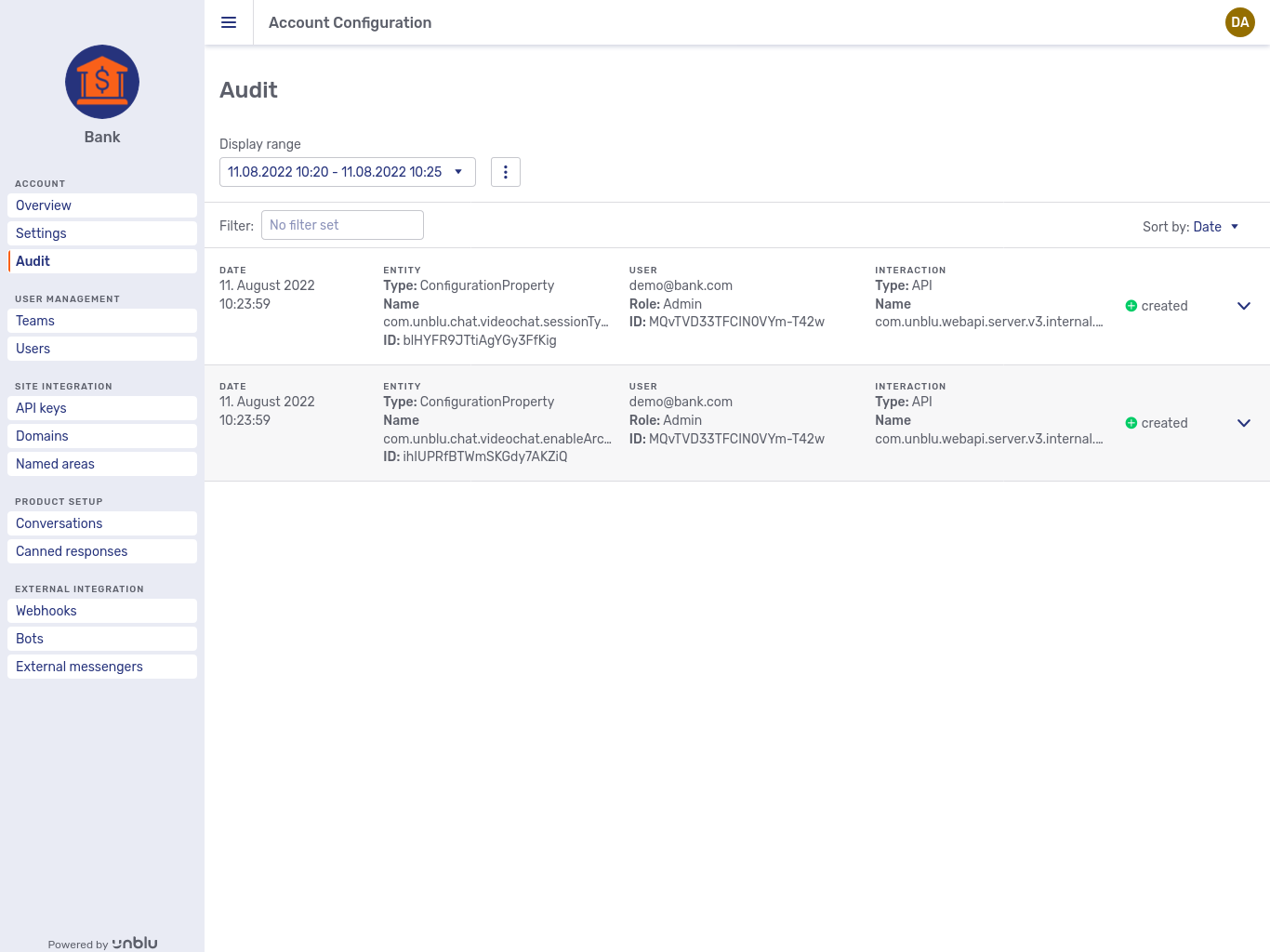
The view opens with a list of the audit log entries of the current day. Each entry in the list contains the following information:
-
The date and time the entry was added to the audit log.
-
A description of the entity that the log entry refers to. The description includes the name, ID, and type of the entity that triggered the log entry.
-
Information on the user who carried out the action that was logged. The details displayed include the user’s username and their user role.
-
The type of interaction. This includes the name of the operation, and how the operation was performed: via the UI or the Unblu web API, for example. The different interaction types are described below.
-
The change type. This specifies whether the operation created, updated, or deleted the entity in question.
By clicking an item, you can expand the entry to display additional information:
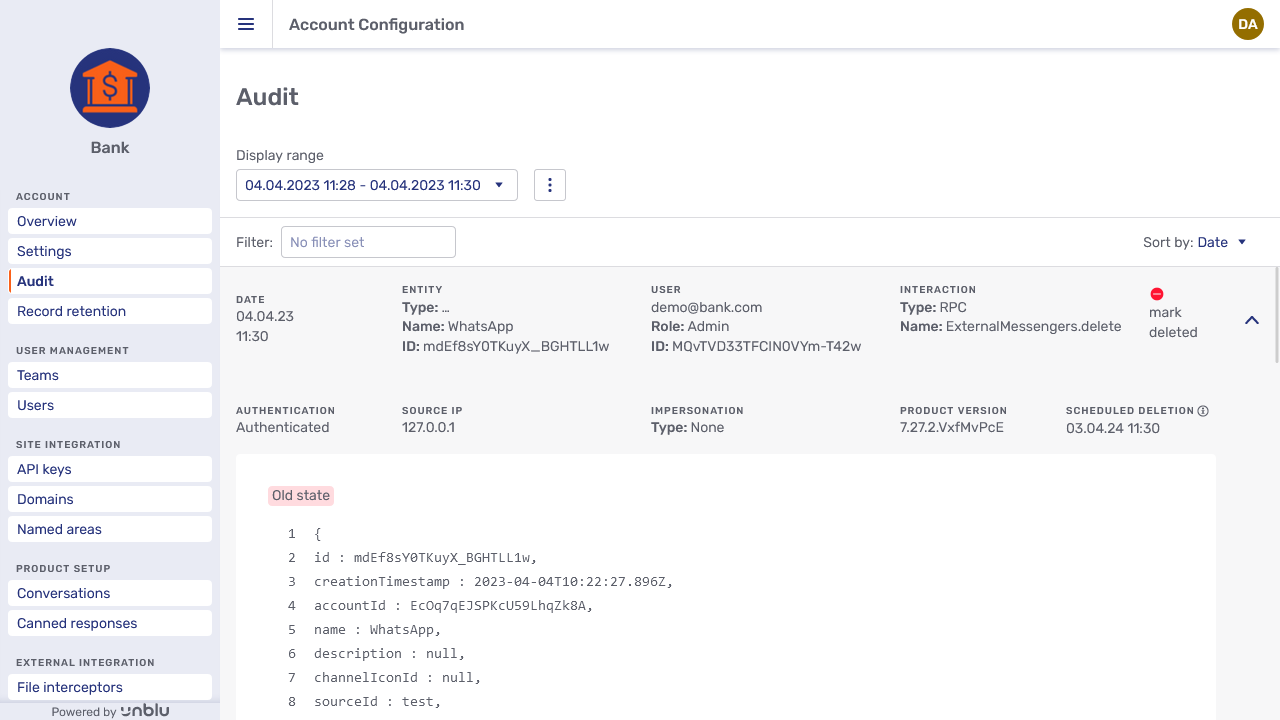
The additional information consists of:
-
The authentication type.
-
The source IP, that is, the IP address the change was made from.
-
The impersonation type.
-
The product version of Unblu.
-
The owner of the entity.
-
A view of the entity before and after the operation was performed.
If the log entry is for the operation that created the entity, you only see the entity’s new state.
If there are more entries than can be displayed, a toast appears at the top of the screen:
(The number of entries displayed depends on how the audit log is configured.) If this happens, or if the log entries you are interested in don’t appear in the default results, you can use the filters to change the search.
Besides the display range, which is shown by default, the audit log offers the following filters:
- Entity type
-
The type of entity that the log entry refers to
- Entity ID
-
The ID of the entity whose log entries are displayed
- Change type
-
The type of change logged: was the entity in question created, updated, or deleted?
- Interaction type
-
The means by which the change was effected. The options available are:
- API
-
The Unblu web API
- RPC
-
An Unblu UI, such the Agent Desk, the Account Configuration interface, or the Global Configuration interface
- Job
-
A job run periodically by Unblu
- Action
-
An action launched when a user interacted with Unblu in some way, for example by initiating a collaboration layer
- Synchronization tool
-
The user synchronization tool
- Internal
-
Any other interaction type
- User role
-
The role of the user whose actions were logged
- User ID
-
The ID of the user who effected the change
- Impersonation type
-
The type of impersonation a superadmin used when carrying out the action logged. Possible values are:
- None
-
The action didn’t involve impersonation
- User (with user’s role)
-
A superadmin performed the action impersonating a user with that user’s role
- User (as superadmin)
-
A superadmin performed the action impersonating a user, but using the
SUPER_ADMINrole - Account
-
A superadmin impersonated into an account
- Owner type
-
The type of the owner of the entity that was affected
- Owner ID
-
The ID of the owner of the entity that was affected
The Filter text field immediately above the list can be used to filter the log entries that are already listed.
See also
For more information, refer to The audit log.
Record retention
The Record retention section lets admins configure the record retention policies for audit logs, conversations, person presences, and webhook logs.
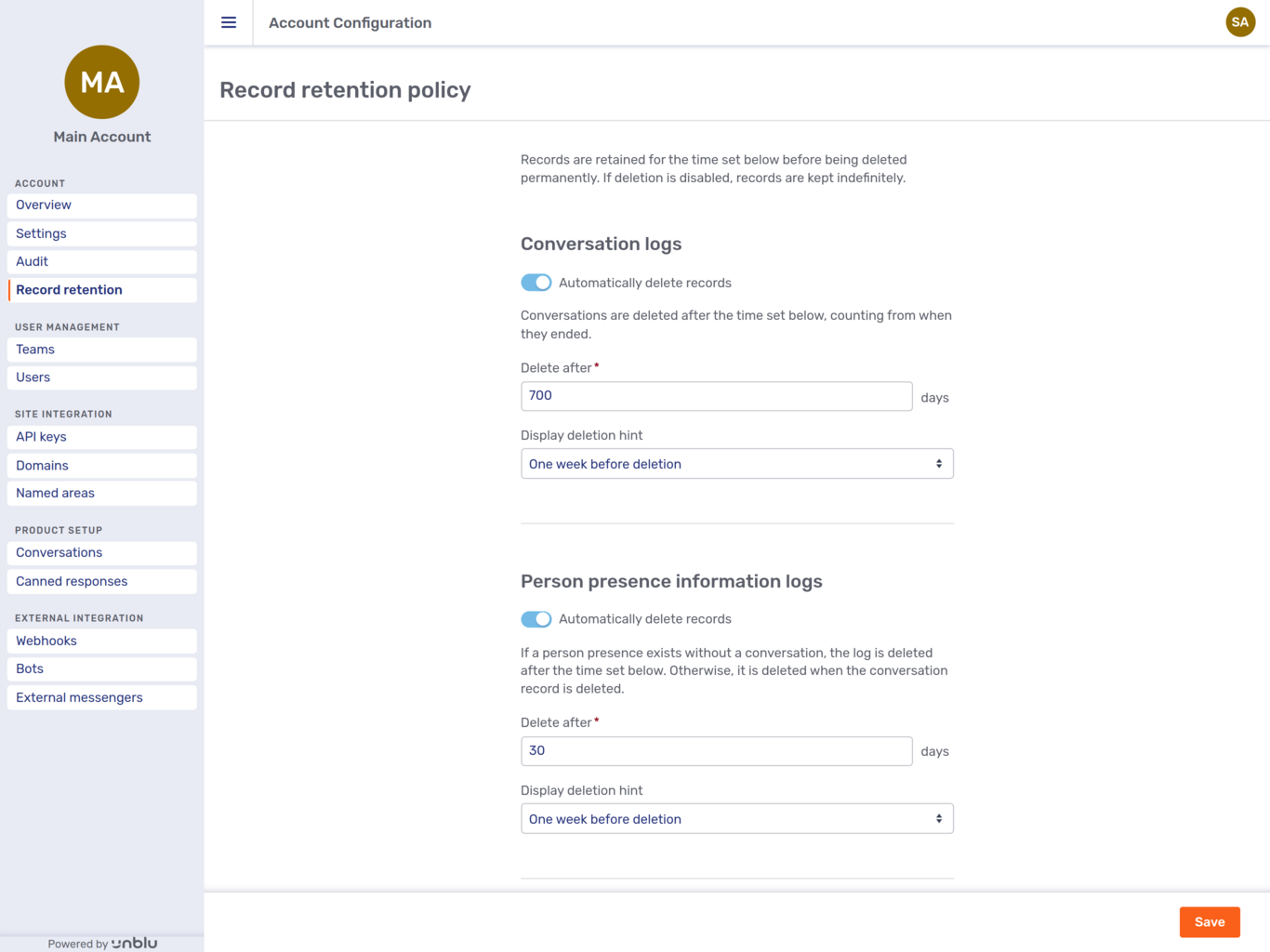
For each entity type, you can specify how long records should remain in the database before being permanently deleted. If you try to enter a value greater than the maximum permissible retention period, an error message appears beneath the input field.
You can also define when Unblu should display information that an entity is scheduled for deletion.
The toggle at the top of each entity’s section of the page can be used to prevent Unblu from automatically deleting entities of that type altogether. This should only be used in exceptional circumstances, for example, if the system you have in place to archive this information isn’t working.
| Record retention for person presences is currently a preview feature. |
See also
For more information on retention policies, refer to Record retention policies.
AI
The AI section of the navigation menu gives you access to the account’s AI-based features: bots, suggestion sources, and conversation summaries.
Bots
|
Only dialog bots can be configured in the Account Configuration interface. Conversation-observing bots are integrated using webhooks. For more information, refer to Bot integration. |
The Bots entry in the navigation menu opens the dialog bots overview. Custom dialog bots and Microsoft Copilot agent dialog bots are listed in separate groups. You can sort the lists by name, onboarding filter, onboarding order, offboarding filter, or offboarding order.
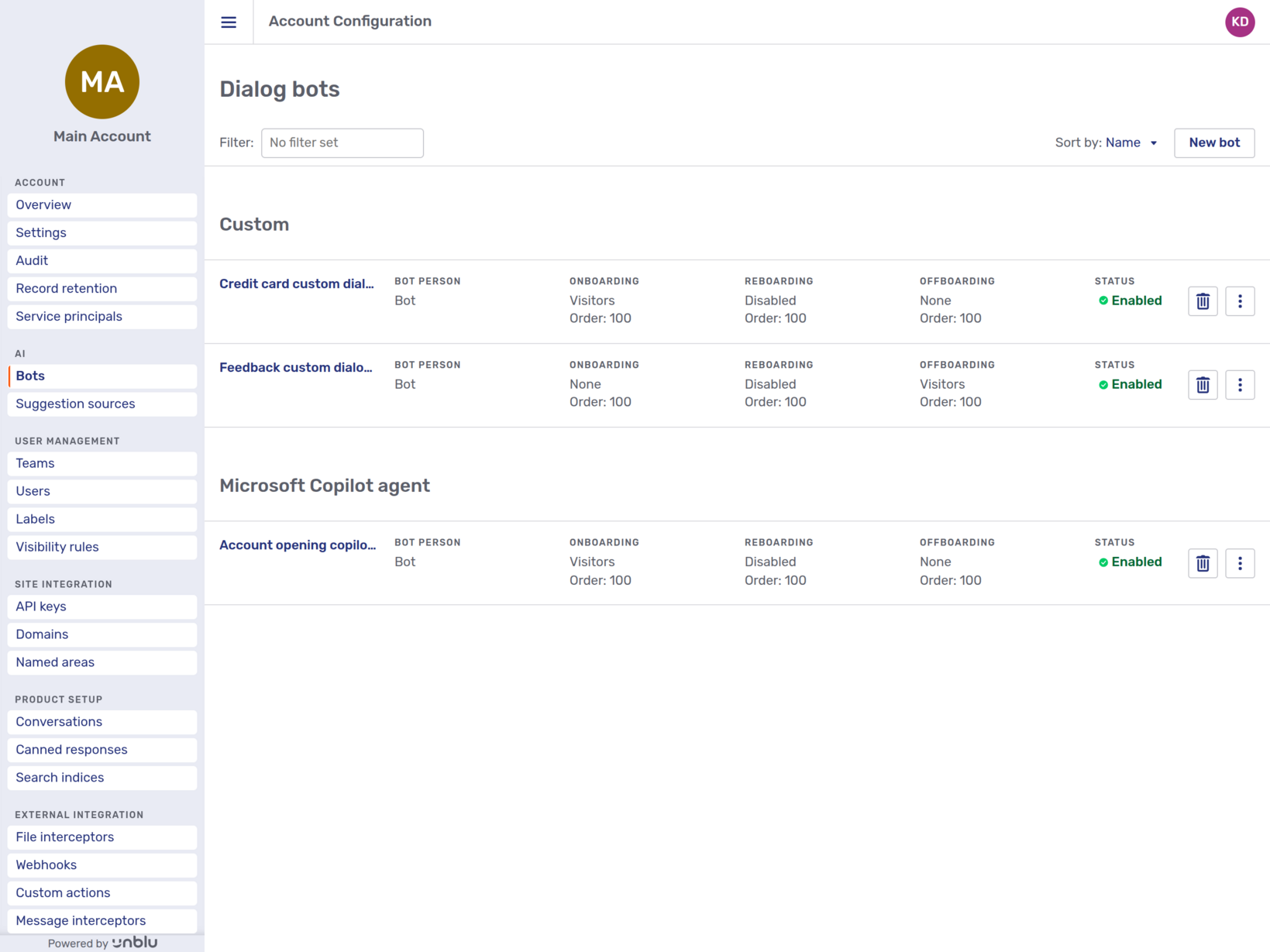
Each bot registered with the account is listed along with information regarding the person used by the bot as well as the filter and order used during onboarding, reboarding, and offboarding. You can also see whether the bot is enabled or not.
In the overview, each dialog bot has a delete button 
As with webhooks, the kebab menu 
New dialog bot
To create a new dialog bot, click the New bot button. This opens a menu where you choose the type of dialog bot you want to create:
-
Custom dialog bots use Unblu web API endpoints and webhooks to interact with a conversation participant.
-
Microsoft Copilot agent dialog bots let Unblu Spark interact directly with an agent configured in Microsoft Copilot Studio.
Clicking a menu entry opens a fly-in page where you can configure your dialog bot.
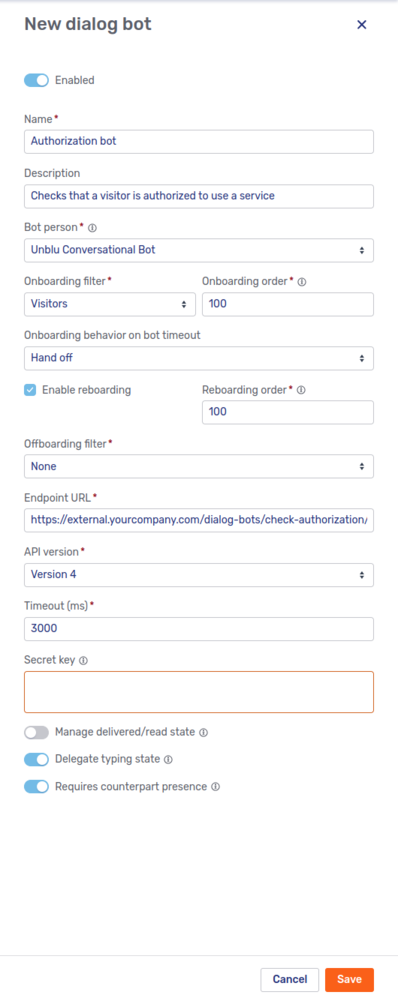
Some of the fields on the fly-in page are exclusive to one or the other type of dialog bot, but many of the fields are shared by both types:
- Enabled toggle
-
A toggle to enable or disable the dialog bot. By default, the Enabled toggle is active, meaning that your new dialog bot is enabled as soon as you click Save.
- Name
-
The name of the dialog bot.
- Description
-
A description of the dialog bot.
- Bot person
-
The person that represents the bot in conversations. For more information, refer to Bot persons.
- Onboarding filter
-
The filter specifies whose onboarding the bot should join: Visitors, Agents, Both, or None.
- Onboarding order
-
If more than one bot takes part in a participant’s onboarding, the number you enter here determines the order in which bots are invited to participate in the process. A bot with a low number gets called before one with a higher number.
The field is only present if you select an onboarding filter other than None.
- Onboarding behavior on bot timeout
-
Specifies what Unblu should do if the bot takes too long to respond. Possible values are Abort and Hand off.
- Enable reboarding
-
Specifies whether the bot is triggered during reboarding.
- Reboarding order
-
A number to determine the bot’s place in the order of bots taking part in the reboarding process. Bots with lower numbers take precedence over ones with higher numbers.
The field is only present if Enable reboarding is checked.
- Offboarding filter
-
The filter specifies whose offboarding process the bot should join: Visitors, Agents, Both, or None.
- Offboarding order
-
Determines the bot’s position in the call order of bots taking part in the offboarding process. A lower number means the bot is called earlier.
The field is only present if you select an offboarding filter other than None.
- Timeout (ms)
-
The time the dialog bot must respond in. If it doesn’t do so, Unblu treats the dialog bot as unreachable and disables it. Unblu no longer attempts to contact the dialog bot until you enable it again.
- Requires counterpart presence
-
If enabled, the boarding process doesn’t start until the bot’s counterpart (the visitor or agent) is online and has opened the conversation.
Enable if the dialog bot needs quick responses to its questions. Disable if the bot is used with external messengers; external participants don’t have an online state.
New custom dialog bot
Besides the fields listed in the previous section, the fly-in page for custom dialog bots contains the following fields:
- Endpoint URL
-
The endpoint URL called to invite the dialog bot to participate in a dialog.
- API version
-
The version of the Unblu web API that the dialog bot uses. Depending on your choice, Unblu uses webhooks or the outbound request mechanism to communicate with the dialog bot.
- Secret key
-
The key you enter here can be used to establish that the invitation was sent by the Unblu Collaboration Server. For more information, see above.
- Manage delivered/read state
-
If active, the toggle specifies that the dialog bot actively informs the Unblu Collaboration Server when a message addressed to it has been delivered or read. This state is reflected in the number and color of the ticks displayed next to the sent message in the UI the human participant sees.
If the toggle isn’t active, the state and thus the UI feedback is managed by the Unblu Collaboration Server.
- Delegate typing state
-
If active, Unblu displays a typing indicator while the dialog bot is preparing a response to messages the other party in the dialog sends. The typing indicator stops after 4 seconds or when the bot sends a response, depending on which event occurs first. The typing indicator has a 1 second debounce. This prevents it from being displayed repeatedly if the other party sends multiple messages in short succession.
If disabled, you can still display a typing indicator using the web API endpoints
/bots/startDialogBotTypingIndicatorand/bots/cancelDialogBotTypingIndicatorto start and cancel the typing indicator, respectively.The conditions when a typing indicator started manually stops are the same as for automatically started typing indicators, that is, after 4 seconds or when the dialog bot sends a response.
New Microsoft Copilot agent dialog bot
The fly-in page for Microsoft Copilot agent dialog bots looks like this:
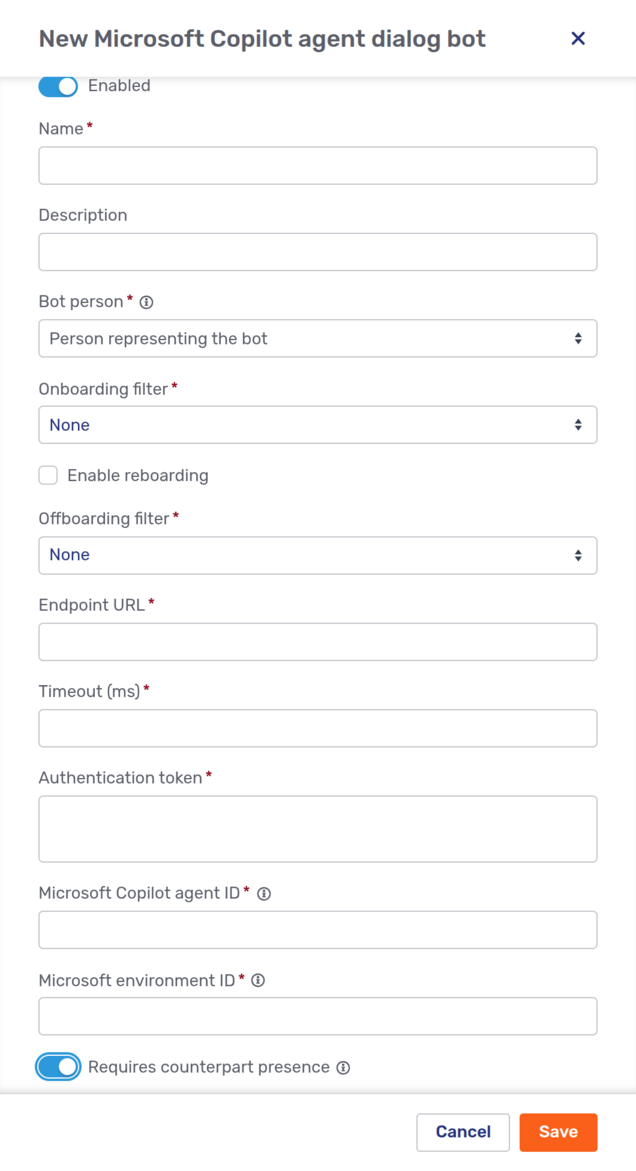
Beside the fields shared by all dialog bots, the page has the following fields:
- Endpoint URL
-
The Direct Line API 3.0 endpoint that Unblu Spark uses to communicate with the agent.
- Authentication token
-
The authentication token that identifies the agent.
- Microsoft Copilot agent ID
- Microsoft environment ID
Refer to Configuring Microsoft Copilot agents in Unblu Spark for information on where you can find the values you need to enter and advice on configuring Microsoft Copilot agents.
General
The General tab lets you modify the same fields as the fly-in page used to create a new dialog bot. For more information, refer to the description of the latter in the preceding sections.
Delivery log
The Delivery log tab contains the same information as the delivery log tab for webhooks. For more information, refer to the description of the latter.
Suggestion sources
Suggestion sources are used to provide agents with possible responses to text messages in chats with visitors or other agents.
The Suggestions sources navigation menu item opens the suggestion source overview.
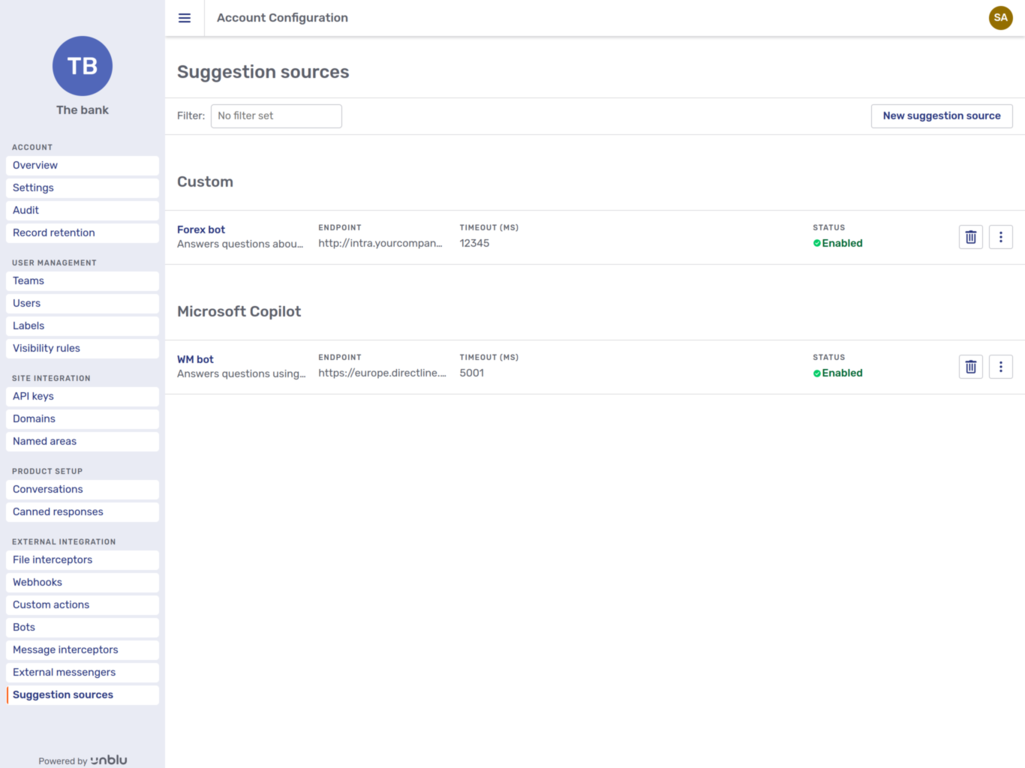
You can see the name, description, endpoint, timeout, and status of each suggestion source configured for the account. Each entry in the overview sports a delete button 

