This year, customer experience is less about the big transformation initiatives and more about finding avenues for differentiation through customer-centricity.
The reason for this is because most banks have already attained a certain level of maturity, with only a few remaining that are starting entirely from scratch. Instead, the spotlight is now shifting towards continuous digital transformation.
More than half (53%) of decision-makers at banks report ongoing efforts to enhance their digital transformation endeavors, marking a 20% increase since 2021.
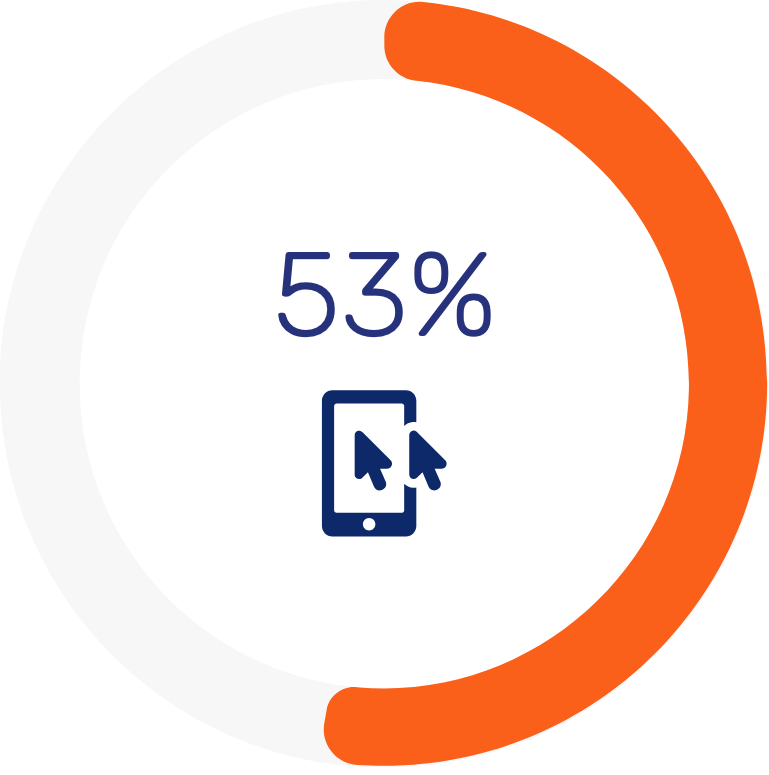
Over half of bank decision-makers (53%) are actively advancing their digital transformation efforts.
Despite the overall positive trend, not all banks share the same success story. Surprisingly, 1% still claim they have no interest whatsoever in digital transformation, and another 8% have no plans for implementation initiatives. Moderately better, 10% are still in the planning phase, signifying that a combined 19% of global banking decision-makers have yet to leverage the potential of digital experiences.
For the 10% in the planning stage, a number of barriers are hindering progress. Among the surveyed individuals, 33% cite the company’s technology strategy as one of the most challenging aspects of their role. This is accompanied by related challenges in data and project management, with 29% and 27% respectively.
1. Mobile-first communication channels
Contact center managers are continuing their efforts to streamline operations by reducing the complexity of vendor relationships they manage. The aim is to enhance customer choice and flexibility while delivering improved interaction experiences through features like video chat or Co-Browsing. A well-established system of this nature can alleviate frustration by eliminating the need for customers to repeat information or input details they’ve already provided.
However, with the growing reliance on mobile devices among customers, there is a mounting demand to offer these experiences within a mobile-first context. One crucial tool to enhance the conversational engagement experience in this context is Mobile Co-Browsing or Co-Apping. Despite being less commonly used compared to traditional Co-Browsing, there aren’t a huge number of solutions on the market and limited awareness.
