|
This document describes version 5 of Unblu. If you’re using the latest major version of Unblu, go to the documentation of the latest version. The support period for version 5 ended on 22 November 2021. We no longer provide support or updates for this version. You should upgrade to the latest version of Unblu. |
Database Persistence Layer - Introduction to the Database
Unblu requires a database as persistence layer to store configuration information (users, teams, named-areas, API-keys, canned responses, conversation templates, account…) and operational data (messages exchanged during conversations).
It is possible to run the collaboration server with an embedded in-memory database, but this is not recommended in production.
| Some personally identifiable information (PII) is stored in the Unblu database. This must be taken into consideration when deciding on the deployment details of the database. |
Features
-
Supports multiple RDBMS.
-
Initial table creation and subsequent updates are performed automatically by Unblu.
-
Operational data, structure setup data, and statistic data can be separated into individual databases.
Supported Platforms
Unblu is compatible with following database platforms:
-
Oracle ≥ V11.2g
-
Microsoft SQL ≥ V2012
-
MySQL ≥ V5.5
-
PostgreSQL ≥ V9.1.22
-
MariaDB ≥ 10.1 Series
Database Setup
Before setup you must ensure the prerequisites are in place:
-
The database must be created by a DB Admin with DBO privileges. The initial database creation must be performed manually and may differ slightly between database types. For example, some types require only a database (Unblu creates the schema), some require a database and schema. The DB schema will be set up by the Unblu system on initial startup.
-
The default charset must be UTF8.
-
The initial DB size requirement is small: < 20MB. (See Note below)
-
The DB size will grow as the system is used and session audit trails are logged. From Unblu version 4.2 these sessions only add a small amount of data (< 20KB per session) to the database when the information stored is purely of textual nature.
| Document sharing will negate these numbers. You can upload files via the file manager and store these in the database or cloud (AWS S3) or disk. If you configure in the database then < 20MB will be too low. You should consult your DB Admin on these matters. For example, while document sharing increases storage requirements it is possible to use, for example, a Remote Blob Store (RBS) provider to add capacity: |
Server Recommendations
For the database itself, two users are required:
-
User with database owner (DBO) privileges. The DBO must have rights to execute the following statements: CREATE, ALTER, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, DROP.
-
Regular DB user with rights to execute the following statements: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT (on Unblu-specific schemas).
On initial setup of the system, the server must be started with DBO privileges so that the DB structure can be established. Once set up, the server will run with the regular user, ensuring that security policies inside large organizations can be adhered to.
| Subsequent Unblu updates will require a start with DBO privileges. |
Configuring Different Database Types
There is a separate configuration for each database type. The following specific configurations per database type need to be established.
| In all of the cases below the user and schema must be created manually. |
| For the sake of convenience all users and schemas listed here are called 'unblu'. You may use any name you wish. |
Oracle Preconditions
| For a deeper insight into SSL with JDBC Oracle thin driver see: SSL With Oracle JDBC Thin Driver |
User unblu GRANT "RESOURCE" TO unblu WITH ADMIN OPTION; GRANT create session to unblu; + ALTER USER unblu DEFAULT ROLE "RESOURCE";
Oracle Configuration Settings
Example:
Note that <ip>:1521:xe in the settings below is a placeholder and must be changed to represent the hostname/listening port/database name.
com.unblu.storage.database.platform=org.eclipse.persistence.platform.database.OraclePlatform com.unblu.storage.database.driver=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver com.unblu.storage.database.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@<ip>:1521:xe com.unblu.storage.database.user=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.password=<pwd> com.unblu.storage.database.schema=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.liquibaseSchema=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.adminUser= com.unblu.storage.database.adminPassword=
MySQL Preconditions - WARNING!
| We have observed three serious issues that can occur when using the default MySQL configuration (Linux and Windows). |
Before creating the schema you must override the MySQL defaults using the instructions below.
1. MySQL - Handling Emojis
There is some special configuration you must perform in order to avoid an SQL exception when users enter emojis into the chat box.
| This change is required as emojis require 4 bytes and the default MySQL can only handle 3 bytes. |
Add the code below to the my.cnf file (in Unix) or the my.ini file (Windows) under [mysqld].
Example:
[mysqld]
character-set-server=utf8mb4
2. Set File Upload Size Limitations
Add the code below to the my.cnf file (in Unix) or the my.ini file (Windows) under [mysqld], and substitute your maximum allowed file size for upload.
Example:
[mysqld]
max_allowed_packet=<size> (Example: 16M)
| The maximum file size is 1 Gigabyte <1G>. |
| You can check the current maximum file size using the following code: |
sql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'max_allowed_packet';
3. Fix MySQL Default Code
In MySQL Workbench run the query below to check if the problem exists in your system:
show variables like sql_mode;
Then check the output. If the sql-mode variable contains either or both of the two entries NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE then perform the steps below. (If neither of these two entries is present in the variable then ensure you have performed the fix for emojis and carry on with creating the schema.)
Example of problem code:
'sql_mode',
'ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE, ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION'
On Linux: To fix the problem open the my.conf file in /etc/mysql for editing and cut the two entries:
NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE
Also ensure that the command [mysqld] which runs the MySQL server daemon is present. The picture below is an example of what the line might look like after editing.