Clicking the delete button deletes the custom action immediately. The toast that appears at the top of the interface lets you undo the action.
The kebab menu 
The New suggestion source button opens a fly-in page with the same configuration options as an existing suggestion source’s General tab, described below.
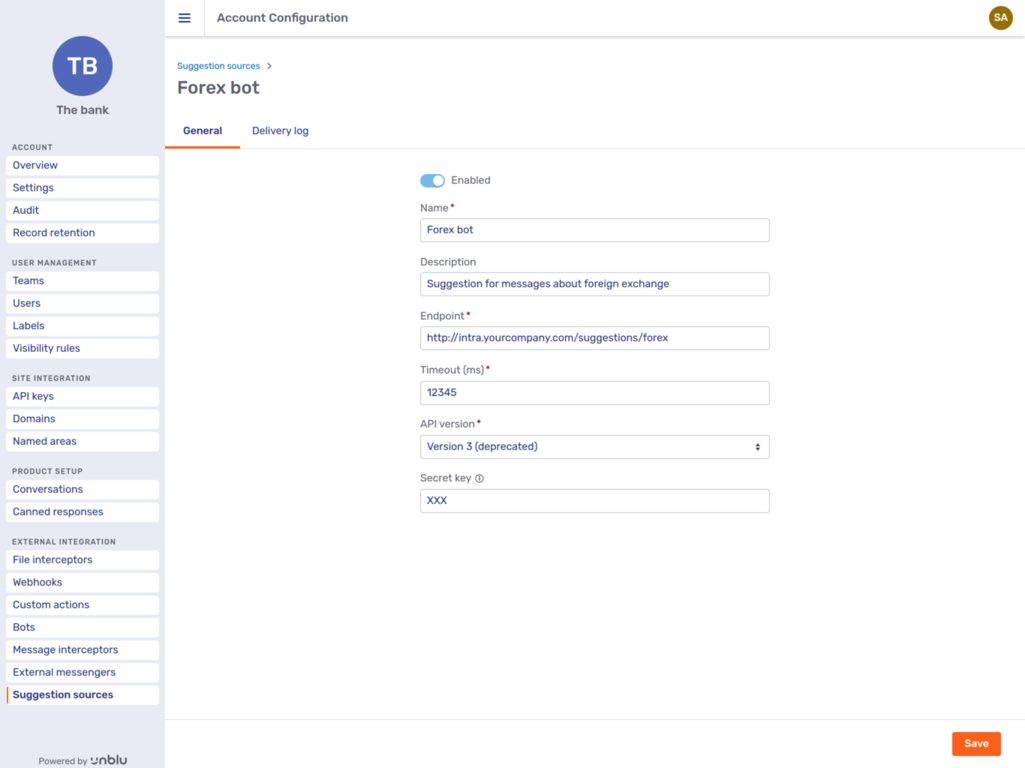
General
Clicking a suggestion source opens its General tab. For custom suggestion sources, the tab looks like this:
The General tab of a Microsoft Copilot suggestion source looks like this:
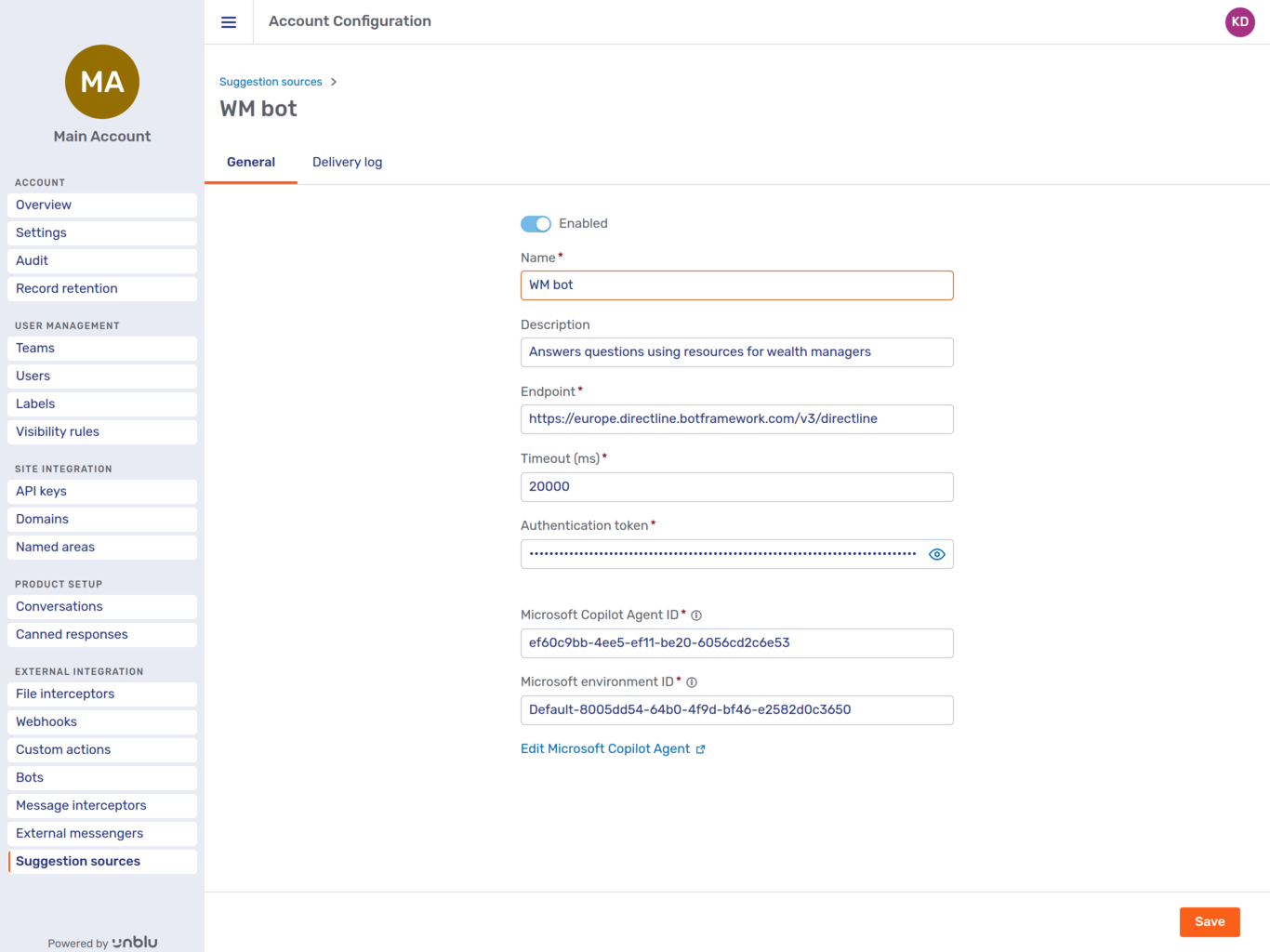
All suggestion sources have the following settings:
-
The availability of the suggestion source in Unblu. This is done with the toggle to enable or disable the suggestion source at the top of the tab.
-
The suggestion source’s name.
-
The suggestion source’s description.
-
The endpoint URL Unblu uses to request chat suggestions.
-
The timeout. If the suggestion source takes longer than this timeout to respond to Unblu’s request for a suggestion, the suggestion source is automatically disabled. For agents that use generative AI for suggestions, set the timeout to 15000 ms or more.
Custom suggestion sources have the following additional settings:
-
The version of the Unblu web API that the suggestion source targets
-
An optional secret key that the suggestion source can use to verify that Unblu requested a suggestion
Microsoft Copilot suggestion sources have the following additional settings:
-
The authentication token needed to access the agent
-
The Microsoft environment ID
-
The Microsoft Copilot Agent ID (referred to as the Copilot Id in Microsoft Copilot Studio)
-
A link that takes you straight to the agent in the Microsoft Copilot Studio
Delivery log
The Delivery log tab lists the requests for suggestions sent to the suggestion source in question. You can sort the list by time or by response code.
Click a request to view the details of the request and of the response Unblu received from the suggestion source.
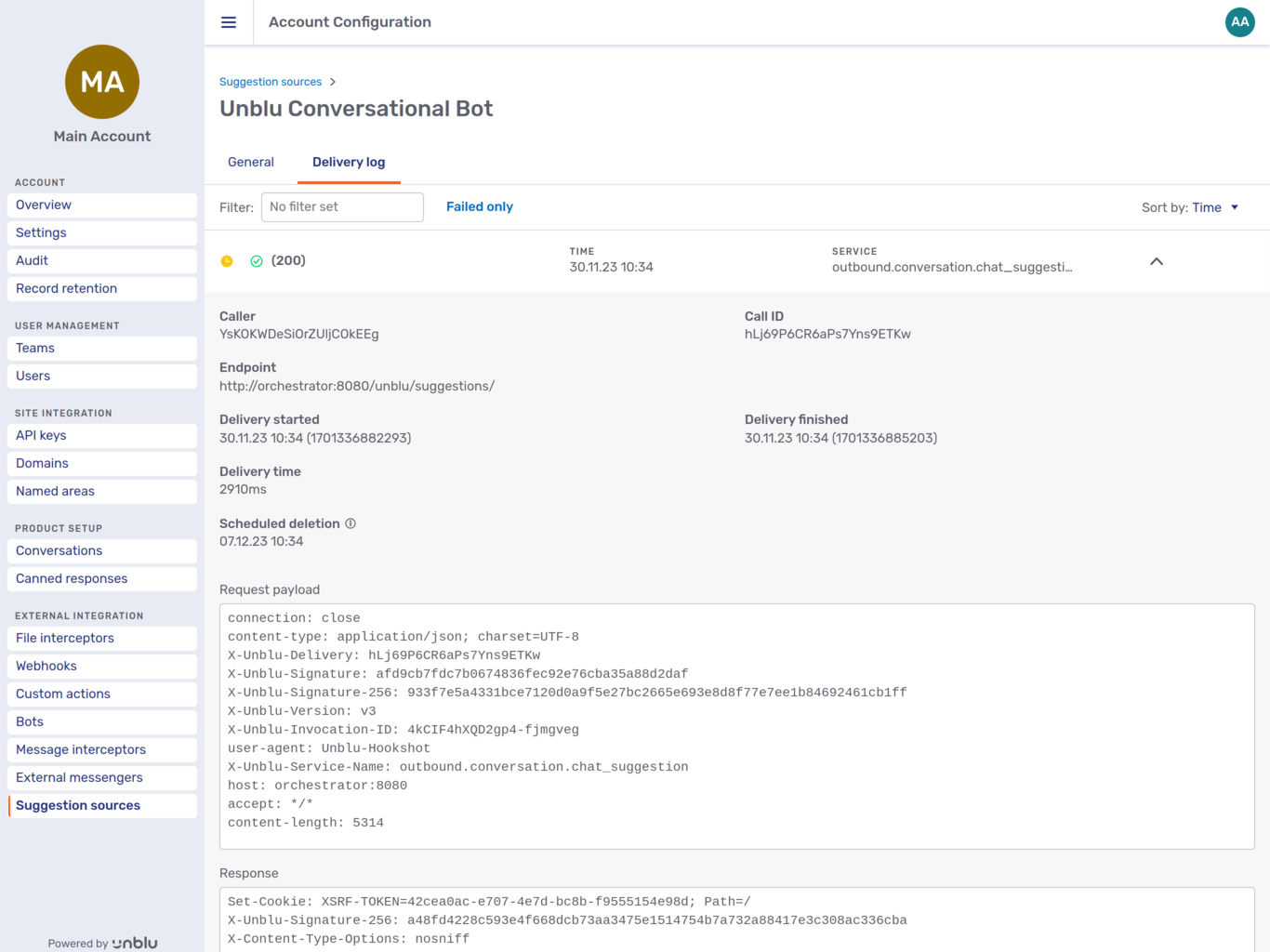
For more information on chat suggestions, refer to Providing agents with suggestions in text chats.
Summaries
Conversation summaries are generated based on summary templates which describe how to generate a summary. The Summaries navigation menu item opens the overview of summary templates.
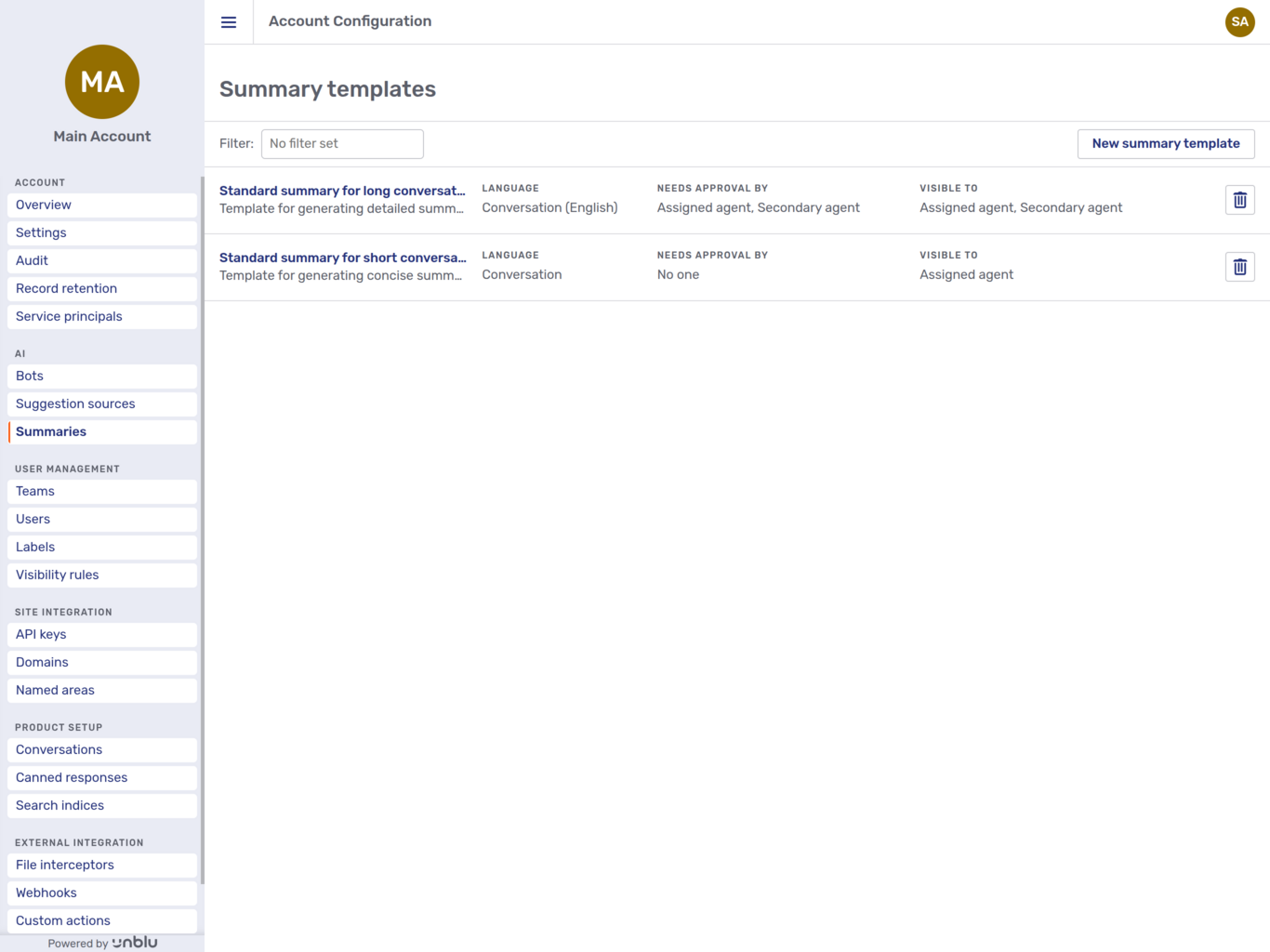
For each summary template, the overview page shows the following information:
-
The summary template’s name and description.
-
The language that summaries based on the template are generated in.
-
Who may approve the summary.
-
Who may see the summary.
-
A delete button
.
Clicking the delete button displays a modal dialog:

Clicking OK deletes the summary template. There’s no way to undo the deletion.
To create a new summary template, click the New summary template button. This opens a fly-in page with the same fields as the General tab, described below, of an existing summary template.
General
Clicking a summary template opens its General tab:
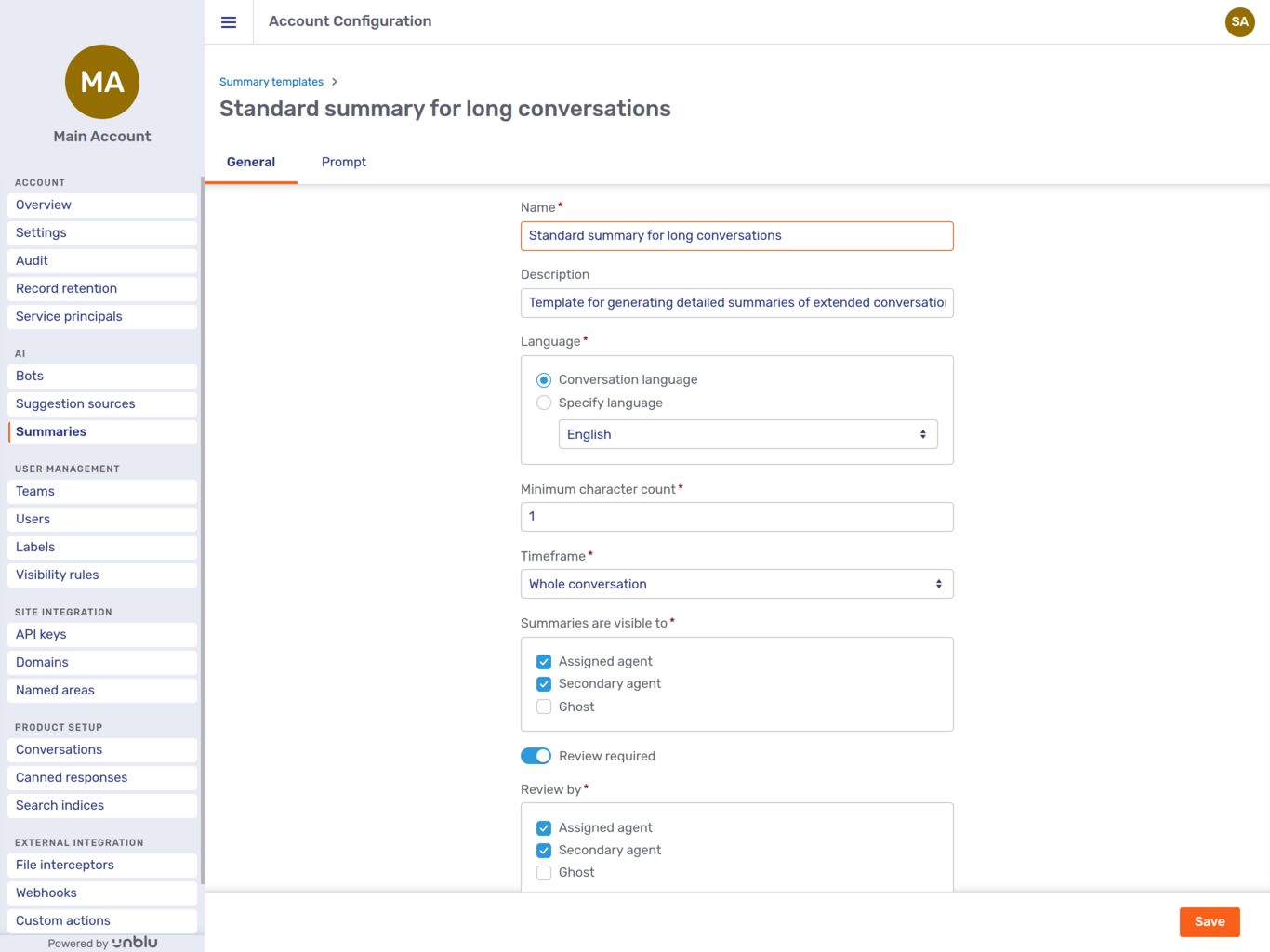
You can see the following settings:
-
The name of the summary template.
-
A description of the summary template.
-
The language that summaries based on this summary template are generated in. You can either choose a specific language or opt to generate the summary in the conversation language.
-
The minimum character count to trigger a summary. If a conversation consists of fewer characters, Unblu doesn’t generate a summary.
-
The timeframe to take into account when generating the summary. You can choose between the following timeframes:
-
The whole conversation. This takes into account all messages of the conversation, including the onboarding phase.
-
The whole conversation without onboarding.
-
Until last summary. If a summary was generated earlier in the conversation, the summary starts when the last summary ended.
-
Until last unassigned. With this timeframe setting, the summary starts when the assigned agent last left the conversation. This option is most likely to be of interest in long-running conversations.
-
Trigger specific
-
-
Which participant types summaries are visible to. You can grant access to the following participant types:
-
The assigned agent
-
Secondary agents
-
Ghost participants
-
-
The Review required toggle. If you switch the toggle on, the summary must be reviewed before it’s saved. Depending on when in the conversation lifecycle the summary is generated, this may mean that the conversation doesn’t end until the summary’s been reviewed.
If the toggle is on, you must specify the participant types allowed to review the summary in the Review by field.
-
Which participant types may review the summary. This field is only available if the Review required toggle is on. You can make the following participant types reviewers:
-
Assigned agent
-
Secondary agents
-
Ghost
Make sure that reviewers can see summaries according to the Visible to field.
-
Prompt
The Prompt tab lets you customize the prompt to use when generating a summary based on this template. The parts of the prompt that you can’t customize are defined in configuration properties.
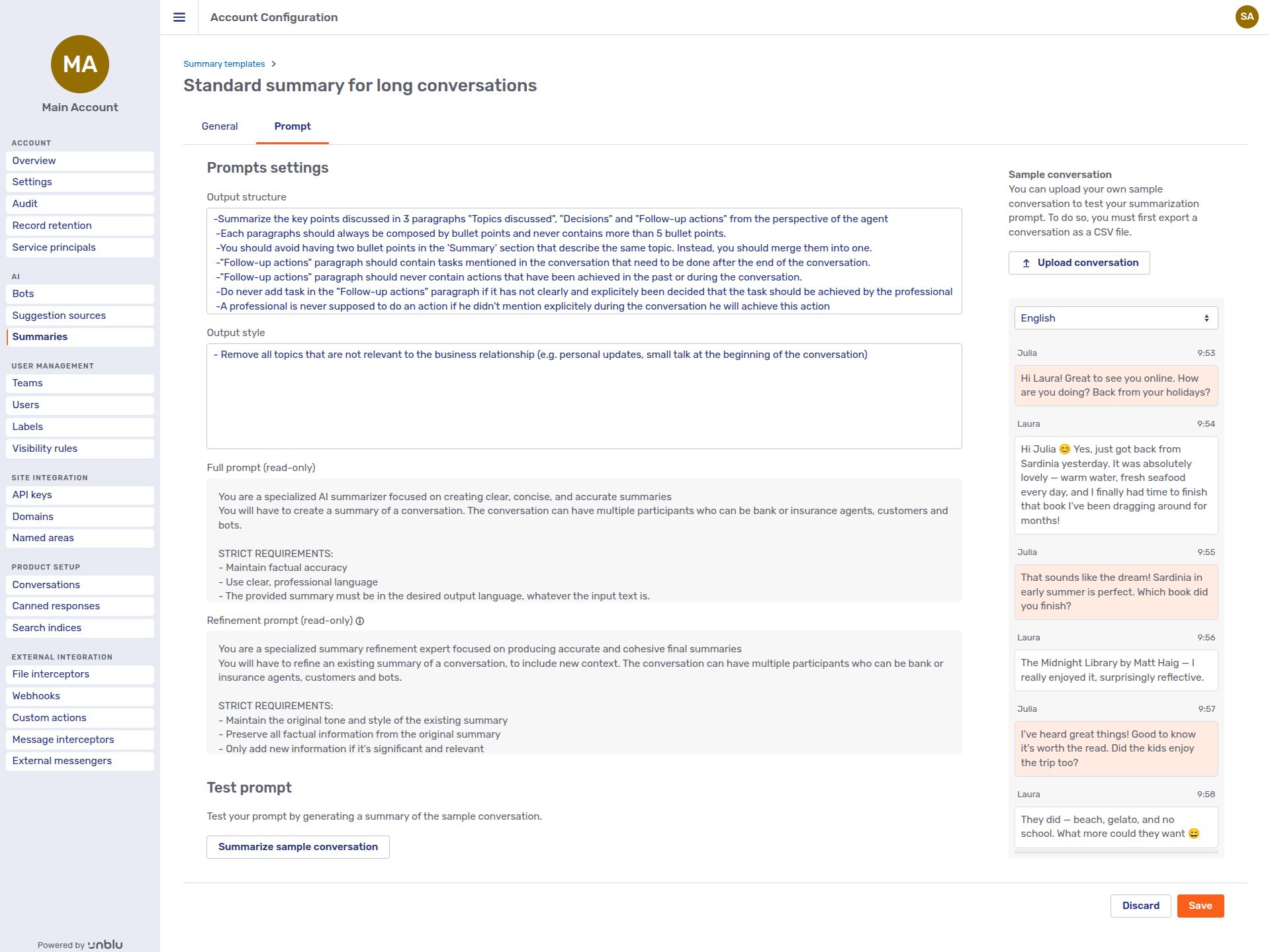
You can customize two aspects of the prompt:
-
Output structure, which replaces the
\{{promptCustomization}\}placeholder in the prompt configuration property. -
Output style, which replaces the
\{{promptStructure}\}placeholder in the prompt configuration property.
Beneath the two input fields, you can see the complete initial and refinement prompts with your customizations. For more information on the different prompts, refer to Define the prompt used for summarization in Generate conversation summaries.
The Test prompt section beneath the prompts lets you test your prompt with the sample conversation you see on the right of the tab. You can upload a conversation of your own to test your prompts by clicking the Upload conversation button above the sample conversation. Note that the file you upload must be in the CSV format used by Unblu to export conversations.
User management
The User management section of the navigation menu gives you access to the account’s teams and users.
Teams
The Teams item in the navigation menu displays an overview of all an account’s teams and subteams. In the picture below, both Business Support and Private Support are subteams of Call Center.
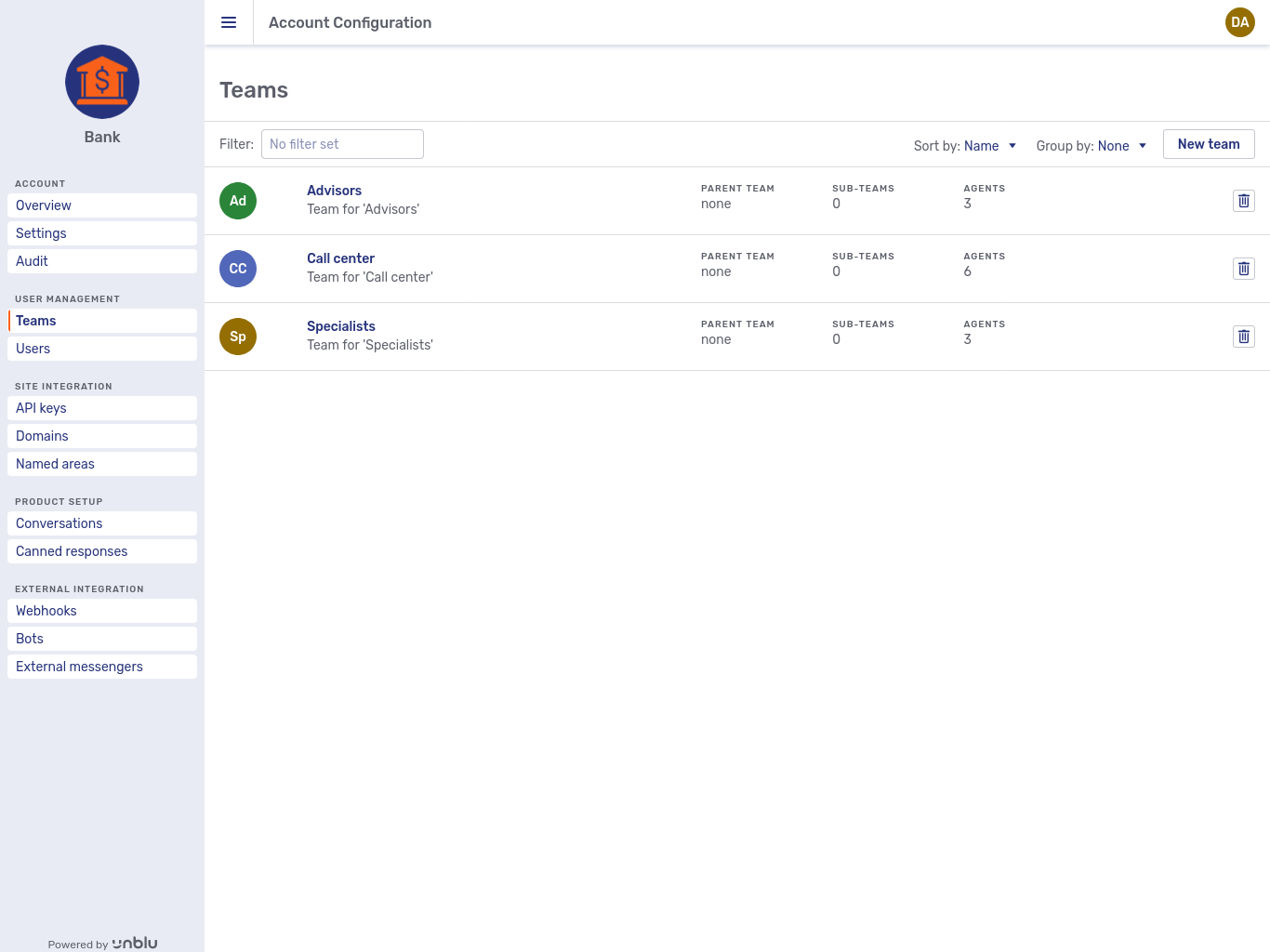
Each entry in the list consists of:
-
The team’s name.
-
A description of the team.
-
The name of its parent team if it has one.
-
The number of subteams it has.
-
The number of agents in the team. Only those agents assigned directly to the team that the entry refers to are counted.
There is a delete button 
Above the list, there are two dropdown menus that affect the sort order and the grouping of the teams in the overview, respectively.
The New team button opens the New team fly-in page, which contains the same fields as the General tab described below.
General
Selecting a team in the overview opens the team’s General tab.

The tab allows you to change the team’s name and description, and to upload an image to use as the team’s avatar. You can also select a different team to be this team’s parent team. If you do so, the team becomes a subteam of that team.
At the top of the tab, you can see whether the team is managed internally—within Unblu—or externally. If you are in override mode, you also have a toggle to switch between internal and external management.
Settings
The Settings tab lets you specify settings for the team you are viewing. It works as outlined above.
Canned responses
Canned responses you create on a team’s Canned responses tab are available only to that team’s members. They aren’t available to members of the team’s subteams.
For information on creating canned responses, refer to the canned responses section of the Agent Desk user guide.
Users
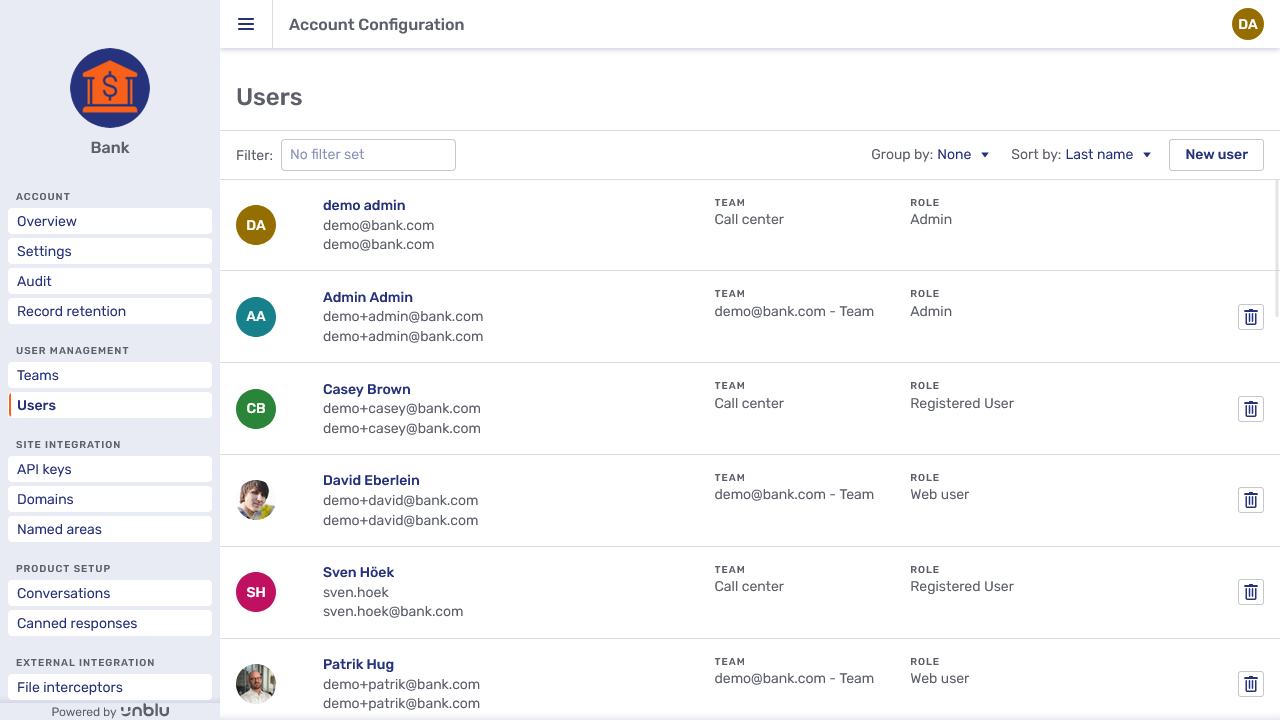
The Users menu item opens an overview of all the users registered with an account:
You can filter the list or group the entries by role or team name. In the picture below, the user list has been filtered to display only supervisors.
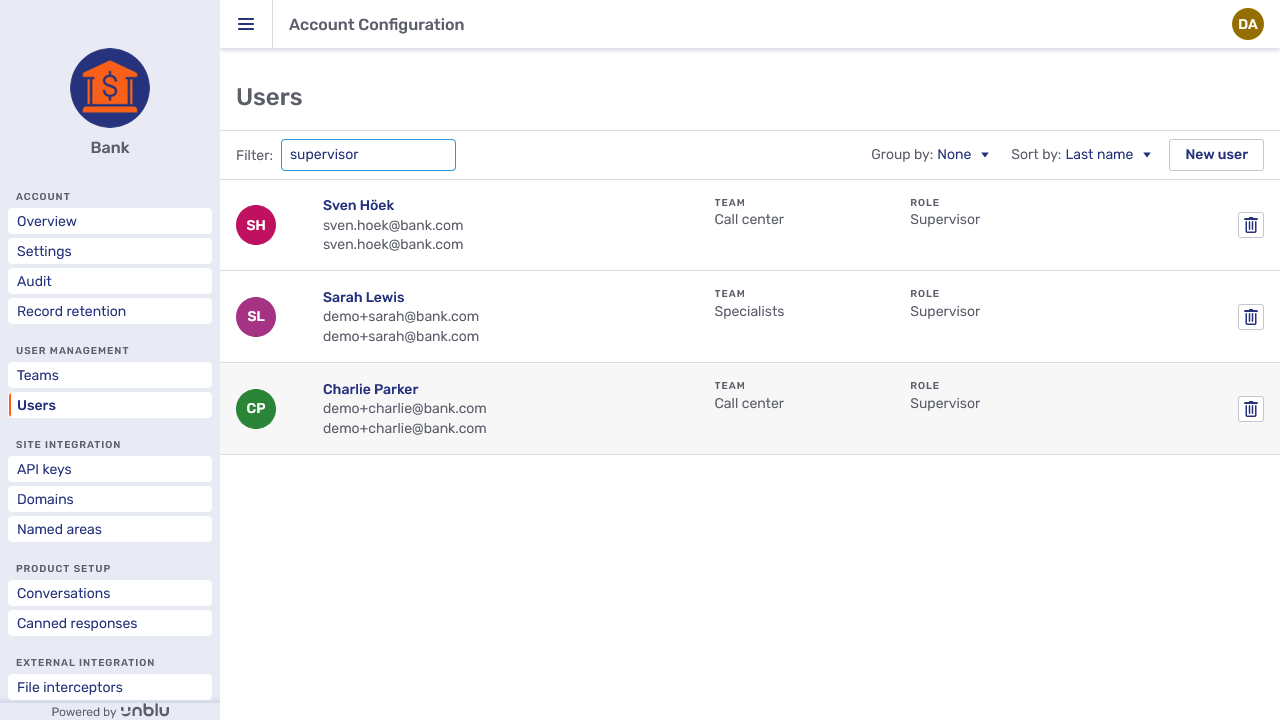
Each entry consists of:
-
The user’s first and last name
-
Their username
-
Their email address
-
The team the user belongs to
-
Their role
| If there is no field to enter the username, that’s because Unblu is configured to use the user’s email address as the username. You can change this behavior with the configuration property com.unblu.storage.user.useEmailAsUsername. |
You can only see users you’re allowed to edit. For example, supervisors can only see users who are members of their own team and their team’s subteams.
The delete button 