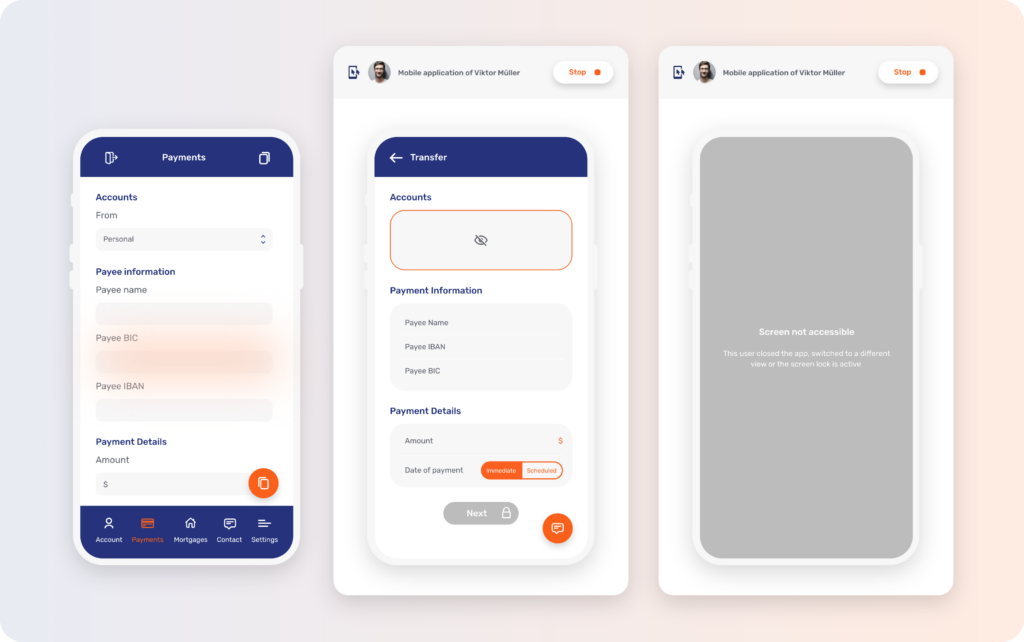
Organizations that have embraced this tool are realizing substantial value in its application, both in avoiding poor experiences and maximizing remote human interaction. A recent example from a Unblu customer illustrates this, with their agents initiating 300,000 Co-Apping sessions to address customer issues in the first year, compared to approximately 65,000 traditional Co-Browsing sessions during the same period.
2. Branch closures even off
Recent years have shown us that traditional branches are struggling to remain viable. But this year we may see this trend taper off as consumer preferences align more closely with the availability of branches. According to a JD Power report, 72% of customers express their intention to utilize their nearby branch at a comparable frequency to the previous year, and 38% consider branches to be indispensable.
It is clear that branches maintain a crucial role in communities, as a considerable number of customers still favor visiting them for more complex advice. Although the majority of British and German customers employ digital methods to initiate account openings, in France and Italy, in-person branches remain the primary choice for such transactions. Additionally, branches play a substantial role in enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty, as in-person support fosters a feeling of trust.
Regarding consumer preferences, the majority of survey participants would like more in-depth services at their branch. The most sought-after feature is self-service tools, with 64% of customers expressing a preference for them. Additionally, 44% are interested in co-working options, and 31% desire a more immersive and personalized experience. Nearly half of the respondents also indicated a desire for lifestyle products and offerings to be accessible at their branch.
