Pivot to thrive: Embracing trends for continued health
There are certain developments that banks simply cannot ignore. According to our research, the following trends are either so advanced or vital to ongoing institutional health that anyone lagging in these areas will find it difficult to perform as expected.
Generative AI: Challenges and opportunities
According to a McKinsey survey, two-thirds of senior digital and analytics leaders believe that Gen AI will change their business practices in a fundamental way (McKinsey). And this is not surprising as Gen AI could add as much as $4.4 trillion annually in value across the 63 use cases analyzed by the McKinsey Global Institute. In the corporate and retail banking sectors alone, the technology could add $56 billion and $54 billion respectively (McKinsey).
The challenges of Gen AI
But make no mistake – the burgeoning, highly powerful technology is still in its infancy and its full repercussions are still being revealed. Generative AI exploded onto the scene and quickly became a critical capability. For banking leaders eager to remain on top of new developments, this left little time to prepare their employees, attract new talent, or navigate the risks.
Forrester predicts that at least eight neobanks and two incumbents will experience a Generative AI-related disaster that will put them in front of regulators (Forrester). They claim that, although banks are controlling their pilot programs closely, it only takes one rogue employee or a negligent third-party collaborator to expose them to risk. This may be breached copyright, leaking customer information, bias-related, or more.
The risk involved with Generative AI is causing general concern, with industry observers urging governments at both a national and local level to bring in new regulations to combat this (EY).
Current opportunities with Gen AI
That isn’t to say that all uses of Gen AI should be avoided – quite the opposite. Organizations must embrace Gen AI or risk being left behind, and there are specific use cases where the technology is safe to use and highly effective. One example of this is the use of Gen AI in Unblu’s Conversational AI offering.
By leveraging Gen AI, companies can use LLMs to draw on their organization’s existing knowledge bases to provide accurate, company-specific answers that better serve their customers. Beyond this, the bot trainer assistant helps to train itself by suggesting more in-depth “intents” (customer questions and corresponding responses) – alongside increasing Live Chat efficiency (Unblu). This allows for a stronger self-service offering and reduces strain on certain channels, while still ensuring there is access to human support when needed.
Mobile-first communication channels
Last year, we reported how contact center managers wished to simplify their operations by reducing the multitude of vendor relationships they manage. To overcome this, many turned to integrate unified communications and contact center platforms.
This remains a key concern for the industry to enhance customer choice and flexibility, providing enhanced interaction experiences using video chat or Co-Browsing, a remote collaboration tool that allows two parties to jointly navigate the internet, documents, or more. A robust system of this type will minimize frustration by avoiding the need for customers to repeat information or input details they’ve already provided.
However, as customers increasingly rely on mobile devices, there is increasing pressure to provide these experiences in a mobile-first context.
Mobile banking for complex tasks
A notable change in this regard is in mobile banking behaviors. In previous years, there has been a strong bias in how customers use mobile. Whether due to trust, technological capabilities, or legacy behaviors dictated by traditional in-person experiences, customers have been reluctant to use mobile for complex transactions or tasks.
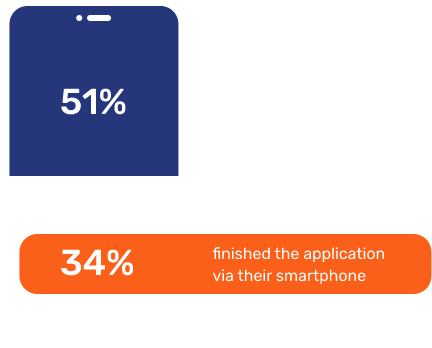
For the first time, this appears to be changing, signaling the beginning of a potential mobile hegemony in banking service contexts. According to Forrester, 51% of UK adults in 2022 with access to the internet who applied for a loan, carried out their research on a smartphone – a jump up from 34% in 2021. In total, 34% finished the application via their smartphone and 14% did it through their mobile app (Forrester).
It appears that with every year that passes, there is an increased reliance and tendency towards mobile. Although mobile banking is now a prerequisite for banking services, the battleground of experience has now entered the granular arena. The financial institutions that are able to offer a smooth, cohesive, and complete experience will succeed in the future.
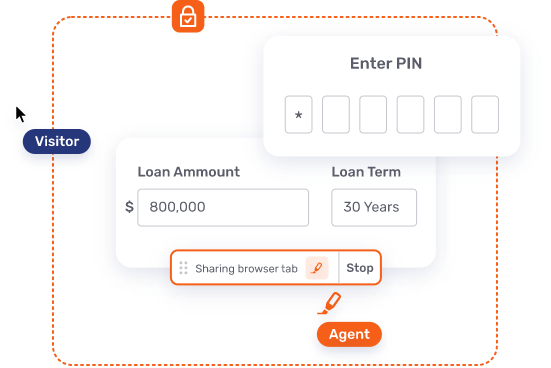
Mobile Co-Browsing or Co-Apping
A key tool to add to the conversational engagement experience is Mobile Co-Browsing or Co-Apping. Co-Apping – where agents and customers can remotely collaborate on an app in a secure environment – remains relatively underused when compared to conventional Co-Browsing. There aren’t as many available solutions on the market or widespread awareness.
However, organizations that have adopted this tool are discovering substantial value in its application. A recent example from an Unblu customer illustrates this trend, as their agents initiated 300,000 Co-Apping sessions to address customer issues in the initial year. In contrast, they conducted approximately 65,000 traditional Co-Browsing sessions during the same timeframe.
The area of unified communication channels is maturing and tools like Co-Apping – alongside AI-powered self-service capabilities – ensure a holistic experience for customers who use mobile platforms