The Sort by dropdown changes the sort order of the list. You can group the users listed by either their role or the team they belong to with the Group by dropdown menu.
The New user button opens the fly-in page of the same name. The possibilities you have here are the same as on the General tab of an existing user. See the following section for further details.
| Not all roles are authorized to create and delete users. For more information, refer to user roles. |
General
Use the General tab to review and change a user’s basic details. Besides common fields such as Name or Description, you can specify the user’s Username and assign them to a particular team.
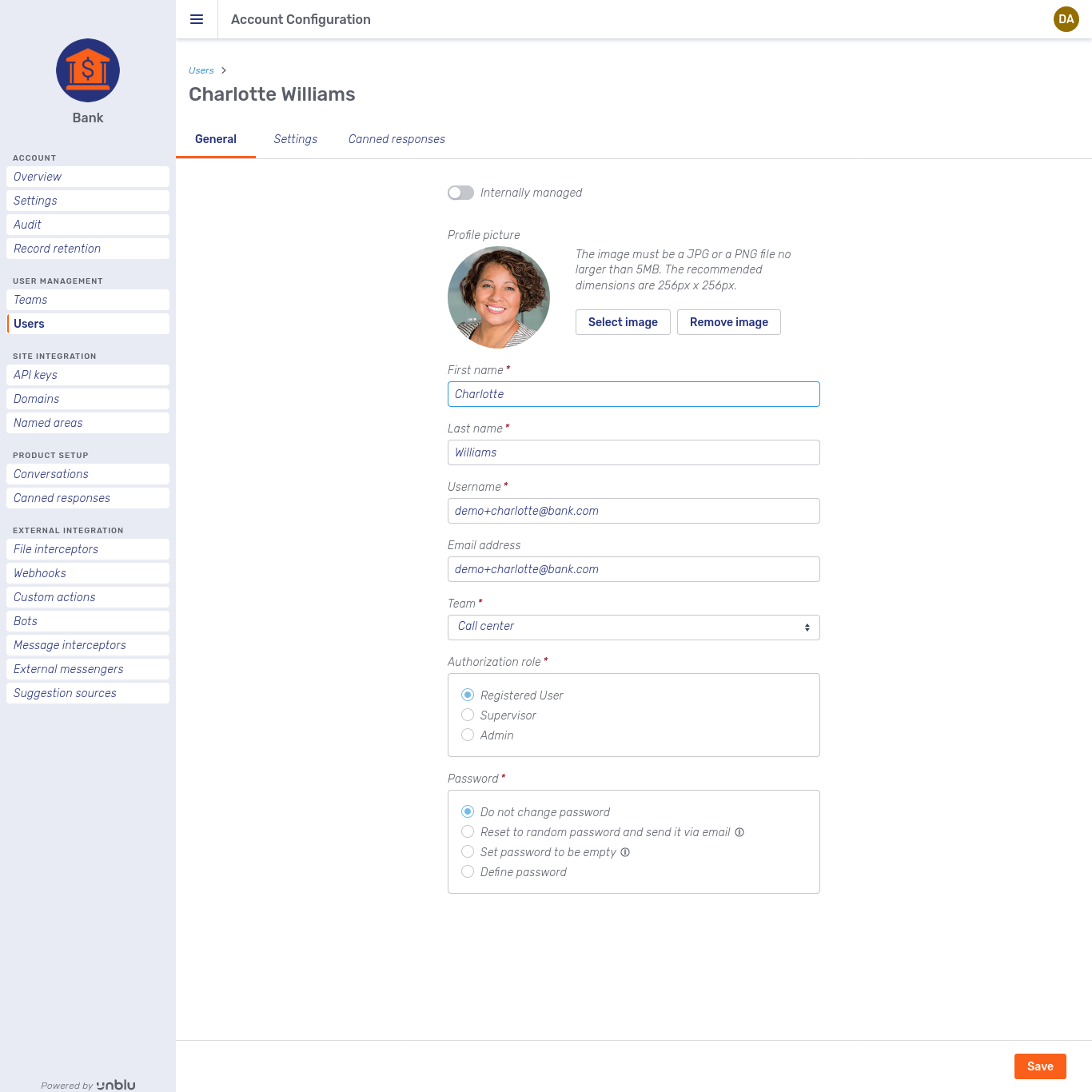
At the top of the tab, you can see whether the user is managed internally, i.e. within Unblu, or externally. If you are in override mode, you will also have a toggle to switch between internal and external management.
In the Authorization Role section, you can only assign a user a role with as many permissions as your own role, or fewer. A supervisor, for example, can only assign the roles Registered User or Supervisor.
The Password section offers the following options:
- Do not change password
-
Leaves the current password untouched. This is the default option.
- Reset to random password and send it via email
-
Most useful when a user has forgotten their password. The change takes effect once you click Save.
- Set password to be empty
-
Used when users are authenticated by some third-party mechanism through ID propagation. If active, the user won’t be able to log in on the Unblu login screen.
- Define password
-
Allows you to specify a password for the user.
When you select this option, two extra fields appear where you can enter and confirm the new password.
| You can’t change the general properties of virtual users in the Account Configuration interface. |
Settings
The Settings tab displays the settings for a particular user. It works as outlined above.
Canned responses
Canned responses you create on a user’s Canned responses tab are available only to that user.
For more information on how to create canned responses, refer to the section on creating canned responses in the Agent Desk user guide.
| Canned responses aren’t supported for virtual users, even though the tab is available in the Account Configuration interface. |
Deputies
The Deputies tab lets you specify deputies for a user.
For information on creating and managing user deputies, refer to Deputies in the Agent Desk user guide.
For information on Unblu’s deputy delegation system, refer to Deputy delegation.
| Deputies aren’t supported for virtual users, even though the tab is available in the Account Configuration interface. |
API secrets
The API secrets tab displays a user’s API secrets. These can be used to authenticate the user when calling endpoints of the Unblu web API.
If you’re viewing yourself, the tab includes a New API secret button. When you click it, the following modal dialog appears:
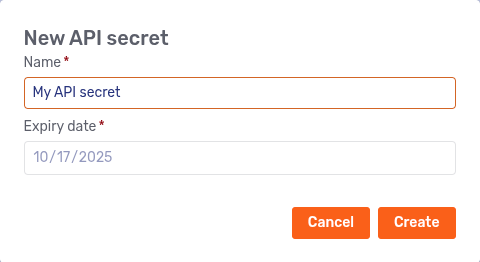
Enter a name and click Create to create the API secret. (The Expiry date field isn’t editable.) The API secret is displayed in a new modal dialog:
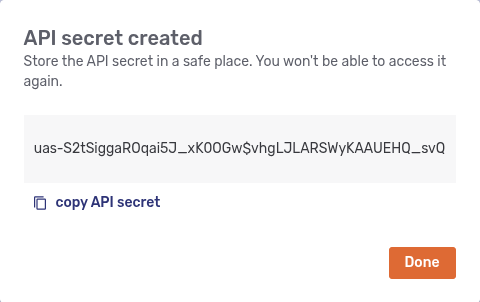
Store the API secret somewhere safe, then click Done to close the modal dialog and return to the list of API secrets.
| There’s no way to retrieve the API secret again once you click Done. |
Labels
The Labels menu entry opens the labels overview, which lists all the labels defined in the account. Each label is listed with its name, its description, who the label may be applied to, and who the label is displayed to.
The delete button 
To create a new label, click the New label button. This opens a fly-in page where you can enter the label’s details. Use the Scoped label switch at the top of page to choose whether the label should be a scoped label.
When you’ve finished, click Save.
To edit an existing label, click its entry on the overview page. This opens the label’s details in a window with the same options as the New label fly-in page. When you’ve finished editing the label, click Save.
For more information on labels and their features, refer to Labels and visibility rules.
Visibility rules
The Visibility rules menu entry opens the visibility rules overview, which lists all the visibility rules defined in the account. Each rule is listed with its name, its description, and the agents and visitors it applies to. If a rule applies to agents or visitors with a specific set of labels, the labels are listed on the overview page.
The delete button 
To create a new visibility rule, click the New rule button. This opens a fly-in page where you can enter the rule’s details. At the top of page, you can choose whether to enable the rule. By default, new visibility rules are enabled immediately.
Once you’ve finished, click Save.
To edit an existing visibility rule, click its entry on the overview page. This opens the rule’s details in a window with the same options as the New rule fly-in page. When you’ve finished editing the label, click Save.
For more information on visibility rules, refer to Labels and visibility rules.
Site integration
The Site integration section of the navigation menu groups configuration options related to integrating Unblu into your organization’s website.
API keys
The API keys menu entry opens the API key overview, which lists all API keys with their name and description.
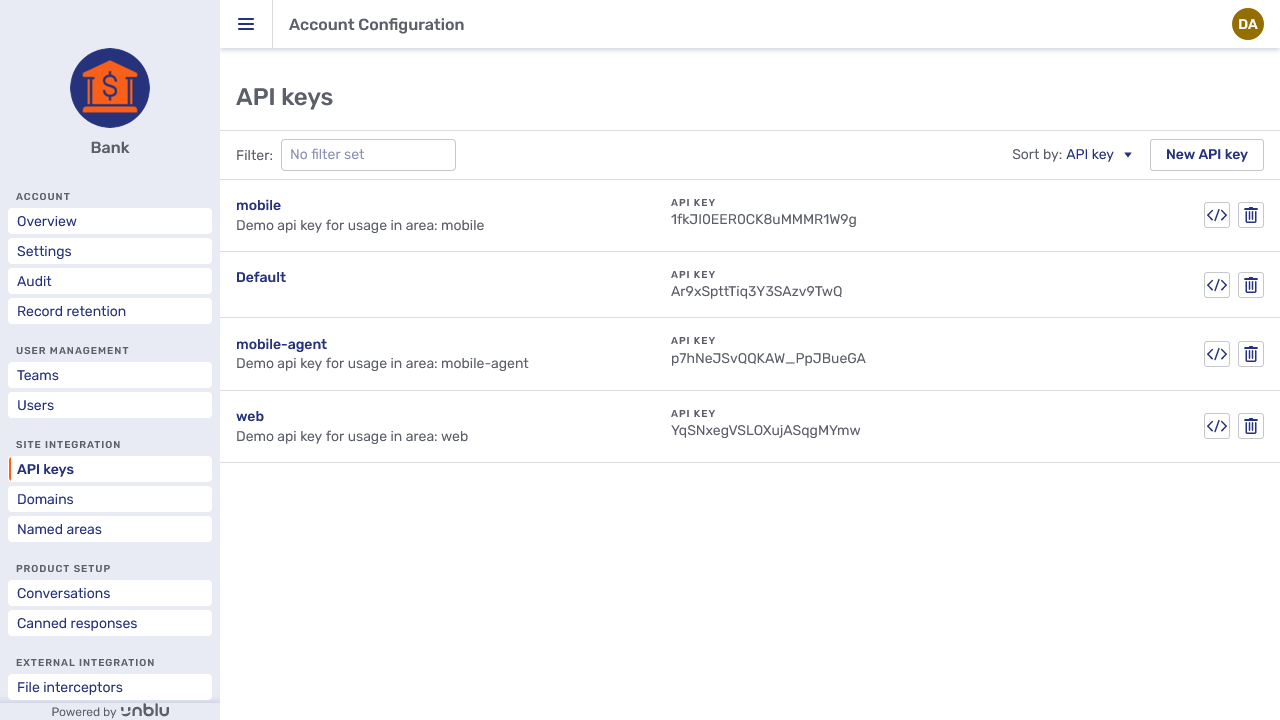
You can sort the list of API keys by name, description, or API key with the Sort by dropdown.
The delete button 
The code snippet button 
Pressing the New API key button opens a fly-in page where you can enter the API key itself along with a name for and a description of the key:
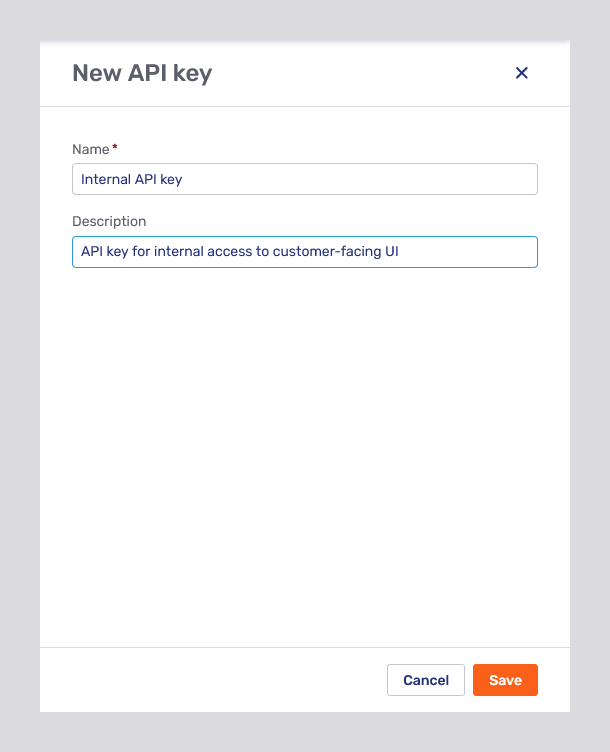
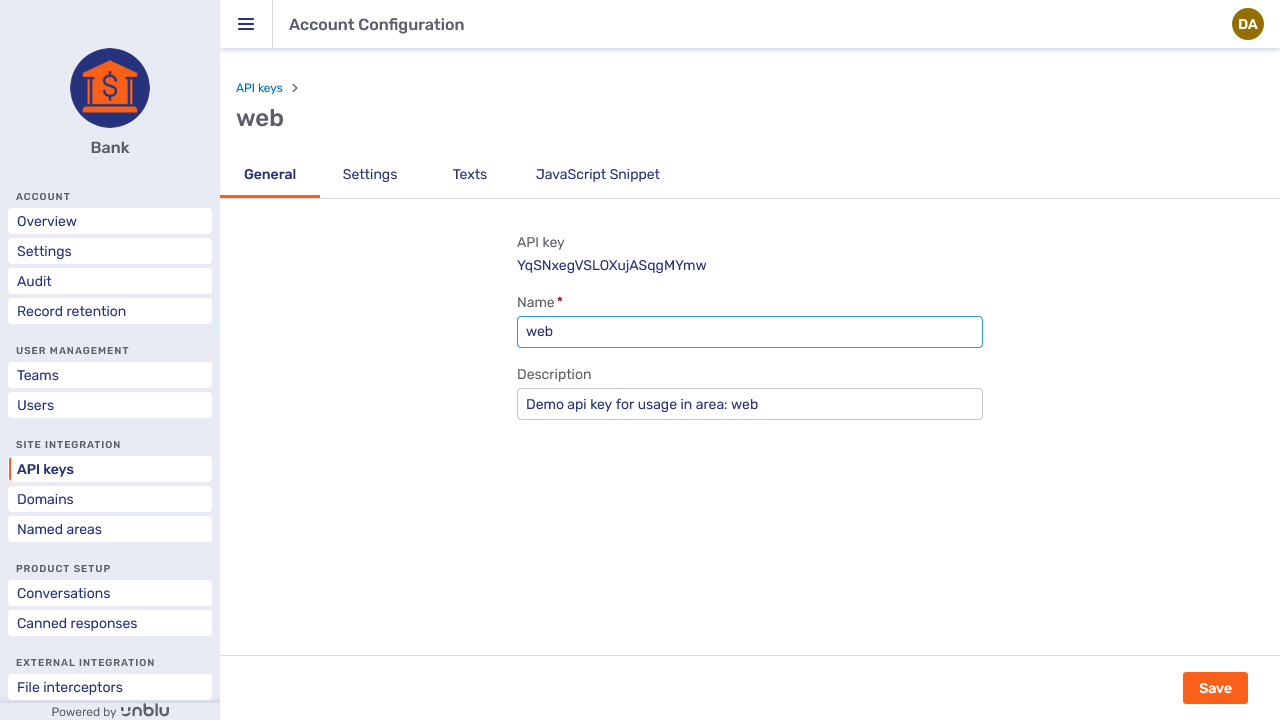
The General tab for API keys is almost the same as the New API key fly-in page. It displays the API key and allows you to edit the key’s name and description. You cannot, however, change the API key itself.
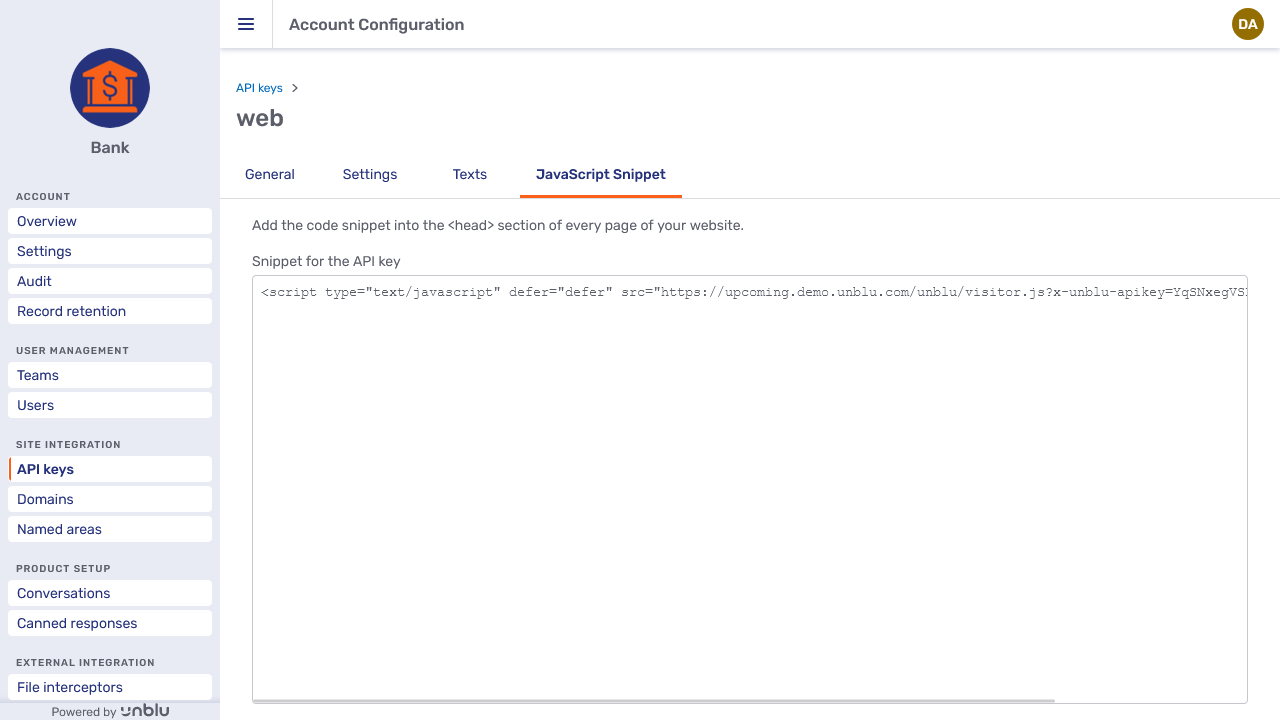
JavaScript Snippet
The JavaScript Snippet tab contains the code you must add to the <head> of each page of your website that you want to provide access to Unblu on.
For more information, refer to API keys.
Domains
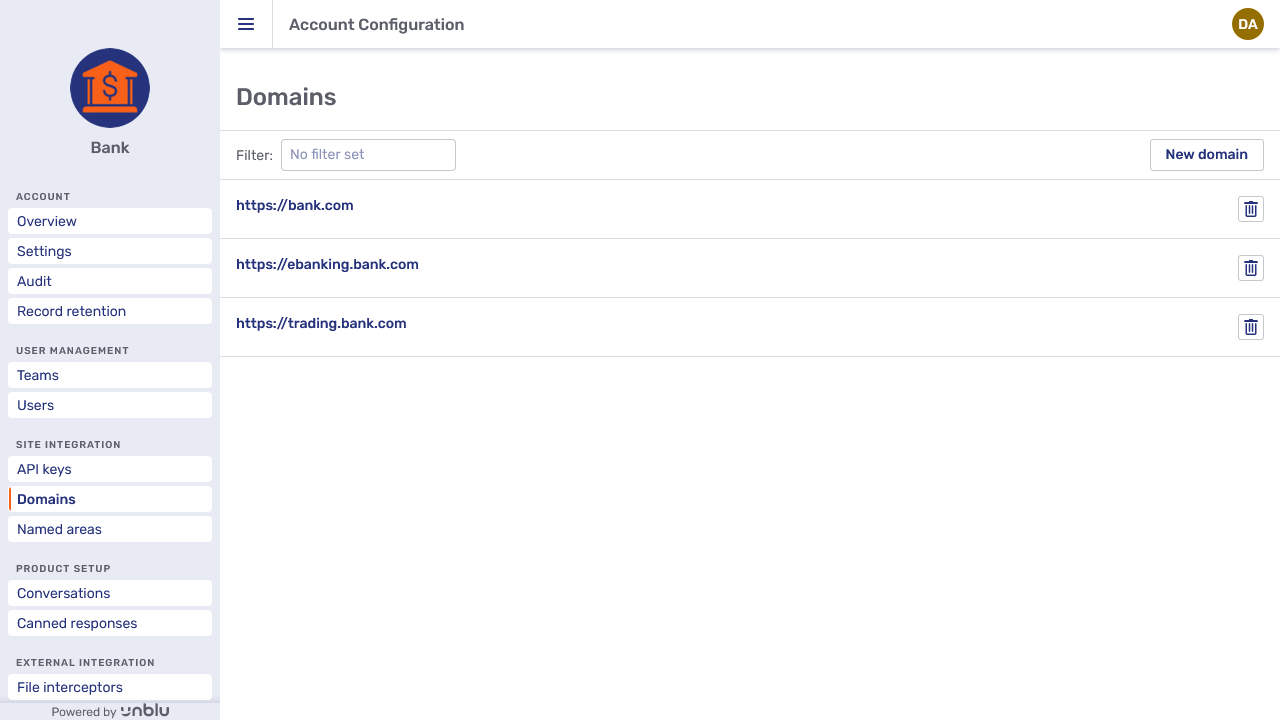
The Domains menu item lists all the domains you have registered for this account.
The New domain button opens the New domain fly-in page. Clicking a domain opens the Edit domain fly-in page. The only difference between the two fly-in pages is the Protocol section: You can choose to add a new domain for both HTTP and HTTPS protocols, whereas for existing domains, you can only select either HTTP or HTTPS.
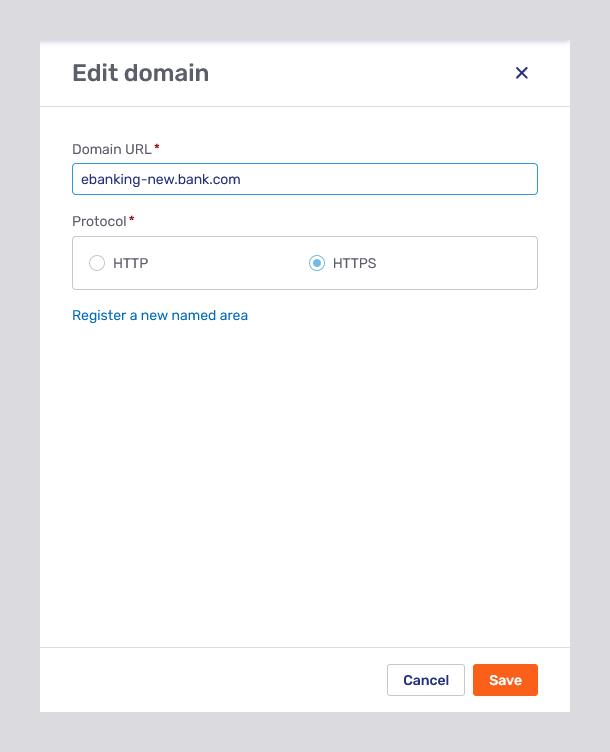
You can specify a particular port for a domain by appending it to the domain’s URL, as has been done for internal.bank.com:1234 in the picture above.
If you try to add a domain that’s already present with the same protocol, the fly-in page displays an error message.
For more information on domains, refer to the appropriate sections of the article on named areas.
Named areas
The Named areas entry in the navigation menu opens the overview of named areas currently defined on the account.
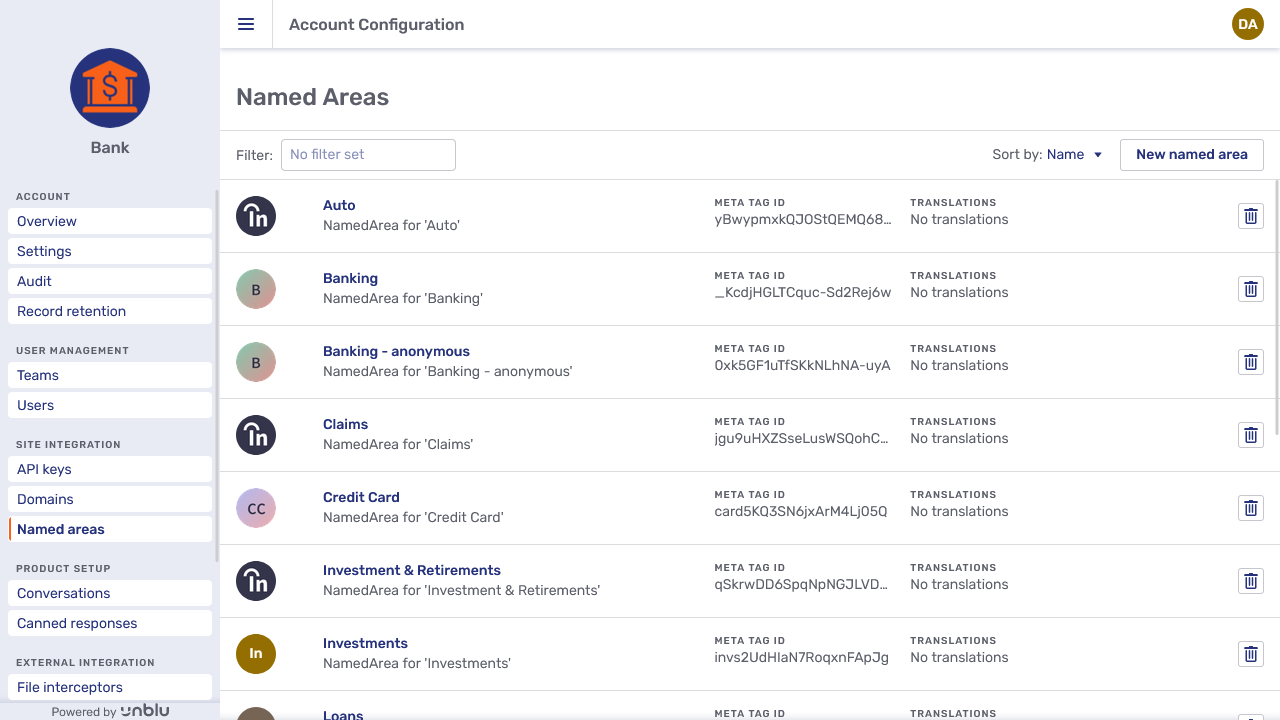
The Sort by dropdown lets you sort the overview by name, description, or type of named area.
The New named area button opens the fly-in page of the same name:
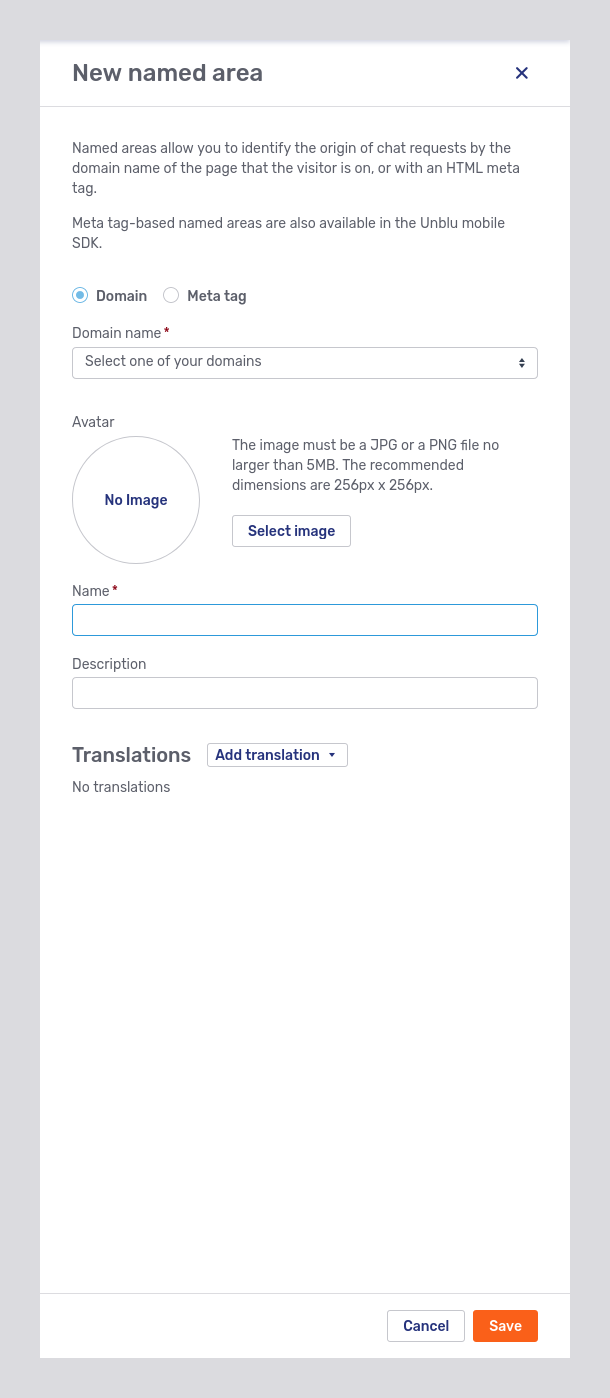
Besides the usual fields such as Name and Description, the fly-in page requires you to specify how the named area should be defined, by Domain or by Meta Tag. Depending on your choice, the fly-in page will display a field where you can select the domain or enter the meta tag ID for the named area. In the picture above, the fly-in page includes a dropdown to select the domain to associate with the named area.
If you select the Meta Tag option, the domain dropdown is replaced by the Meta Tag ID field:
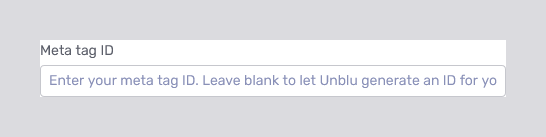
As the hint in the field says, you can either provide a meta tag ID of your own or leave the field blank and let Unblu generate a unique meta tag ID for the new named area.
A domain or meta tag ID may only be associated with one named area. If you try to assign a domain or meta tag ID that’s already associated with an existing named area to another named area, the fly-in page displays an error message.
It isn’t possible to change a named area’s defining attribute once you have saved it.
Clicking an entry in the overview gives you access to that named area’s configuration.
The delete button 