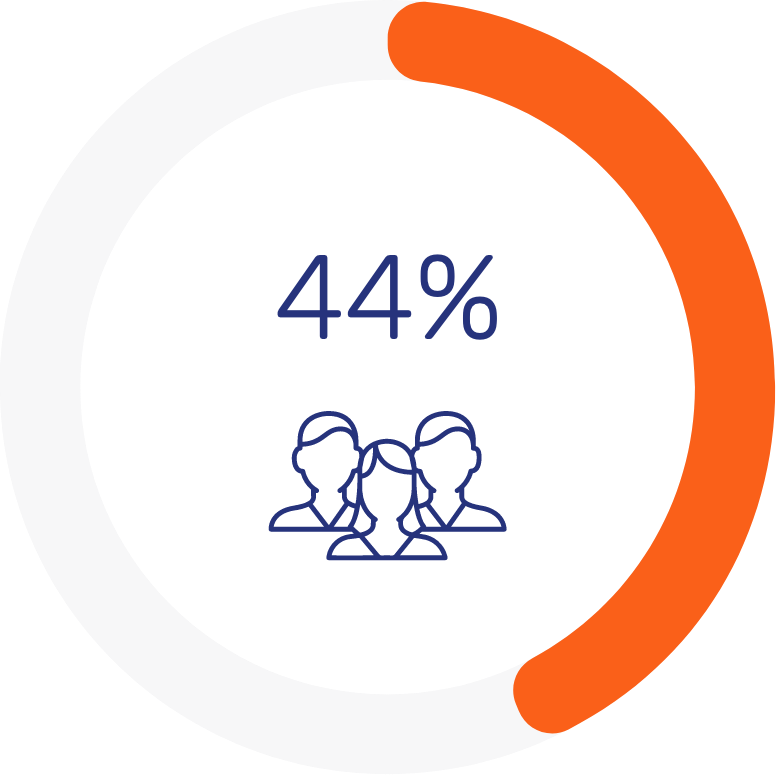
44% of customers show interest in co-working spaces within their banking branches.
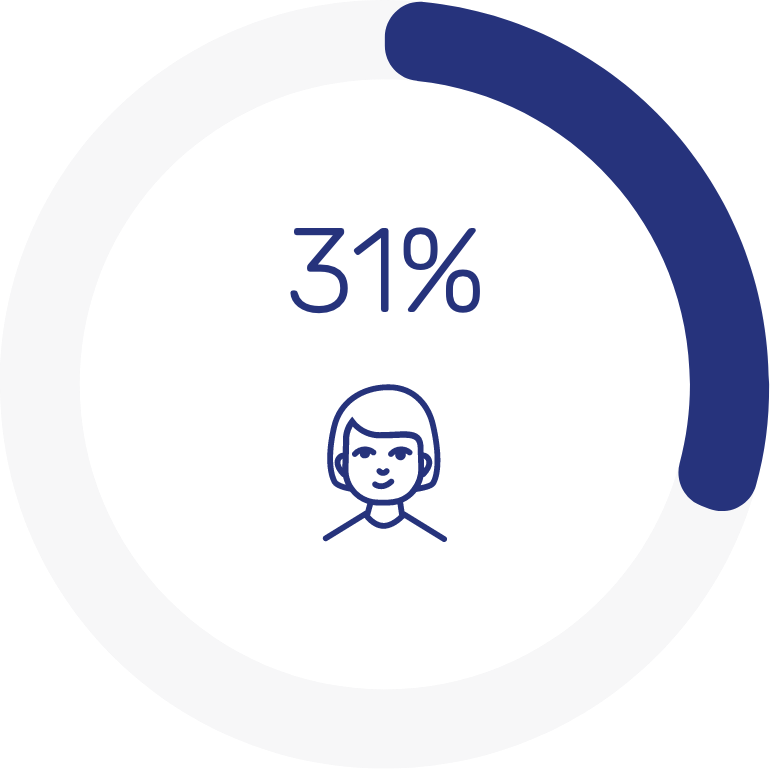
A significant 31% of customers are seeking a more immersive and personalized banking experience.