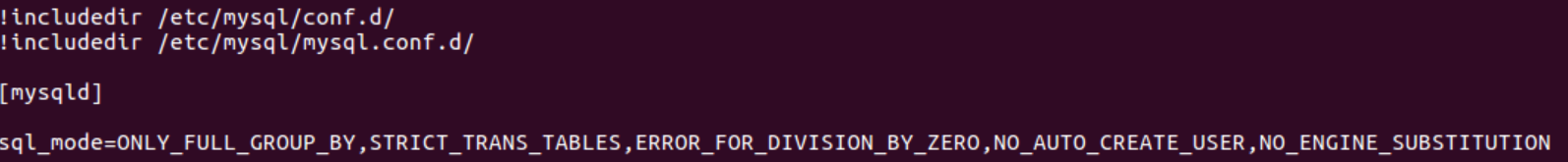
On Windows: To fix the problem open the my.ini file in C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server (version#) then cut the entries NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE and save the file.
User unblu
Schema unblu
To create the Unblu schema run the following:
create database Unblu DEFAULT CHARACTER SET = utf8 DEFAULT COLLATE utf8_general_ci
MySQL Configuration Settings
Example:
Note that <ip>:3306/unblu in the settings below is a placeholder and must be changed to represent the hostname/listening port/database name.
com.unblu.storage.database.platform=org.eclipse.persistence.platform.database.MySQLPlatform com.unblu.storage.database.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver com.unblu.storage.database.url=jdbc:mysql://<ip>:3306/unblu com.unblu.storage.database.jdbcProperties=connectTimeout=60000,socketTimeout=60000,useUnicode=yes,characterEncoding=UTF-8,useLegacyDatetimeCode=false,serverTimezone=UTC,autoReconnectForPools=true com.unblu.storage.database.user=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.password=<pwd> com.unblu.storage.database.schema=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.adminUser= com.unblu.storage.database.adminPassword=
Microsoft SQL Configuration Settings
Example:
Note that: <server-name>:1433;DatabaseName=unblu in the settings below is a placeholder and must be changed to represent the hostname/listening port/database name.
com.unblu.storage.database.platform=org.eclipse.persistence.platform.database.SQLServerPlatform com.unblu.storage.database.driver=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver com.unblu.storage.database.url=jdbc:sqlserver://<server-name>:1433;DatabaseName=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.user=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.password=<pwd> com.unblu.storage.database.schema=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.liquibaseSchema=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.adminUser= com.unblu.storage.database.adminPassword=
PostgreSQL Preconditions
User unblu (Privileges: Can create databases)
Schema unblu_liqu (Privileges: User: unblu ≥ USAGE + CREATE)
PostgreSQL Configuration Settings
Example:
Note that: <ip>:5432/postgres in the settings below is a placeholder and must be changed to represent the hostname/listening port/database name.
com.unblu.storage.database.platform=org.eclipse.persistence.platform.database.PostgreSQLPlatform com.unblu.storage.database.driver=org.postgresql.Driver com.unblu.storage.database.url=jdbc:postgresql://<ip>:5432/postgres com.unblu.storage.database.user=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.password=<pwd> com.unblu.storage.database.main.schema=unblu_main com.unblu.storage.database.stats.schema=unblu_stats com.unblu.storage.database.liquibaseSchema=unblu_liqu com.unblu.storage.database.adminUser= com.unblu.storage.database.adminPassword=
MariaDB Preconditions
User unblu
Schema unblu
To create the Unblu schema run the following:
create database unblu DEFAULT CHARACTER SET = utf8 DEFAULT COLLATE utf8_general_ci
MariaDB Configuration
com.unblu.storage.database.platform=org.eclipse.persistence.platform.database.MySQLPlatform com.unblu.storage.database.driver=org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver com.unblu.storage.database.url=jdbc:mysql://<ip>:3310/unblu com.unblu.storage.database.jdbcProperties=connectTimeout=60000,socketTimeout=60000,useUnicode=yes,characterEncoding=UTF-8,useLegacyDatetimeCode=true,serverTimezone=UTC,useSSL=false com.unblu.storage.database.user=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.password=<pwd> com.unblu.storage.database.schema=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.liquibaseSchema=unblu com.unblu.storage.database.adminUser= com.unblu.storage.database.adminPassword=
All Possible Database Settings
All of the configurations below can be added at the schema level. For example, the statistics database can become very large over time and it may be that you would want to use a separate server for the statistics database. Connection and pool parameters can be added to the configuration file. In such a case all other schemas would use the default connection pool.
com.unblu.storage.database.platform com.unblu.storage.database.driver com.unblu.storage.database.url com.unblu.storage.database.jdbcProperties com.unblu.storage.database.user com.unblu.storage.database.password com.unblu.storage.database.schema com.unblu.storage.database.liquibaseSchema com.unblu.storage.database.adminJdbcProperties com.unblu.storage.database.adminUser com.unblu.storage.database.adminPassword com.unblu.storage.database.poolInitial com.unblu.storage.database.poolMax com.unblu.storage.database.readPoolUrl com.unblu.storage.database.readPoolUser com.unblu.storage.database.readPoolPassword com.unblu.storage.database.readPoolInitial com.unblu.storage.database.readPoolMax com.unblu.storage.database.adminUser= com.unblu.storage.database.adminPassword=