For more information, refer to the article on named areas.
General
Besides the usual descriptive fields, the General tab for a named area includes the attribute defining that named area, that is, the domain or meta tag ID associated with it. This attribute can’t be changed.

If the named area is defined by a meta tag ID, the General tab includes two code snippets:
-
An HTML meta tag. Add this snippet to each page where you want to use this named area.
-
A set of code snippets intended for mobile apps, one for iOS apps and one for Android apps. Replace
<UNBLU_SERVER_URL>and<API_KEY>in the snippets with the respective values for your account.
Product setup
The Product Setup section groups the main configurable aspects of visitor interaction, that is, conversations and canned responses.
Conversations
Clicking Conversations in the navigation menu opens the overview of conversation templates defined for the account:
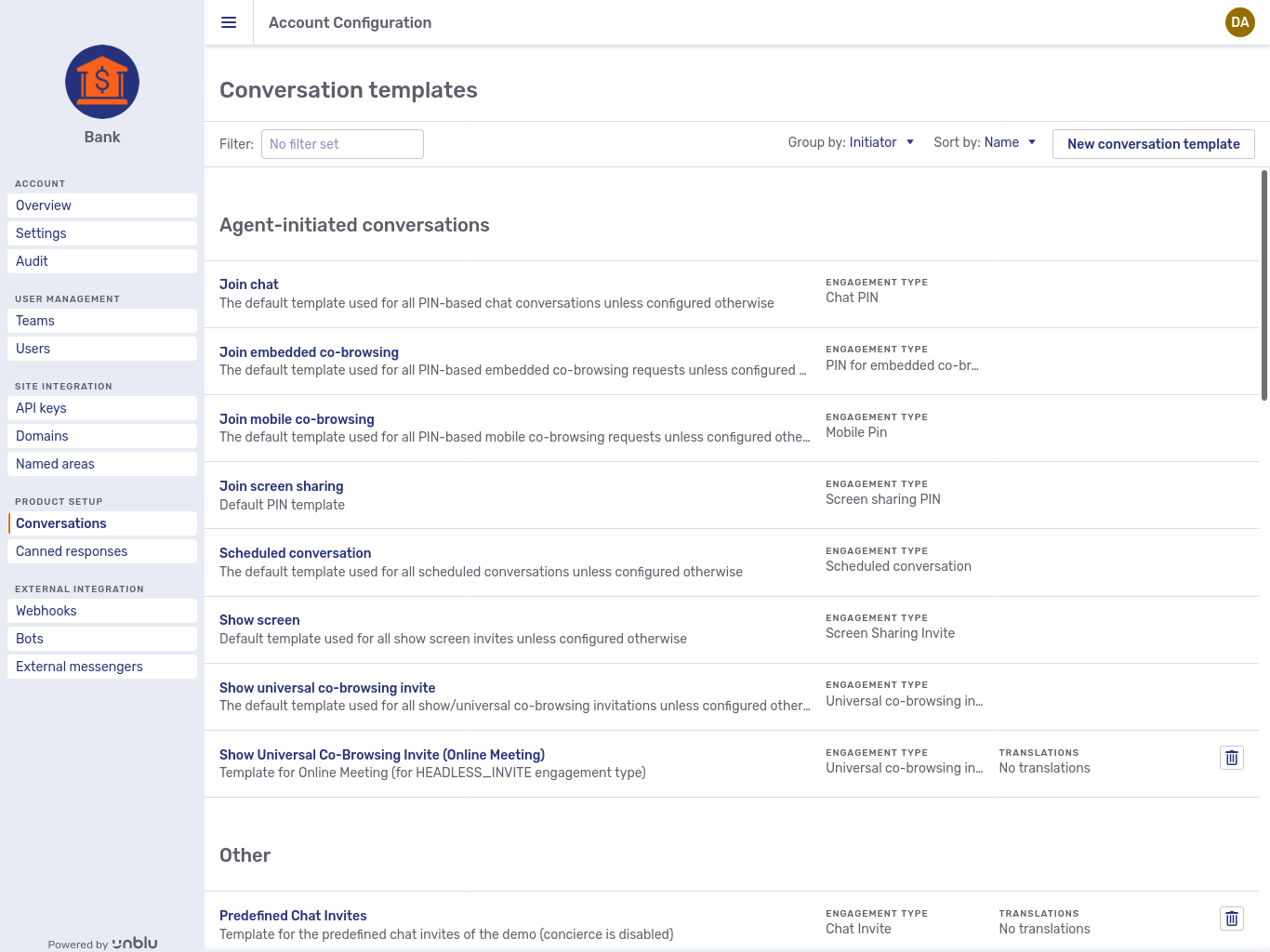
The list can be sorted by description, engagement type, or name with the Sort by dropdown. Using the Group by dropdown, you can group templates by engagement type, initiator, join type, or media type.
All the templates you are authorized to delete sport a delete button 
When you delete a conversation template, a toast appears at the top of the interface allowing you to undo the action.
Clicking the New Conversation Template button opens the modal page of the same name. Set the template’s name, give it a description, chose the engagement type it should be used for, define the conversation visibility, and specify whether conversations based on the template should inherit changes to its configuration and text properties, then click Save. You can then configure the template on its Settings and Texts tabs. To access them, simply click the template in the overview.
| Review Elements of a conversation for more information on conversations and engagement types before creating new conversation templates. |
General
A conversation template’s General tab has the same fields as the New conversation template fly-in page. See the previous section for further information.
Settings and texts
The Texts tab mentions that you can use Markdown to format texts defined for conversation templates. The preview to the right of the Translation text field shows you what the formatted text looks like:
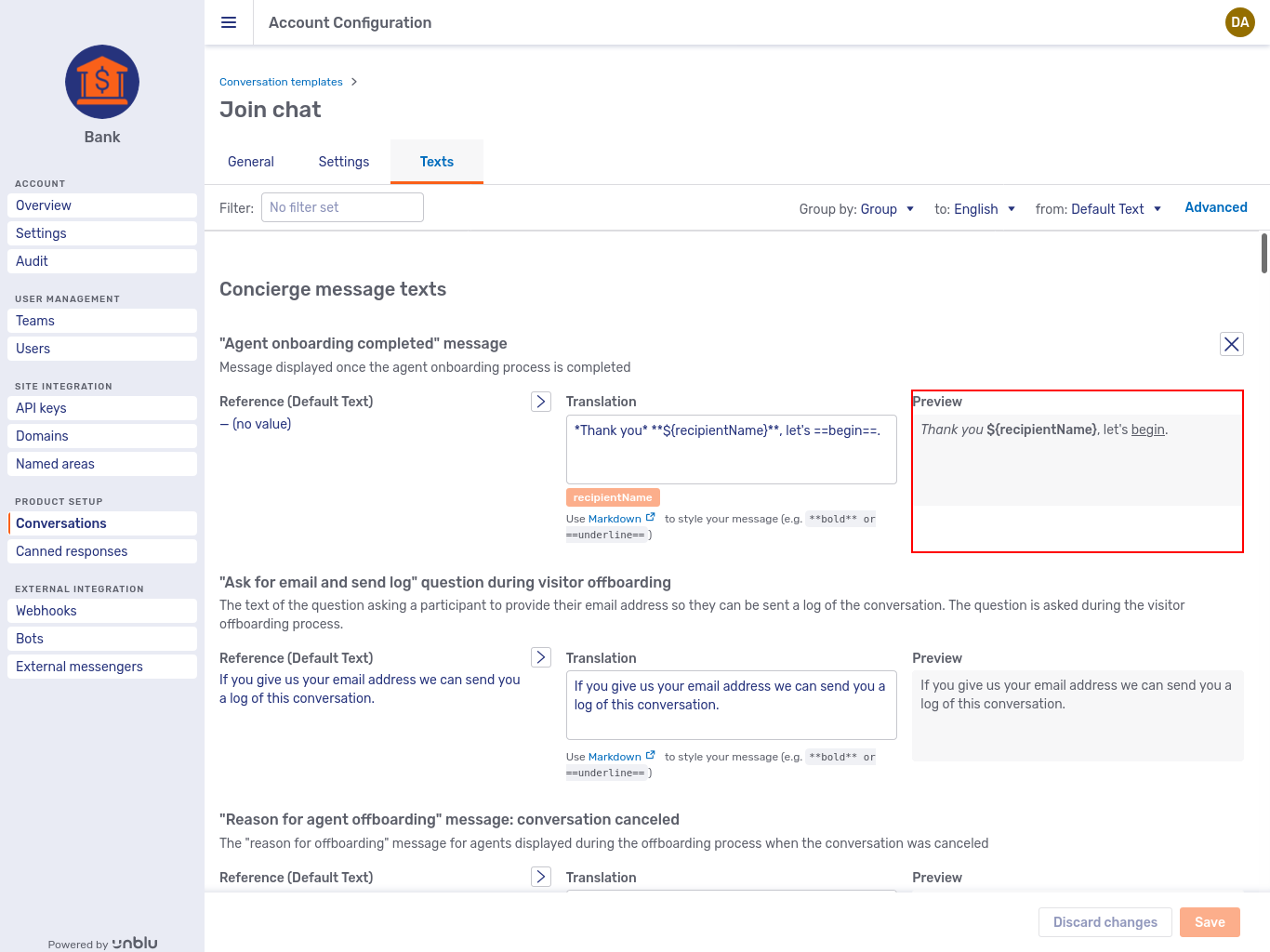
Settings and texts that you define on a conversation template are applied to each conversation based on that template.
Canned responses
Canned responses that you create in the Canned responses section are available to all agents and teams in the account.
There are two predefined placeholders, $(visitor_name) and $(agent_name), that can be included in the text of a canned response. You can also specify your own custom placeholders when you create a canned response.
When a canned response is used, predefined placeholders are automatically replaced by the correct value for the conversation. You have to replace your custom placeholders with the appropriate values for the conversation yourself.
For more information on how to create canned responses, refer to Canned responses in the Agent Desk user guide.
If you want to restrict the use of a canned response to a particular team, set it up on the Canned response tab of that team instead. To create a canned response for a single user, do so on that user’s Canned response tab.
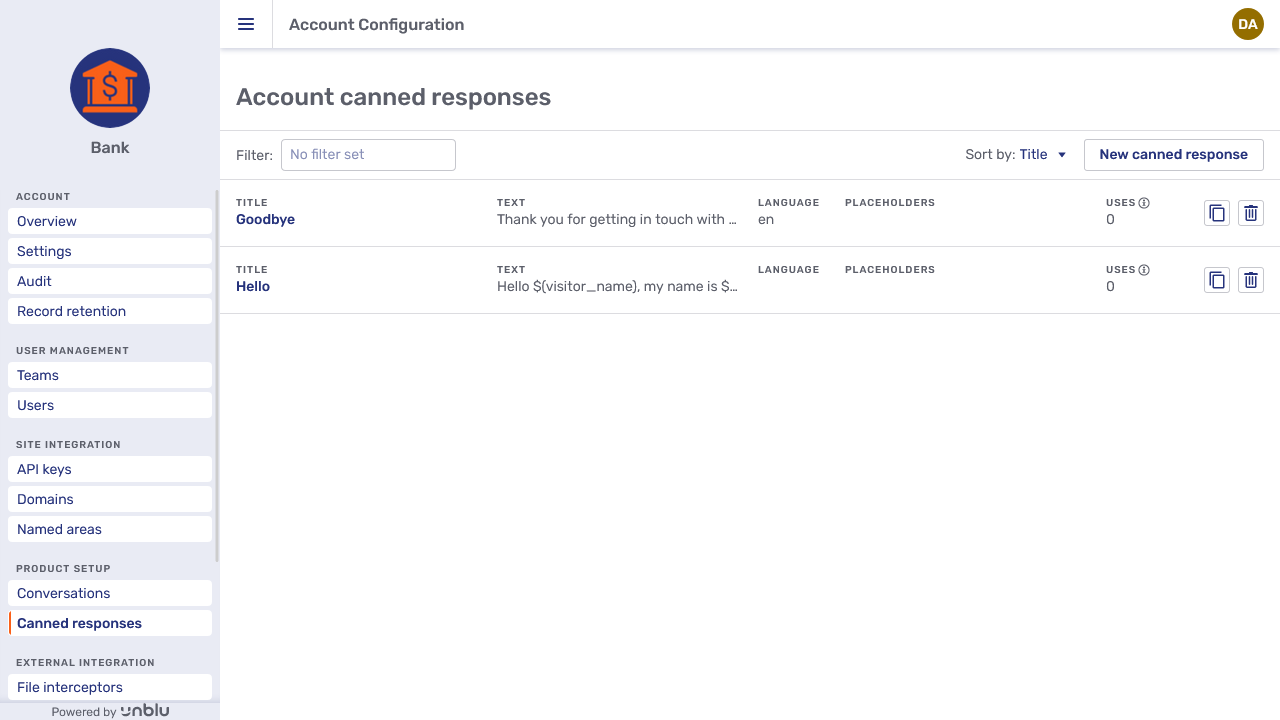
For more information on how to create canned responses, refer to the section on creating canned responses in the Agent Desk user guide.
When you click a canned response’s delete button 
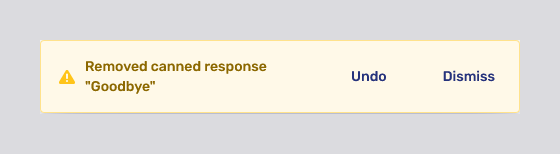
Canned response usage statistics
The Uses column in the screenshot above shows how many times a given canned response has been used. The time period during which uses are counted is defined with the configuration property com.unblu.agent.cannedresponses.list.ui.pastDaysToCountUsageFor. The default is 30 days.
The Account Configuration interface shows overall usage for all agents. Each agent can also see their own usage in the Agent Desk canned responses tab.
Comprehensive usage statistics can be accessed using the conversation.cannedresponse_used webhook for export and analytics purposes. The web API also provides search and count services. For more information on these services, refer to the `CannedResponsesUsage`section of the Unblu web API reference.
Search indices
Clicking the Search indices entry in the navigation menu opens the search index overview:
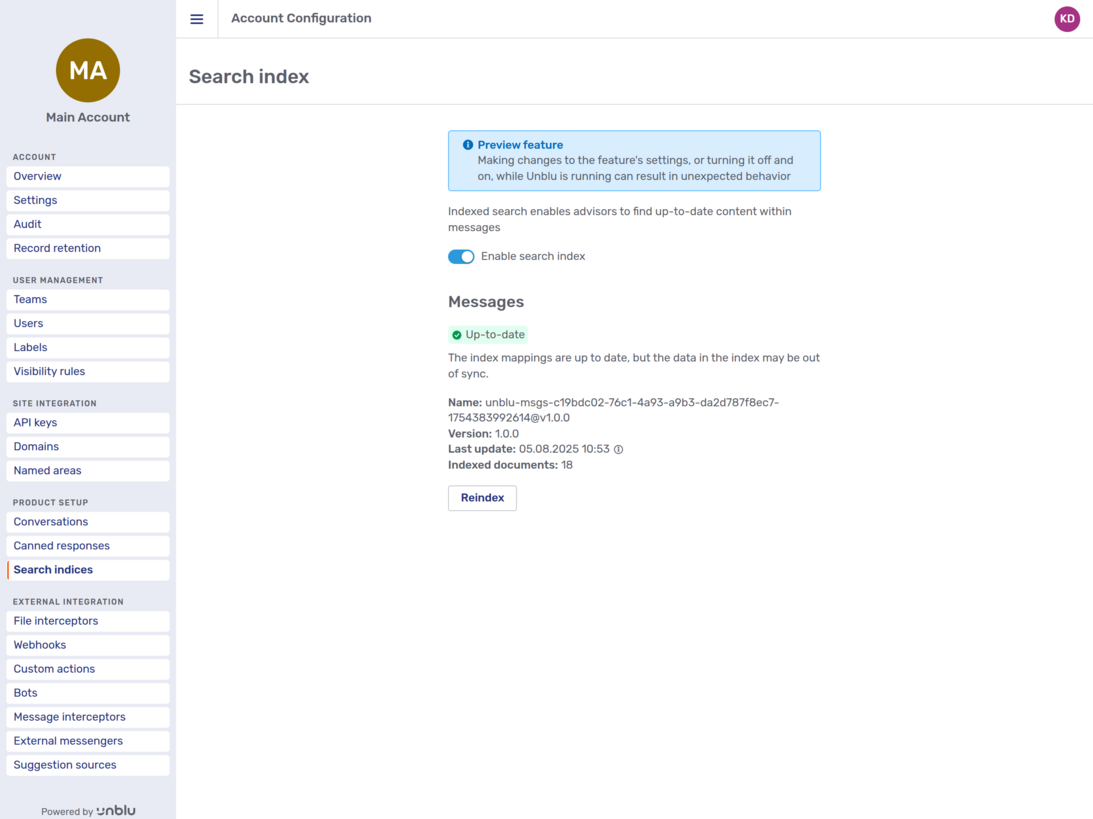
The toggle sets the value of the configuration property com.unblu.conversation.index.enableIndexing.
If you enable indexing, the overview shows you various information about the indices for the Unblu account in question:
-
The status of the index
-
The name of the index
-
The version of the schema used by the index
-
When the index was last updated
-
The number of documents indexed
It also displays buttons to recreate the indices.
| At present, only conversation messages are indexed. |
For more information on search indices, refer the sections on indexing in the articles Full-text search in Unblu and Configuring Unblu full-text search.