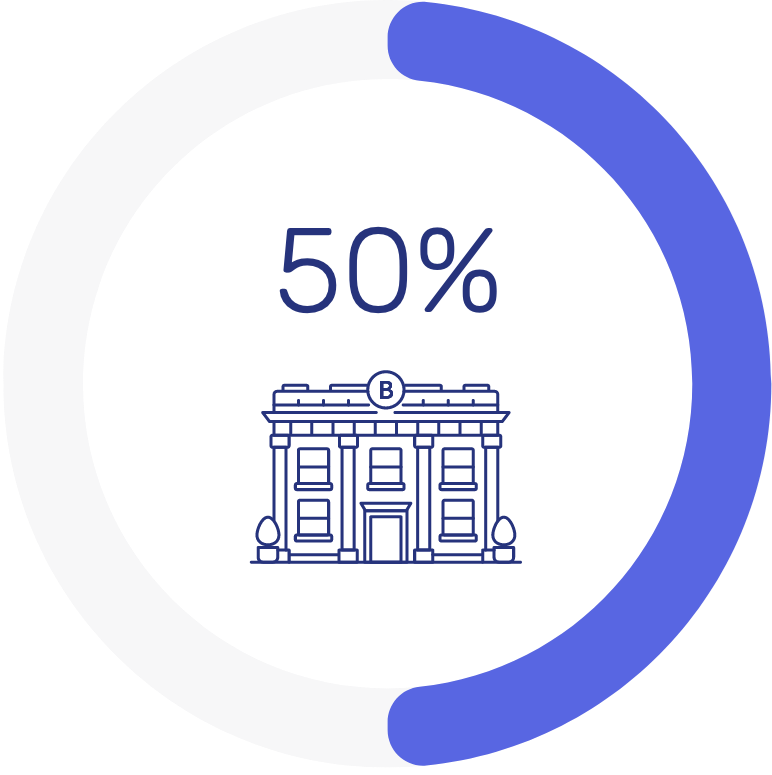
Nearly 50% of survey respondents want lifestyle products and services available at their bank branches
Given these findings, it becomes clear that the future of branches is strong, provided they take on different forms. Several approaches are surfacing to address these challenges, such as repurposing branches into community hubs and providing enhanced digital yet in-person experiences.
Want to find out more?

3. Generative AI: Challenges and opportunities
In 2023, Generative AI made a significant impact, reshaping our collective understanding of the capabilities of artificial intelligence. According to a McKinsey survey, approximately two-thirds of leaders in digital and analytics at the senior level anticipate that Generative AI will bring about fundamental changes in their business practices.
This comes as no surprise, considering that Generative AI has the potential to contribute up to $4.4 trillion in annual value across the 63 examined use cases, according to the McKinsey Global Institute. Specifically, in the corporate and retail banking sectors, the technology is projected to bring an additional $56 billion and $54 billion, respectively.
However, it’s important to understand that this technology is still in its early stages. Generative AI’s quick emergence left little room for banking leaders to prepare their employees, attract fresh talent, or navigate associated risks – especially for those keen on staying abreast of new advancements. Forrester anticipates that at least eight neobanks and two established financial institutions will face a Generative AI-related crisis, leading them to regulatory scrutiny.
The overall risk associated with Generative AI is prompting industry observers to advocate for the implementation of new regulations by both national and local governments to address these concerns.
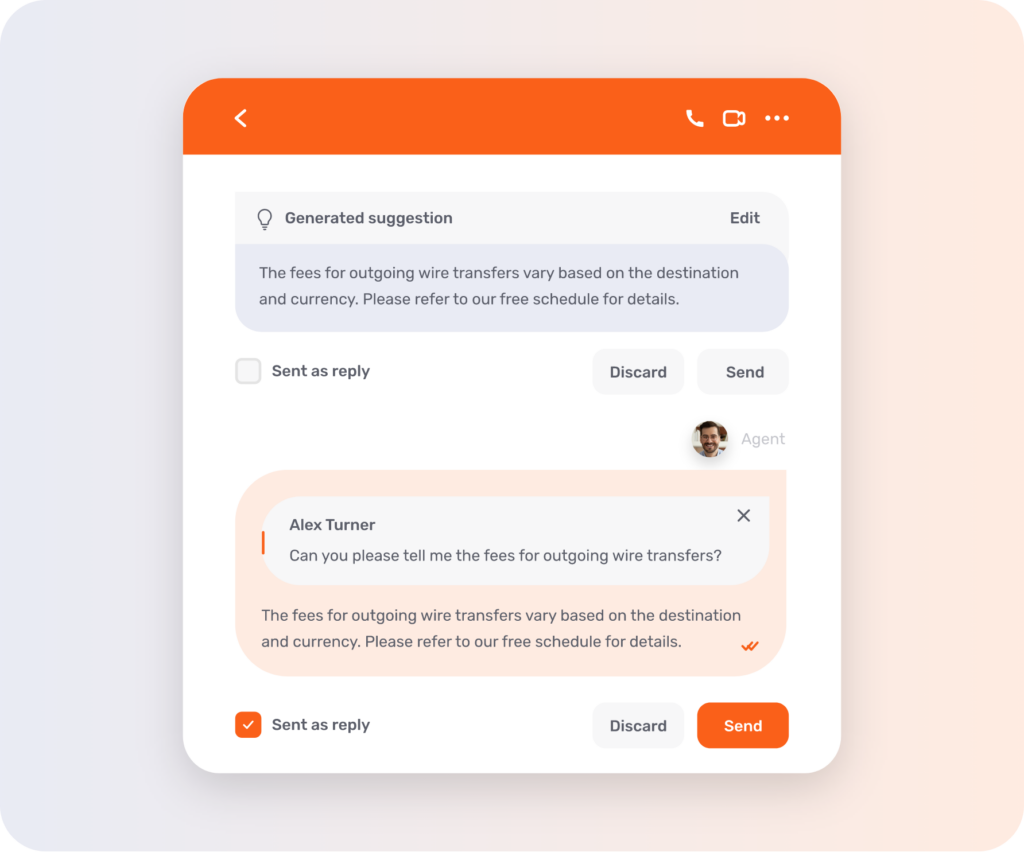
This doesn’t imply that all applications of Generative AI should be avoided. There are particular scenarios where the technology is not only safe but also exceptionally efficient. A case in point is the utilization of Generative AI in Unblu’s Conversational AI offering.
Through harnessing Generative AI, businesses can tap into existing knowledge bases using LLMs, utilize the bot trainer assistant for improved intents, and enhance the efficiency of Live Chat operations.
4. Hyper-personalization: The shaky world of niche journeys
There is a growing trend of neobanks concentrating on specialized market segments tailored to specific target identities. Instances of this trend include Daylight, a banking platform for the LGBTQ+ community, Credit Karma specializing in loans, and Aspiration, which is dedicated to sustainability-focused banking.