Continued cybersecurity threats
Despite warnings and strategic hardening practices, cybersecurity remains a key concern in the financial world. As institutions evolve to face new threats, the nature of these threats change as well – becoming increasingly sophisticated as a result.
In response, there are cybersecurity and anti-fraud regulations, which are increasing the compliance burden on institutions. There is particular emphasis on managing risks associated with third- party vendors, which will require greater due diligence.
These regulatory pressures, combined with economic burdens, could speed up the consolidation of industry institutions as M&A agreements serve to mitigate risk (The Financial Brand).

Seamless and secure CX
Customer experience is once again at the forefront of retail banking trends. But continued annual resurgence of this issue does not mean the challenge is lessened for banks. Instead, it appears that financial institutions must take even greater steps to redefine digital experiences. Alongside more user-friendly mobile apps as previously discussed, this also requires leveraging automation and digitalization to improve speed in back-office processes (The Financial Brand).
According to Forrester, challenger banks and mutuals provide better CX experiences than traditional banks. In France, Germany, Italy, and the UK specifically, the survey found that traditional banks are below the industry average.
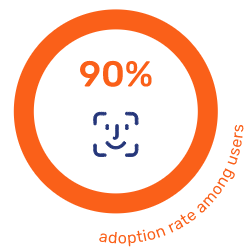
A part of this journey towards experience excellence, Digital ID is emerging as a fundamental aspect of improved end-to-end CX to more efficiently verify the user identity to reduce fraud and improve security. Governments – such as Denmark with its national ID – are leading the way in promoting this, with a 90% adoption rate among users. There is also an EU Digital Identify Wallet initiative underway to unify European digital identification, with other projects in the works in the US, Australia, Canada, and more (Capgemini).
Digital ID in Denmark
Cloud migration in financial services
The financial services industry has been historically slow to embrace cloud migration but we can confidently say this has now changed. Since 2020, there has been a huge push in this area, which is currently entering a new phase. In 2021, only 20% of large banks had undergone cloud migration as investments in scaling legacy systems and custom apps complicated the process and slowed adoption.
Challenges undoubtedly remain, but the tide is turning. Whereas cloud migration was initially used for business continuity and disaster management – spurred on by the COVID-19 pandemic – it is now entering a phase of maturity. This has shifted the focus from goals focused solely on cost reduction and productivity to a more innovative focus (Capgemini).

Financial institutions are increasingly changing how they deliver value to their customers as a result of this, exemplified by the rise of “as-a-service” or “as-a-platform” models. As such, financial services firms are better positioned to amalgamate capabilities from various providers to produce complex customer journeys (Forrester).
Branch closures even off
The ongoing trend of branch closures may begin to ease as consumer needs fall in line with branch availability. One report found that 72% claim that they will use their local branch at the same rate that they did the previous year, with 38% describing branches as essential (JD Power).
The fact is that branches continue to play an important role in communities, with many customers still preferring to visit them for complex advice. While most British and German customers use digital means to open accounts, in France and Italy in-person branches remain the main port of call for opening accounts (Forrester). What’s more, branches also contribute significantly to customer satisfaction and loyalty as in-person support promotes a sense of trust (Forrester).
As for consumer preferences, most survey respondents want more than simple transactional services at their branch. Self-service tools were the most requested, with 64% of customers opting for those, while 44% would like co-working options and 31% a more immersive experience. Almost half of respondents further said that they would like lifestyle products (hyper-personalized offers based on customer data that go beyond traditional finance offerings) to be available at their branch (Capgemini).

Approaches to phygital CX challenges
Changes in consumer behavior that move more frequently and sporadically between physical and digital platforms are challenging banks. Few have responded effectively to these changes and traditional branch channels feature multichannel silos that threaten smooth experiences.
The above findings suggest that the future of branches is more than viable, although not in the same format. For some, this means moving from branch-centric inbound models to more digital, outbound approaches (PWC). On the other hand, some banks are choosing to embrace physical experiences that are augmented or enhanced by digital channels, allowing for a more cost-effective and profitable branch network (Valiant Bank).
Key Takeaways
Embracing Generative AI:
The emergence of Generative AI presents both challenges and opportunities for banking institutions. While the technology promises significant value addition across various sectors, its infancy raises concerns regarding risks, regulation, and employee preparedness.
Mobile-Centric Banking Evolution:
Increasing reliance on mobile devices is reshaping banking behaviors, with a notable shift towards utilizing mobile platforms for complex transactions. The adoption of mobile Co-Browsing or Co-Apping, alongside AI-driven self-service capabilities, enhances customer experience and supports mobile-first communication channels.
Hybrid Physical-Digital Banking Experience:
Banks are reimagining their branch networks to adapt to changing consumer preferences, leveraging digital solutions to augment physical experiences. The convergence of physical and digital channels, coupled with a focus on seamless and secure customer experiences, signifies the evolution of the phygital banking landscape.