Branches
Clicking the Branches entry in the navigation menu opens the branches overview. By default, the list of branches is sorted by name.
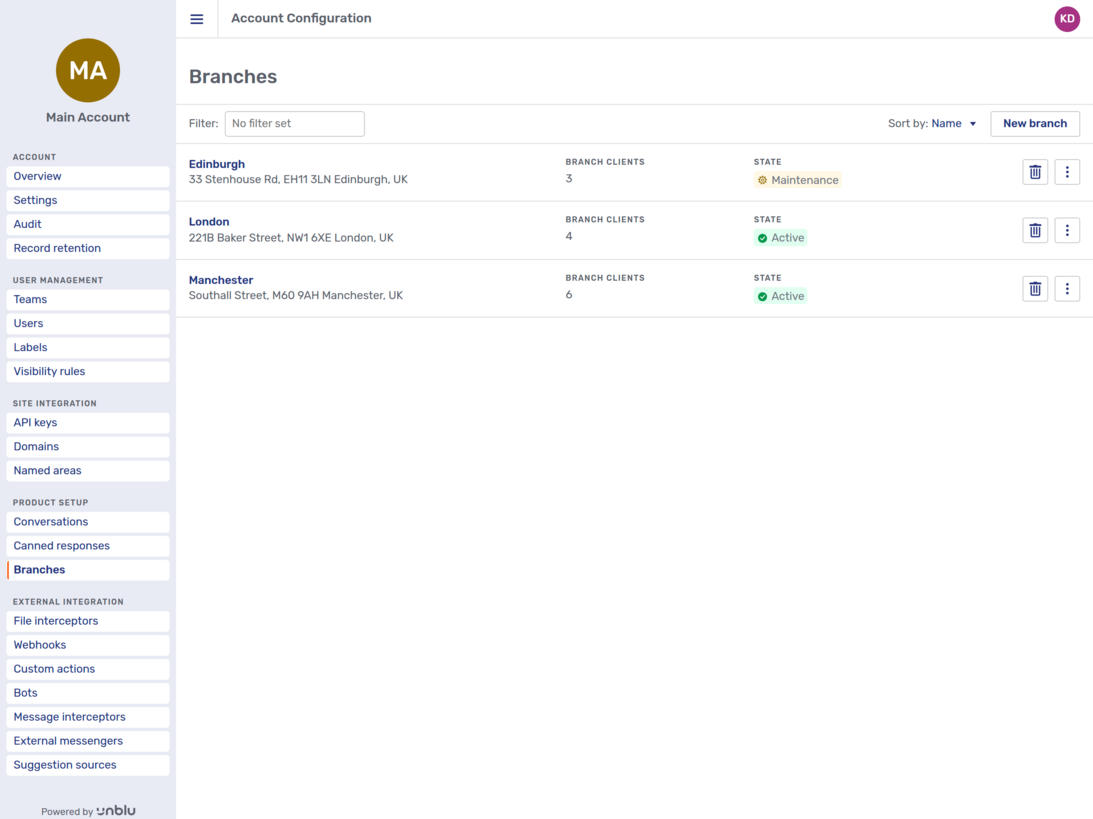
Each branch is listed with its name and address, the number of Unblu Branch clients at the branch, and the state of the branch.
Branches have one of three states:
-
Active: The branch appears in the Agent Desk and the Branch client setup UI.
-
Maintenance: The branch doesn’t appear in the Agent Desk, but it does appear in the Branch client setup UI.
-
Inactive: The branch doesn’t appear in the Agent Desk or the Branch client setup UI. This is the default state for new branches.
Deleting a branch using the delete button 
The kebab menu 
Clicking a branch in the overview opens the Branch editor:
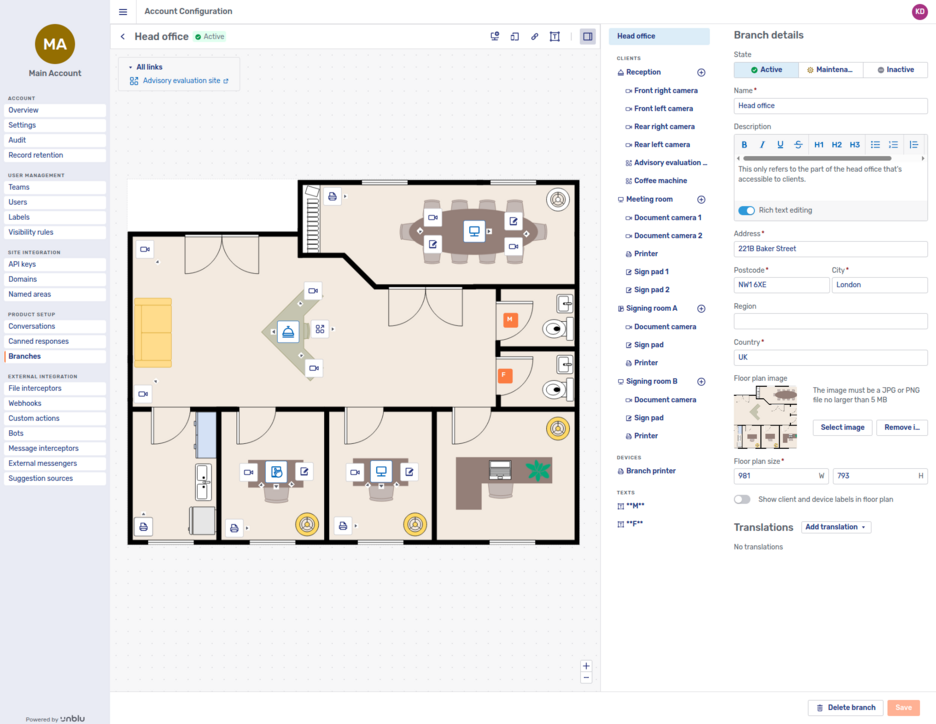
In the Branch editor, you can add various elements to a branch:
-
Floor plan
-
Links
-
Texts
You can also change the state of the branch.
Refer to the dedicated article for a more detailed discussion of the Branch editor’s features.
Creating branches
Clicking the New branch button in the upper right-hand corner opens the New branch fly-in page:
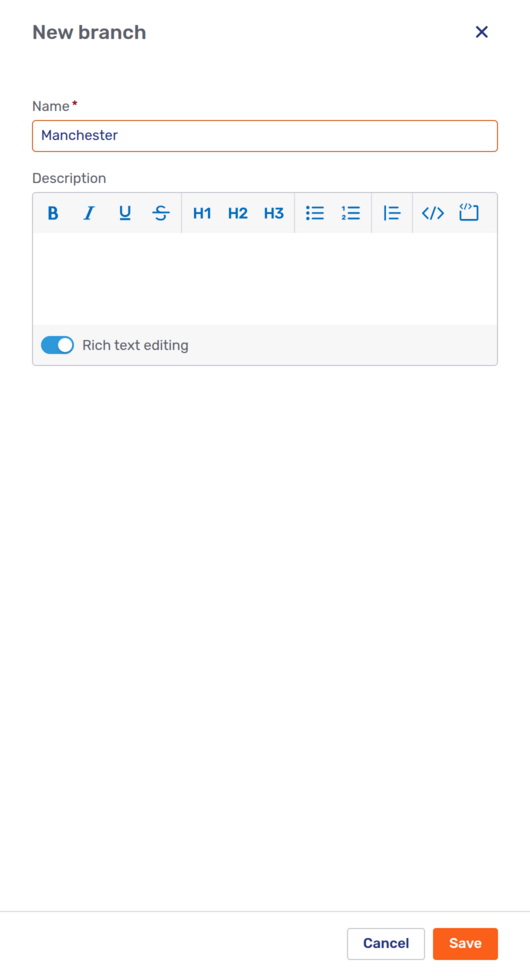
Enter the name of the branch. If you want, you can add a description. The description is displayed in the Branch client setup UI.
When you’ve finished, click Save to create the branch. It’s created with the state Inactive. The new branch appears in the branch overview immediately.
External integration
The External integration section contains configuration options for ways to integrate Unblu into external applications.
File interceptors
File interceptors allow you to review files uploaded to conversations before they’re made available to other participants.
Clicking the File interceptors entry in the navigation menu opens the file interceptor overview. By default, the file interceptors are listed in the order they’re called.
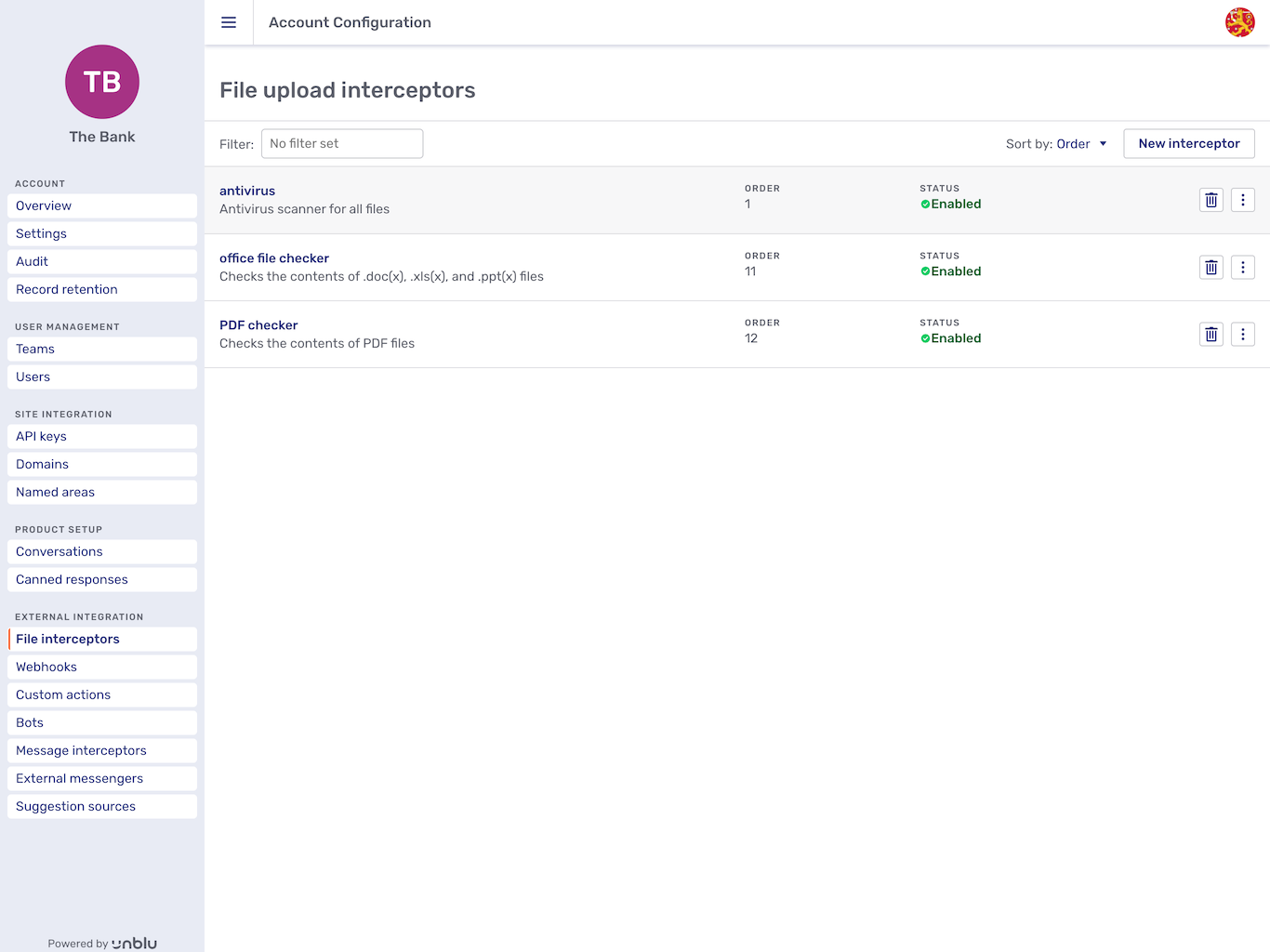
Each file interceptor is listed with its name, its description (if present), its position in the order the interceptors are called, and its status. Clicking an interceptor in the list opens its General tab, which displays its settings.
Deleting a file interceptor using the delete button 
The kebab menu 
Grouping these two functions in one place provides a convenient way to test your file interceptors:
-
When you click the kebab menu button and select Send ping event, a modal dialog appears.
If you click OK, the ping event is sent to the interceptor’s endpoint URL.
-
Now click Delivery log in the kebab menu to check the file interceptor’s delivery log and verify that it was delivered successfully.
Creating file interceptors
To create a file interceptor, click the New interceptor button in the upper right-hand corner of the screen. This opens the New file interceptor fly-in page:
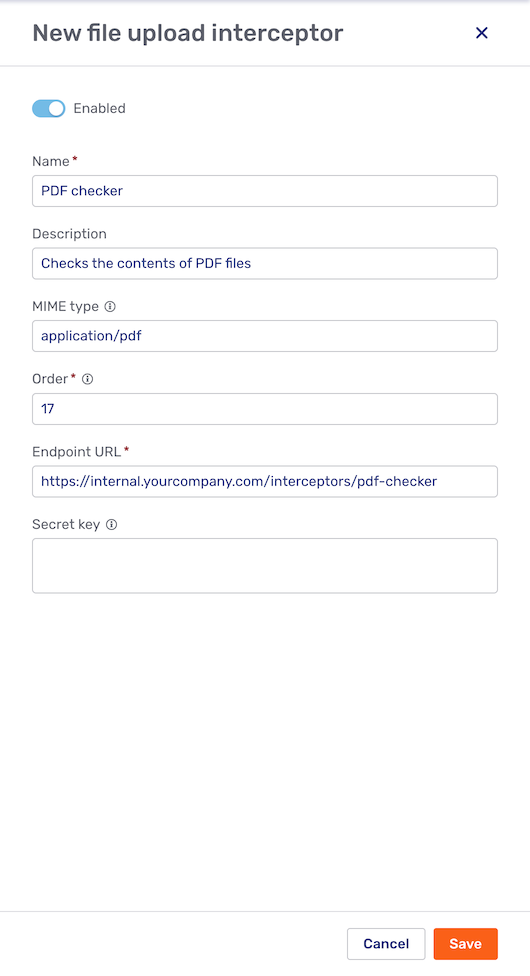
At the top of the fly-in page is a switch to enable or disable the file interceptor. By default, new file interceptors are enabled.
For more information on disabling file interceptors, refer to the section Disabling file interceptors of the article File interceptors.
The fields Name and Description are used to provide the name and description, respectively, of the file interceptor.
| Each file interceptor must have a unique name. |
The other fields are:
- MIME type
-
A regular expression that matches the MIME type of the files to evaluate. Use the regular expression syntax described in the documentation of the Java
Patternclass.The MIME type is provided by the uploader, that is, the participant’s browser, or the bot.
- Order
-
The file interceptor’s position in the order that Unblu calls the interceptors. If two or more file interceptors have the same order, the order in which Unblu calls them isn’t specified. If the order the interceptors are called in isn’t important to you, you can assign them all the same order, for example 0.
- Endpoint URL
-
The URL where Unblu sends the
file_upload_interceptor.new_filewebhook for the file to be evaluated. - API version
-
The version of the Unblu web API that the file interceptor targets.
- Secret key
-
An optional secret to ensure calls to the endpoint are coming from the Unblu Collaboration Server.
See also
For more information on file interceptors, refer to File interceptors.
Webhooks
|
The functionality of the Webhooks section is also available via REST calls. For more information on using webhooks in Unblu, refer to Webhooks technical details. |
The Webhooks section provides an overview of all the webhooks registered with your account. You can sort the overview by name or by endpoint URL with the Sort by dropdown.
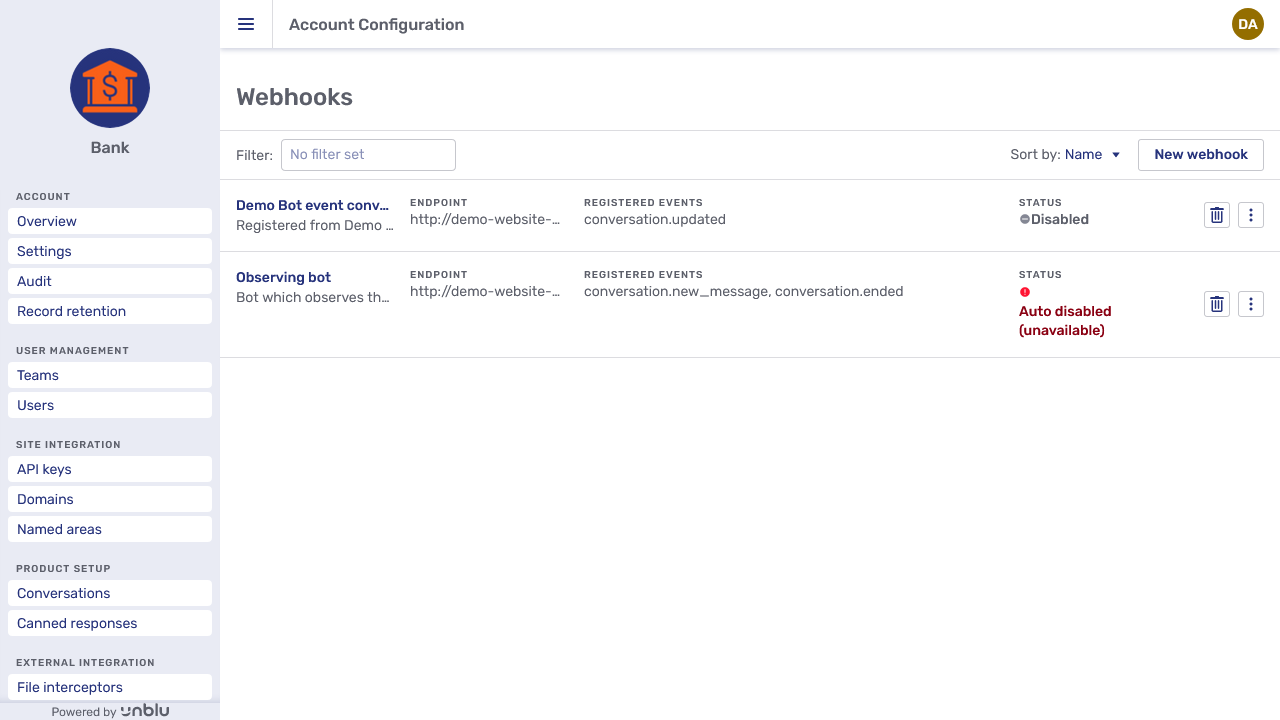
Each webhook is listed with its name, its endpoint URL, the events which will trigger a notification, and its status. Clicking a webhook opens its General tab, which provides exactly the same possibilities as the New webhook fly-in page described below.
Deleting a webhook using the delete button 
The kebab menu 
Grouping these two functions in one place provides a convenient way to test your webhooks:
-
When you click the kebab menu button and select Send ping event, a modal dialog appears.

If you click OK, the ping event is sent to the webhook’s endpoint URL.
-
You can now check the webhook’s delivery log to verify that it was delivered successfully.
Creating webhooks
Register new webhooks with the New webhook button. This opens the following fly-in page:
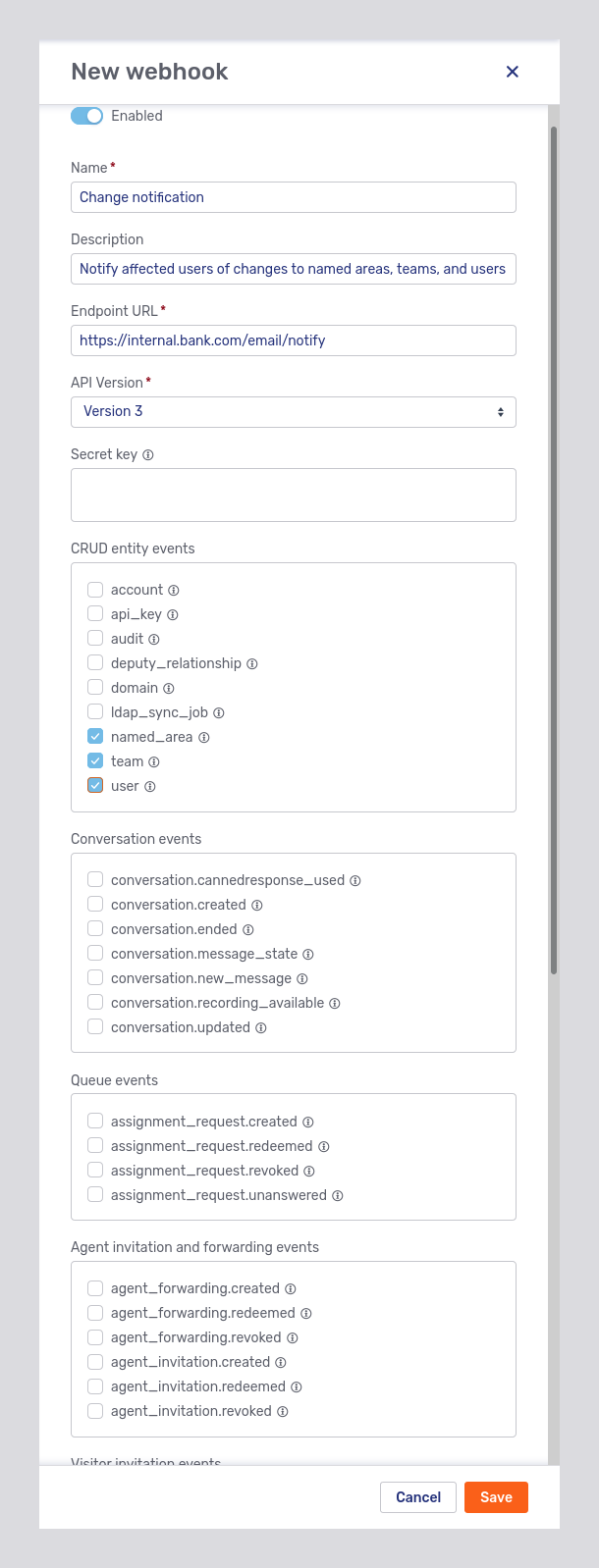
Besides the webhook’s name and description, the fly-in page allows you to specify:
-
The webhook’s endpoint URL
-
The version of the Unblu web API it uses
-
The events that should be sent to the webhook
-
A secret key (not visible in the picture above) The key is used to generate an SHA1 HMAC of the request body sent to the webhook’s endpoint. By comparing the body’s raw content with the contents of the
x-unblu-signatureheader, you can verify that the notification came from the Unblu Collaboration Server.
By default, the toggle at the top of the fly-in page that enables or disables a new webhook is set to Enabled.
Delivery log
The Delivery log tab lists all delivery attempts to a particular webhook. You can sort the delivery log by event, response code, retry number, and time using the Sort by dropdown.
The picture below show an unsuccessful delivery:
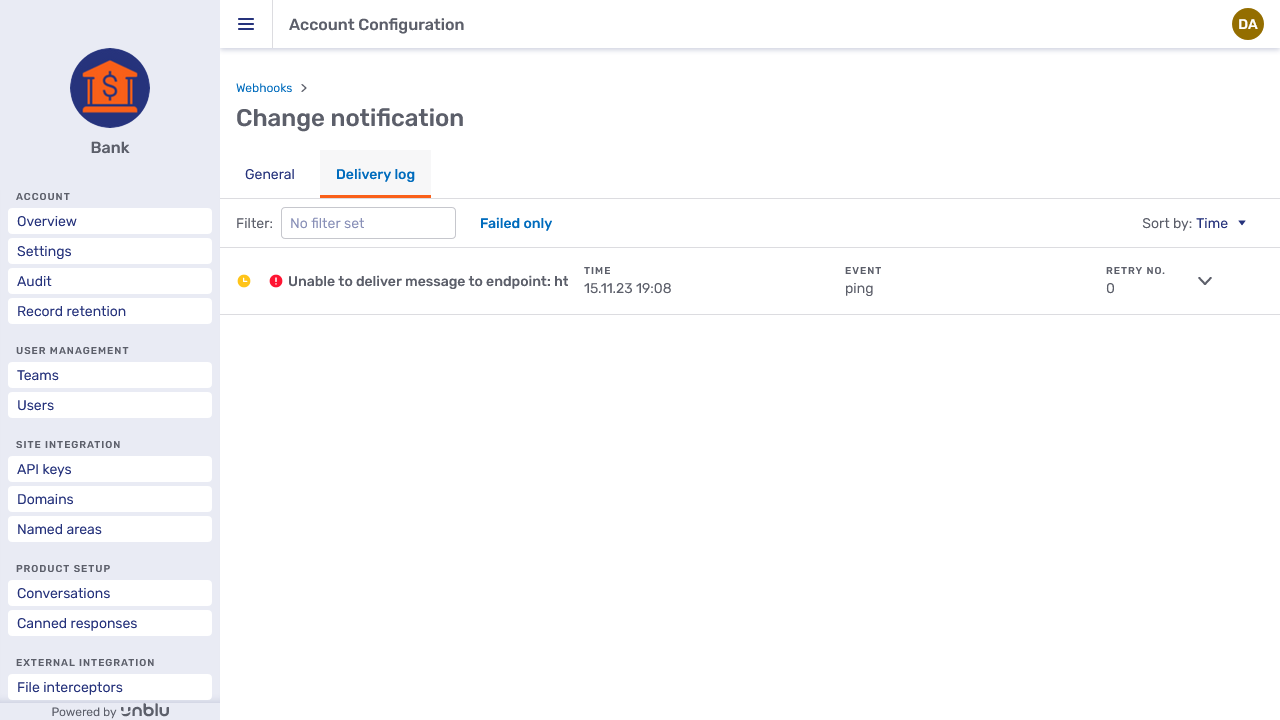
For more information, click the chevron button 
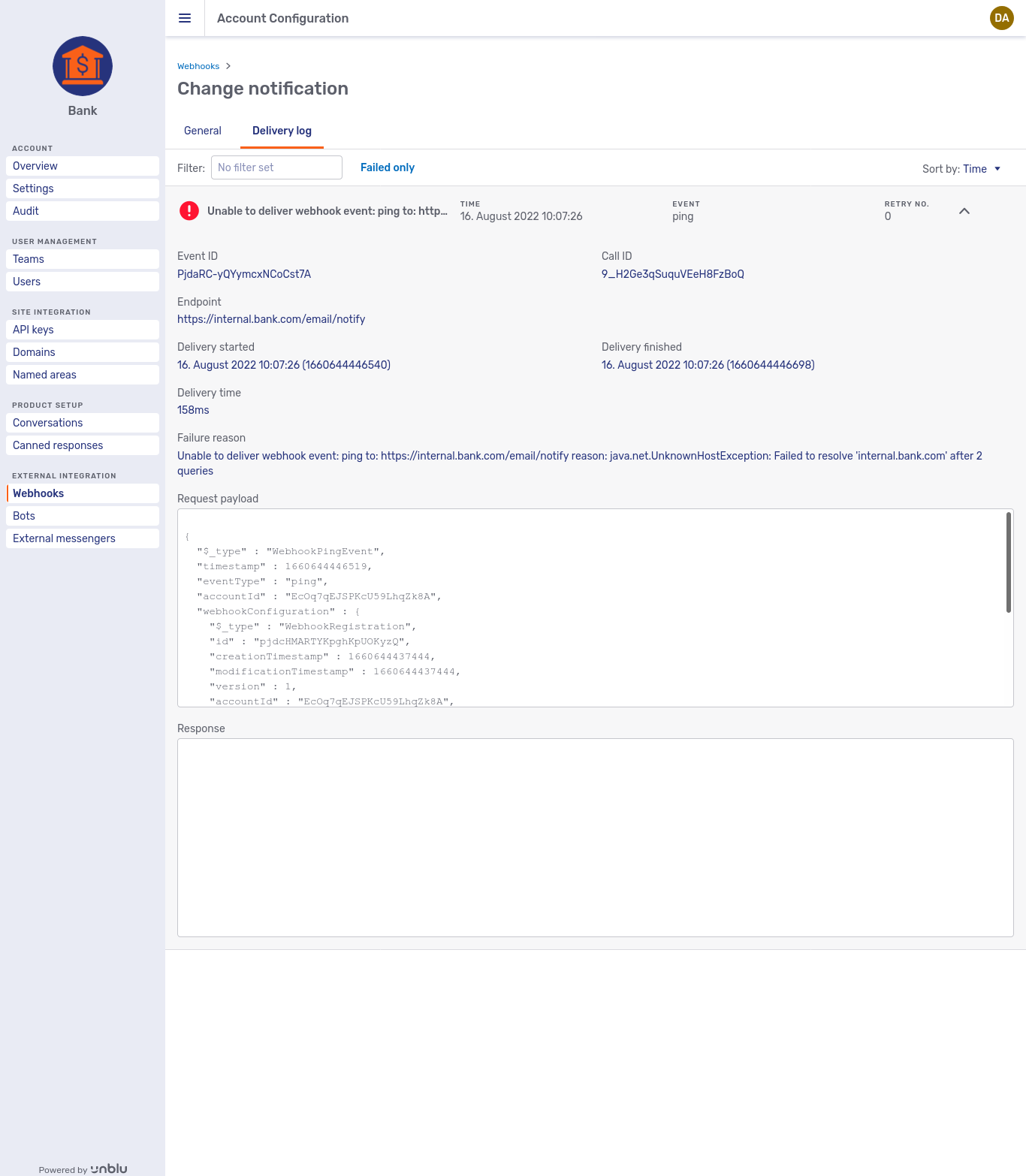
You can access the Delivery log tab by clicking either on a webhook in the overview or on a webhook’s kebab menu and selecting Delivery log.
Custom actions
The Custom actions entry in the navigation menu opens the custom actions overview. The custom actions are grouped by type: custom conversation actions, custom person actions, and custom message actions.
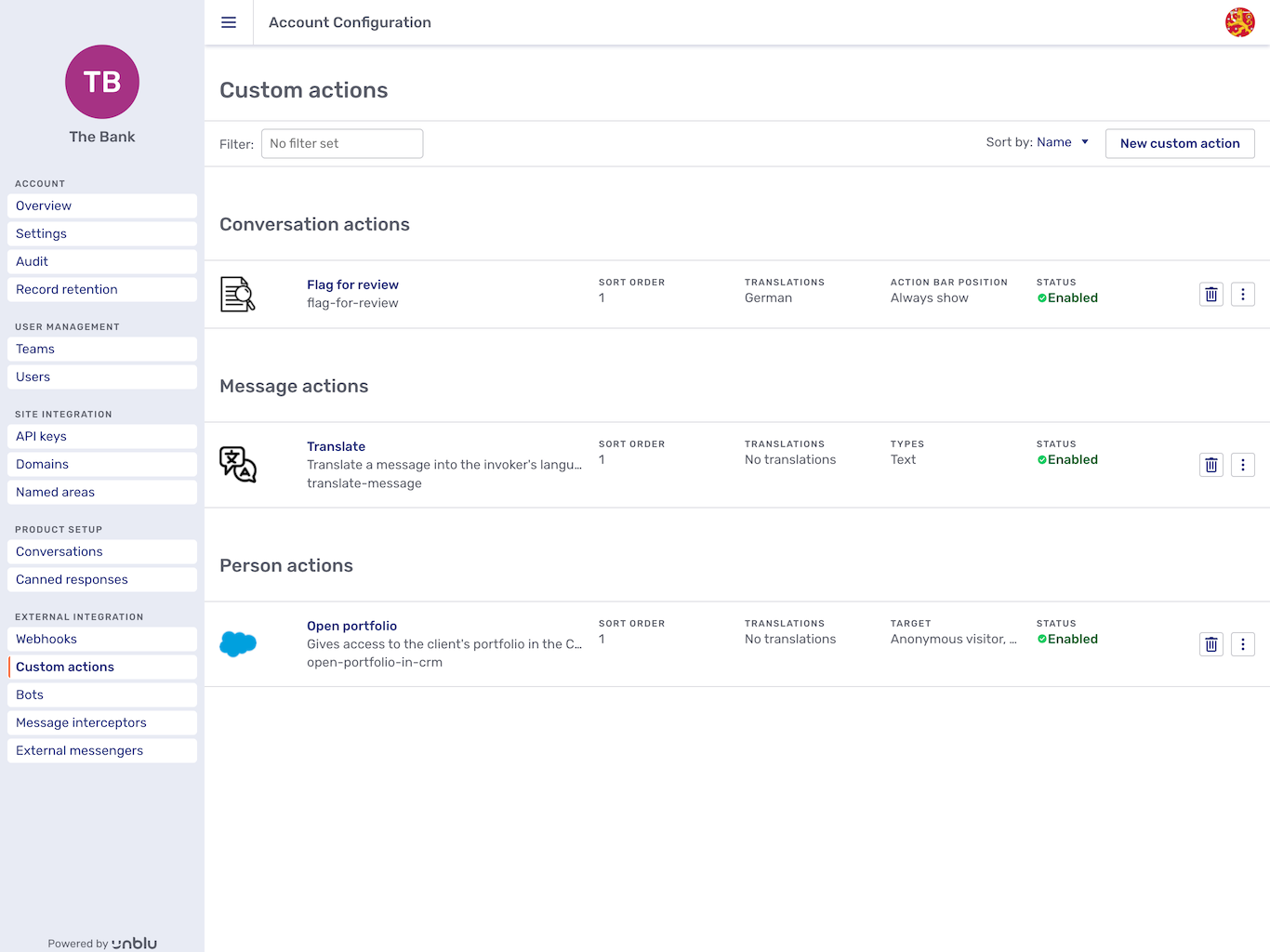
In the overview, each custom action has a delete button 
Custom actions that trigger a webhook have a kebab menu 
Clicking a custom action’s name displays the action’s details. You can edit the custom action’s details. To save your changes, click Save.
New custom action
The New custom action button at the top of the custom actions overview opens a context menu where you can choose the type of custom action you want to create. Making a selection opens the New custom action fly-in page:
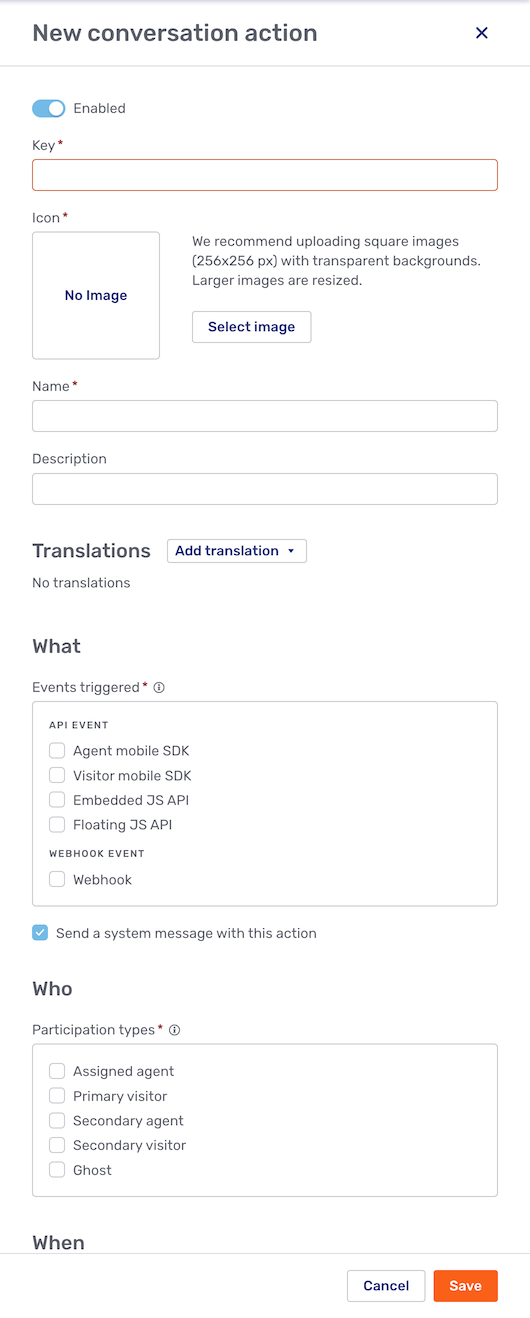
For information about the options you have when creating a custom action, refer to Creating custom actions.
When you click Save, the fly-in page closes and your new custom action appears in the custom action overview.
Message interceptors
Message interceptors prevent users from leaking sensitive data. They let you block messages in live chats and secure text messaging conversations.
The Message interceptors menu item lets you create, manage, and delete message interceptors. It opens the message interceptor overview. Internal and external message interceptors are listed separately:
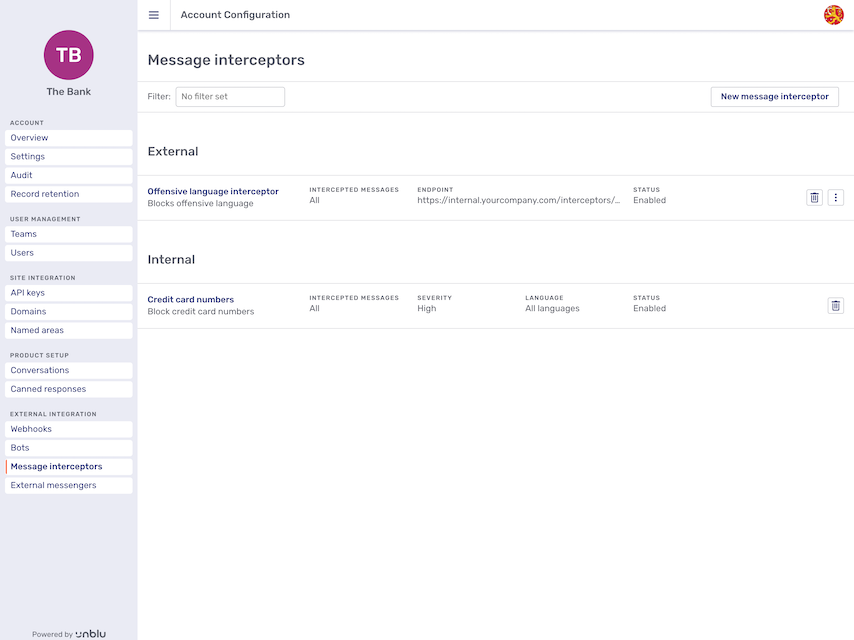
Entries for both internal and external message interceptors have a delete button 

Entries for external message interceptors also have a kebab menu 
Clicking the entry of an internal message interceptor opens a fly-in page that displays the interceptor’s details.
Clicking the entry of an external message interceptor displays the interceptor’s details in the main area of the window. It also gives access to the Delivery log tab for the interceptor.
Internal message interceptors
To create an internal message interceptor, click the New message interceptor button and select Internal. This opens the Internal interceptor fly-in page:
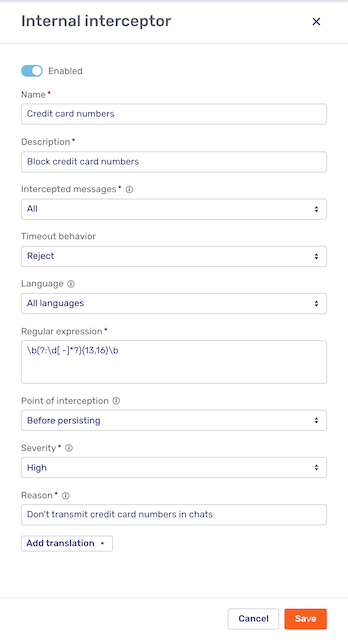
At the top of the fly-in page is a switch to enable or disable the message interceptor. By default, new interceptors are enabled. For more information on disabling message interceptors, refer to the section Disabling message interceptors of the article Message interceptors.
The fields Name and Description are used to provide the name and a description of the message interceptor, respectively.
| Each message interceptor must have a unique name. |
The other fields are:
- Intercepted messages
-
Specify whether messages sent by the visitor, the agent, or both are evaluated by the interceptor.
- Timeout behavior
-
If the interceptor doesn’t respond within the defined time, Unblu behaves as specified here. There are two options:
-
Reject: The message is treated as if it had been rejected.
-
Continue: The message is treated as if it had been approved.
-
- Language
-
The language of the conversation the message interceptor should apply to. You can apply an interceptor to conversations in all languages or a specific language. If you have a regular expression to block credit card numbers, for example, you probably want it to evaluate messages in all languages. An interceptor to block offensive language, on the other hand, would have to be tailored to each language individually. In that case, you’d select a specific language.
- Regular expression
-
The regular expression the message is evaluated against. For more information, refer to the relevant section the article Message interceptors.
- Point of interception
-
The point of interception determines whether the message is evaluated by the message interceptor before or after it’s persisted by the Unblu Collaboration Server. This can have an impact on the syntax of the regular expression. For more information, refer to the relevant section the article Message interceptors.
- Severity
-
The severity determines how rejected messages are displayed to different participants. For more information, refer to the relevant section the article Message interceptors.
- Reason
-
When the message interceptor rejects a message, Unblu displays the reason for the rejection.
-
For messages intercepted before persisting, the rejection reason is displayed above or below the text input field in the Agent Desk or Visitor UI, respectively.
-
For messages intercepted after persisting, the rejection reason appears beneath the chat bubble that would normally display the message.
If the interceptor you’re creating applies to all languages, you can add localized versions of the reason text by clicking the Add translation button. Select the language you want to add a localized reason text for, enter the translated reason text in the input field that appears, and click Add. The localized reason text appears beneath the Add translation button.
To edit a localized reason text, click the Edit button
next to the localized text. To delete a localized reason text, click the Delete button
next to the localized text.
-
| Changes to internal message interceptors are only applied to conversations that start after you save the change. |
External message interceptors
To create an external message interceptor, click the New message interceptor button and select External. This opens the External interceptor fly-in page:

The Enabled switch and the fields Name, Description, Intercepted messages, and Timeout behavior have the same purpose as for internal message interceptors, described above.
- Endpoint
-
The URL where Unblu sends the
message_interceptor.new_messagewebhook for the message to be evaluated. - API version
-
The version of the Unblu web API that this interceptor is targeting. This determines the technical details of how Unblu and the interceptor interact.
- Secret key
-
An optional secret to ensure calls to the webhook endpoint are coming from the Unblu Collaboration Server.
See also
For more information on message interceptors, refer to Message interceptors.
External messengers
The External messengers menu item gives access to the configuration options for external messengers such as WhatsApp. It opens the external messengers overview:
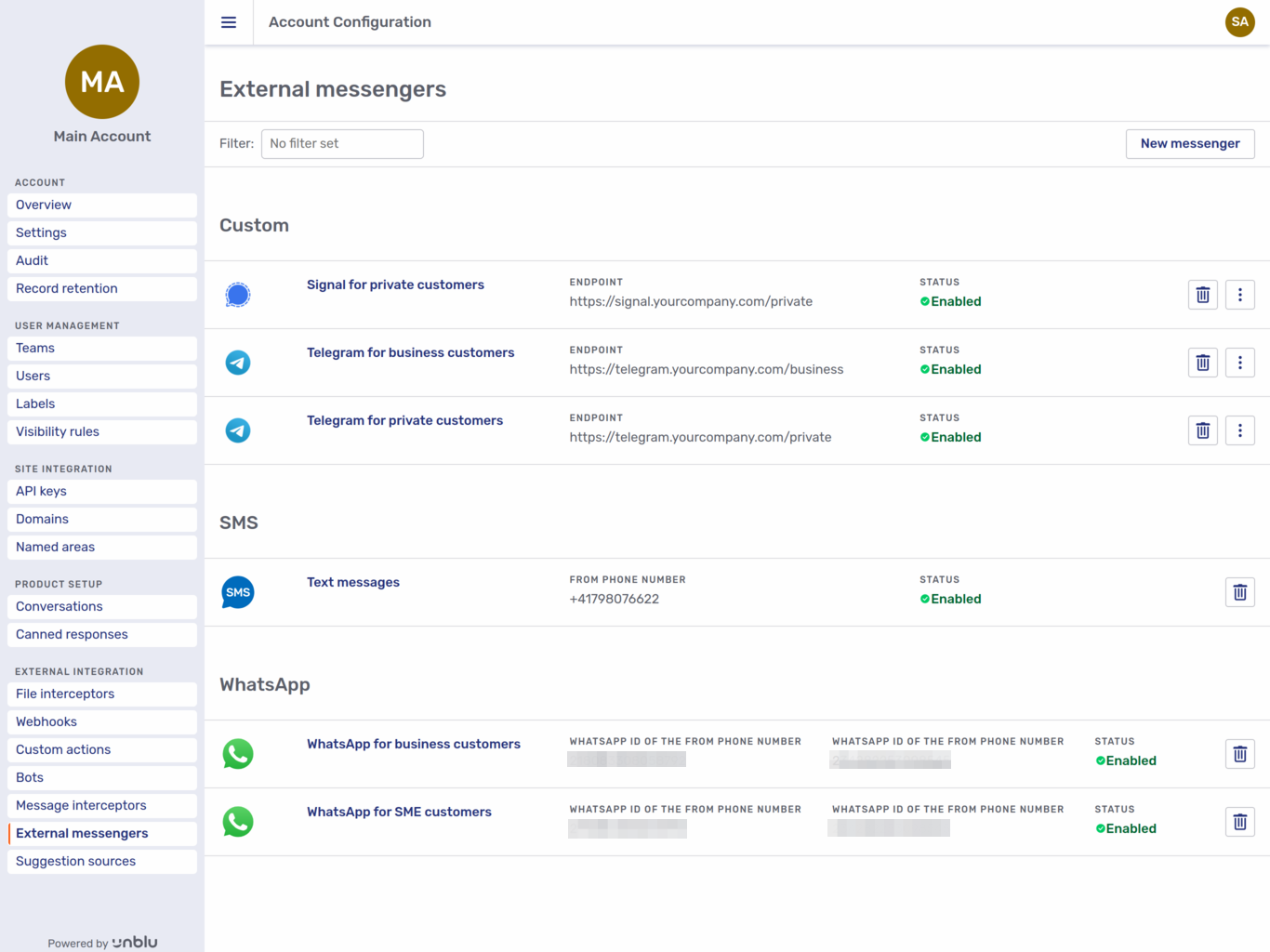
You can see the name, description, endpoint, and status of each external messenger configured for the account. Like webhooks and bots, each external messenger has a delete button 
The delete button opens a modal dialog:
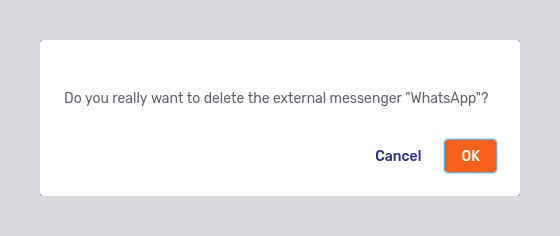
Clicking OK deletes the external messenger configuration immediately.
Custom external messengers also have a kebab menu 
The New messenger button opens a menu where you can choose the type of external messenger you want to integrate. Choose between SMS, Unblu’s Twilio integration for sending text messages, WhatsApp for sending WhatsApp messages, and Custom for all other external messengers. Clicking an option opens a fly-in page with the same configuration options as the General tab of an existing external messenger of the same type.
All external messenger types let you to enter the following information:
-
Whether the messenger’s enabled or not. When you create an external messenger, it’s enabled by default.
-
An image to use as the messenger’s icon, for example in the Agent Desk
-
The messenger’s name
-
A description of the messenger
The remaining fields depend on the type of external messenger.
Custom
For custom external messengers, the fly-in page has fields for the following additional settings:
-
The endpoint URL
-
The version of the Unblu web API that the external messenger targets
-
The timeout, in ms, before Unblu considers the external messenger unreachable and disables it
-
An optional secret key
-
A toggle to specify whether the read and delivered states of messages sent to the external messenger are managed by the external messenger or by Unblu. This state is reflected in the number and color of the ticks displayed next to a message in the UI.
-
A toggle to specify whether the external messenger channel supports more than one conversation per contact
-
If you opt to use version 4 of the Unblu web API, you have a toggle to specify whether the external messenger channel supports outbound communication to create contacts and/or conversations.
If you enable outbound communication, two additional fields appear that describe the contact identifier:
-
The name of the contact identifier
-
The type of contact
You can also add translations of the contact identifier’s name.
-
SMS
SMS external messengers have the following additional fields:
-
Your Twilio Account SID
-
Your Twilio authentication token
-
The phone number text messages should be sent from
-
The name of the conversation template to use for inbound chat requests that are created by text message.
If the conversation template you enter doesn’t exist, Unblu uses the default conversation template for the engagement type
CHAT_REQUESTorOFFLINE_CHAT_REQUEST, respectively. -
The recipient type for inbound text messages. Choose between Account, Named area, Team, and Agent.
-
The name of the recipient for inbound text messages. Which value you must enter depends on the recipient type:
-
For the account, the value you enter is irrelevant.
-
For named areas, it must be the name of the named area, not the ID.
-
For teams, it must be the team name.
-
For agents, it must be the username.
-
WhatsApp external messengers have the following additional fields:
-
Your WhatsApp Business Account ID
-
The WhatsApp phone number ID of the phone number you want the WhatsApp external messenger to use. Don’t enter the phone number itself.
-
An access token for your WhatsApp application
-
The WhatsApp application secret used to validate webhook payloads
-
The name of the conversation template Unblu should use for inbound chat requests that came from WhatsApp.
The conversation template must be for the engagement type
CHAT_REQUESTorOFFLINE_CHAT_REQUEST. If the conversation template you enter doesn’t exist, Unblu uses the default conversation template for the engagement typeOFFLINE_CHAT_REQUEST. -
The recipient type for inbound text messages. Choose between Account, Named area, Team, and Agent.
-
The name of the recipient for inbound text messages. Which value you must enter depends on the recipient type:
-
For the account, the value you enter is irrelevant.
-
For named areas, it must be the name of the named area, not the ID.
-
For teams, it must be the team name.
-
For agents, it must be the username.
-
WhatsApp message templates
WhatsApp external messengers have a Message templates tab that lists your WhatsApp message templates:
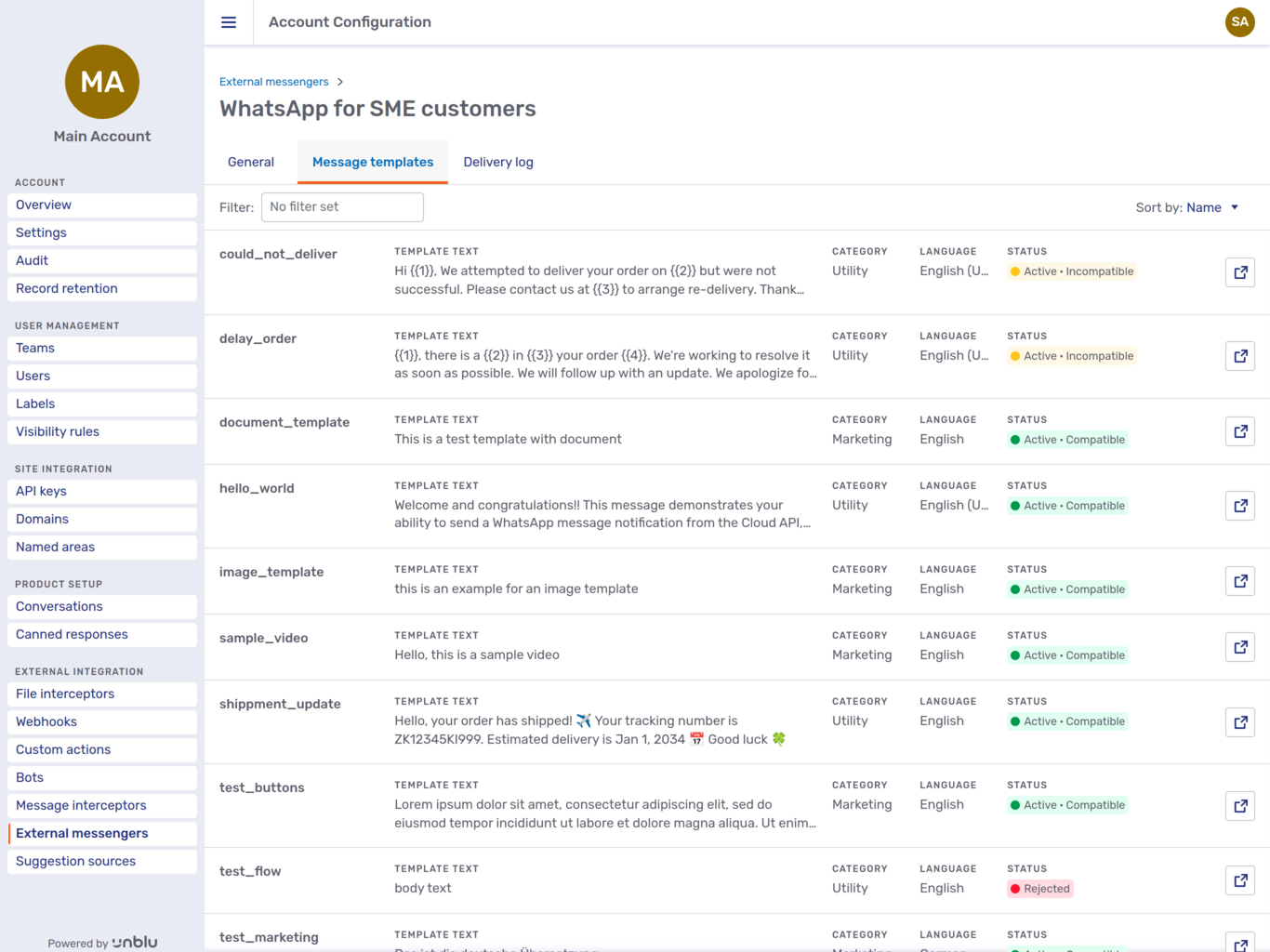
The tab shows basic information about the message template, such as its name, text, category, and language. Most importantly, it displays the message template’s status. The status of a message template is defined by WhatsApp. For an overview of possible statuses, refer to the WhatsApp documentation.
The status of active message templates also contains information about the template’s compatibility with Unblu. You can only use templates marked as Active - Compatible with Unblu. For information on the limitations of integrating WhatsApp and Unblu, refer to Limitations.
Each message template has an Open button 
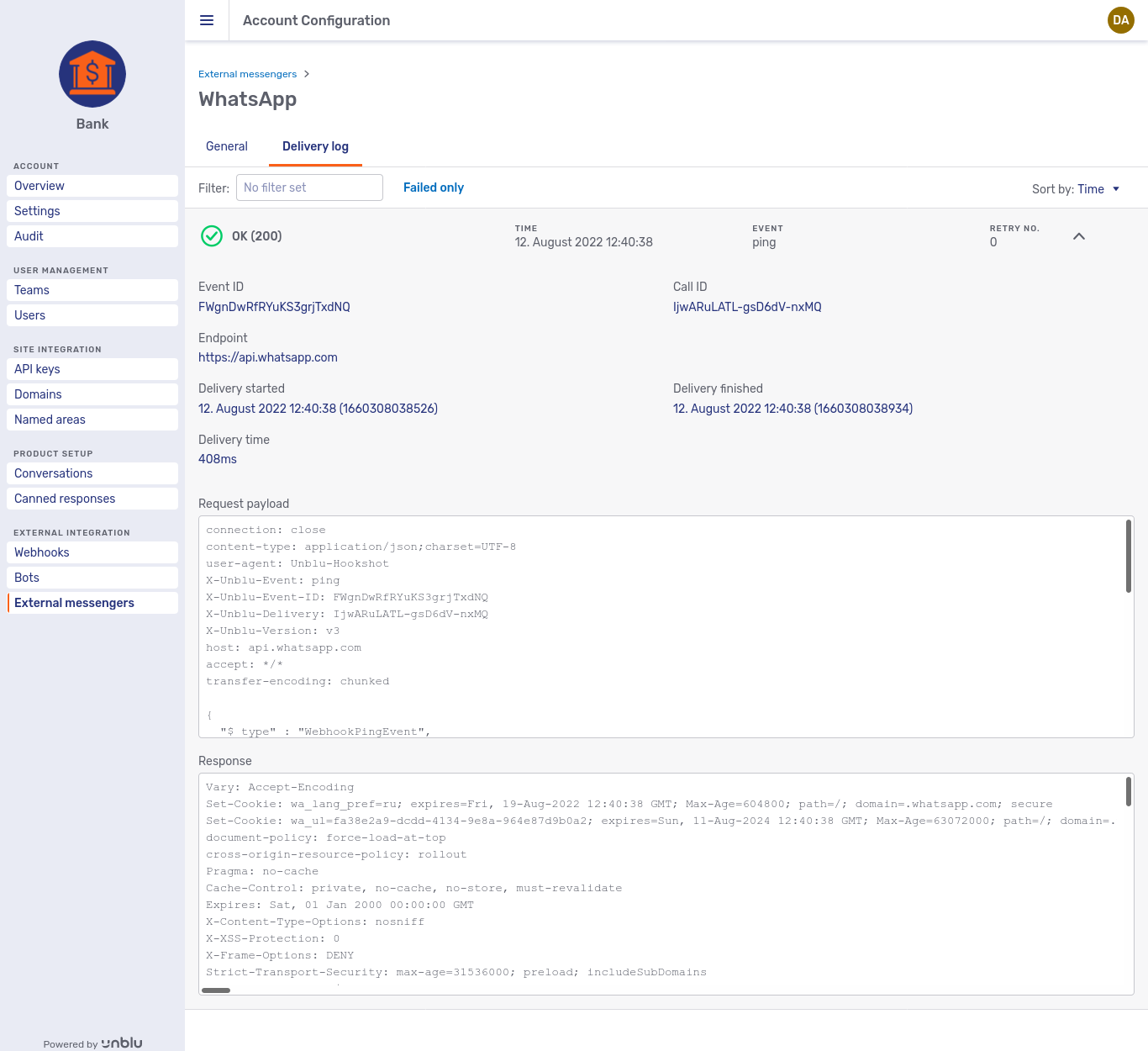
Delivery log
The Delivery log tab provides a list of all the calls the Unblu Collaboration Server made to the external messenger’s endpoint. Here’s an example of a successful delivery, expanded with the chevron button to show the request sent and the response received:
Service principals
Service principals let people carry out administrative tasks using Unblu’s web API without needing a user for that purpose.
The Service principals menu item gives you access to service principals that are instances of the ADMIN role in the Unblu account in question. Clicking the menu item opens the service principals overview.
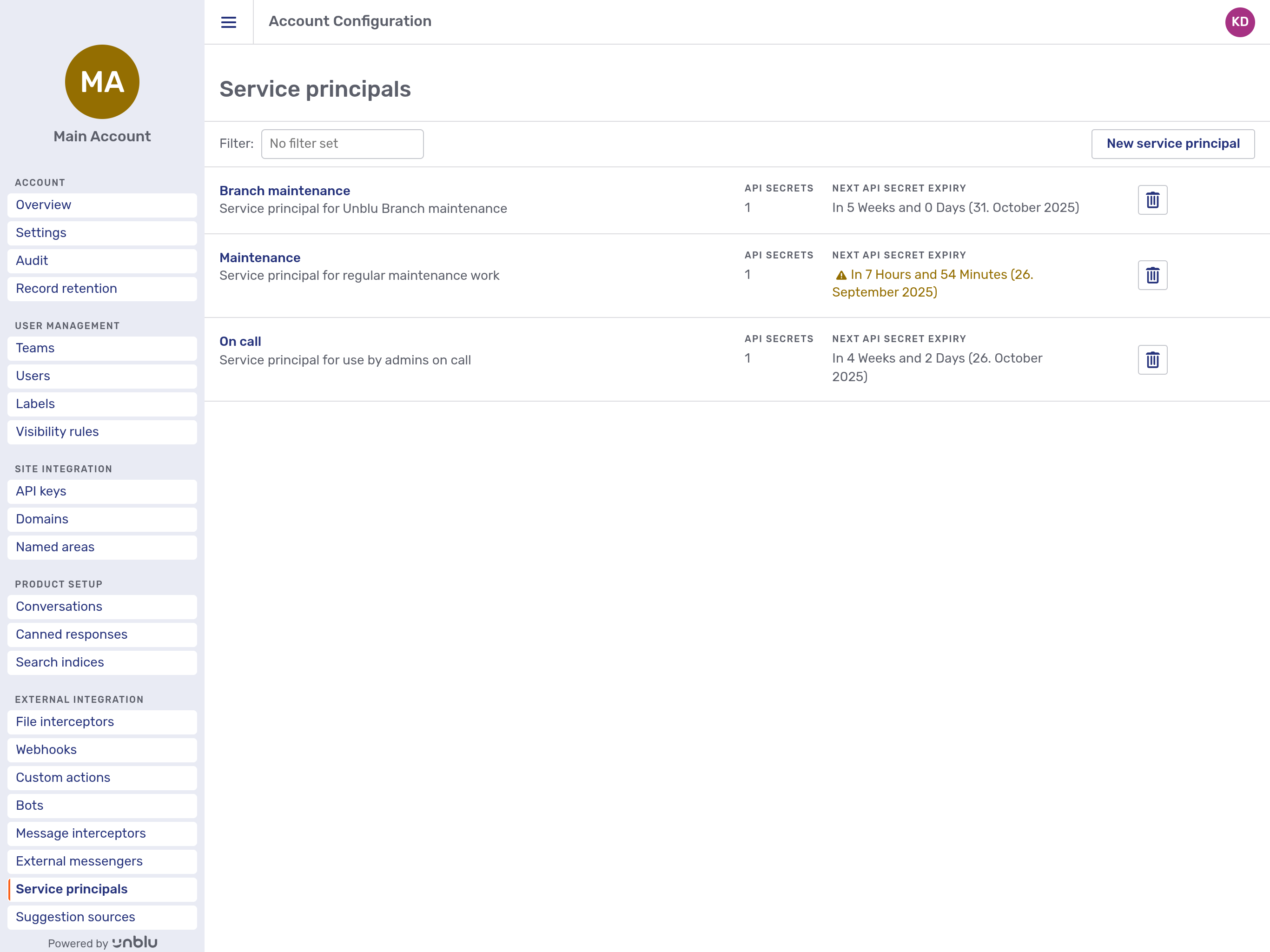
Each service principal is listed with its name, description, the number of API secrets it has, and when an API secret will expire next.
Each entry in the overview also has a delete button 
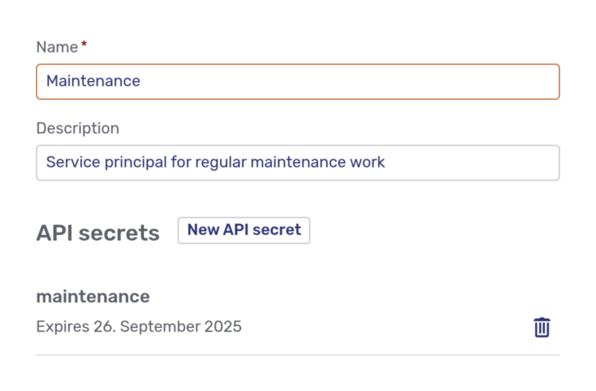
Clicking the New service principal button opens a fly-in page where you enter a name and a description. Clicking the Save button at the bottom of the fly-in page saves the new service principal and opens its details page:
This is also the view displayed when you click a service principal in the overview.
API secrets for service principals
To use a service principal, it must have a valid API secret. To create one, click the New API secret on the service principal’s details page. This opens a modal dialog:
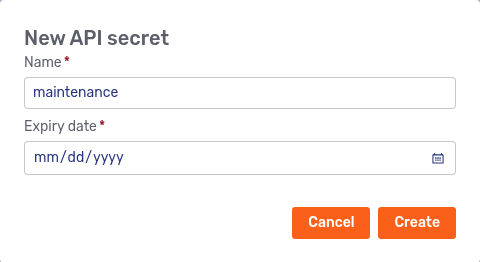
Enter a name for the API secret, specify the expiry date, and click Create. The API secret is displayed in a new modal dialog:

Store the API secret somewhere safe, then click Done to close the modal dialog and return to the service principal details page.
| There’s no way to retrieve the API secret again once you click Done. |
Suggestion sources
Suggestion sources are used to provide agents with possible responses to text messages in chats with visitors or other agents.
The Suggestions sources navigation menu item opens the suggestion source overview.

Suggestion sources are grouped by type (Custom and Microsoft Copilot). You can see the name, description, endpoint, timeout, and status of each suggestion source configured for the account. Each entry in the overview sports a delete button 

Clicking the delete button deletes the custom action immediately. The toast that appears at the top of the interface lets you undo the action.
The kebab menu opens a context menu where you can open the suggestion source’s delivery log tab or send it a ping event.
New suggestion source
The New suggestion source button lets you select the type of suggestion source you want to configure, Custom or Microsoft Copilot. Doing so opens a fly-in page with the same configuration options as an existing suggestion source’s General tab, described below.
General
Clicking a suggestion source opens its General tab. For custom suggestion sources, the tab looks like this:

The General tab of a Microsoft Copilot suggestion source looks like this:

All suggestion sources have the following settings:
-
The availability of the suggestion source in Unblu. This is done with the toggle to enable or disable the suggestion source at the top of the tab.
-
The suggestion source’s name.
-
The suggestion source’s description.
-
The endpoint URL Unblu uses to request chat suggestions.
-
The timeout. If the suggestion source takes longer than this timeout to respond to Unblu’s request for a suggestion, the suggestion source is automatically disabled. For agents that use generative AI for suggestions, set the timeout to 15000 ms or more.
Custom suggestion sources have the following additional settings:
-
The version of the Unblu web API that the suggestion source targets
-
An optional secret key that the suggestion source can use to verify that Unblu requested a suggestion
Microsoft Copilot suggestion sources have the following additional settings:
-
The authentication token needed to access the agent
-
The Microsoft environment ID
-
The Microsoft Copilot Agent ID (referred to as the Copilot Id in Microsoft Copilot Studio)
-
A link that takes you straight to the agent in the Microsoft Copilot Studio
Delivery log
The Delivery log tab lists the requests for suggestions sent to the suggestion source in question. You can sort the list by time or by response code.
Click a request to view the details of the request and of the response Unblu received from the suggestion source.

For more information on chat suggestions, refer to Providing agents with suggestions in text chats.