However, not every neobank within these niches is guaranteed to thrive. For instance, Daylight has already declared its closure due to issues stemming from mis-management. Some may have to pivot or undergo acquisition since the market for these specialized offerings is not yet sufficiently mature for sustained expansion.
This doesn’t imply that these strategies lack value altogether. If anything, the emergence of inclusive finance has demonstrated the existence of a demand and potential profitability. Expanding on this, fintech companies or traditional institutions are likely to capitalize on this insight, possibly through acquisitions, to offer products and positive experiences tailored to extremely specific customer journeys.
Although these specialized journeys are not commonplace, when they do align with customer needs, they prove to be exceptionally effective. A case in point is Settld, a financial platform that specifically caters to individuals dealing with the loss of loved ones.
5. A boom in embedded finance
Embedded finance – meaning the provision of financial services through non-financial channels – is undergoing a surge in growth. In total, 72% of those surveyed anticipate that a majority of financial products will be delivered through this method.
Several applications in Asia are taking the lead in this by integrating e-commerce, rewards, travel booking, on-demand services, games, and more into their lifestyle platforms. Notable instances include Singapore’s Grab and Indonesia’s Gojek platform, which utilize data from deliveries, taxi applications, and digital wallets to develop financial products for underserved customers.

Through the utilization of open data, they can effectively evaluate risk levels even in the absence of credit reference agencies.
6. The benefits (and drawbacks) of open banking
Open banking is a significant advancement in enhancing positive customer experience, empowering individuals to have a clearer insight into their data, investments, and overall financial well-being. This advantage extends to fintech companies, particularly those that function as secondary accounts for customers.
However, for traditional incumbents, the transition to open banking is a double-edged sword as it challenges the foundations of their business models. Incumbent banks find themselves compelled to acknowledge and adopt the value of open banking, foreseeing increased collaboration partnerships with fintech entities.
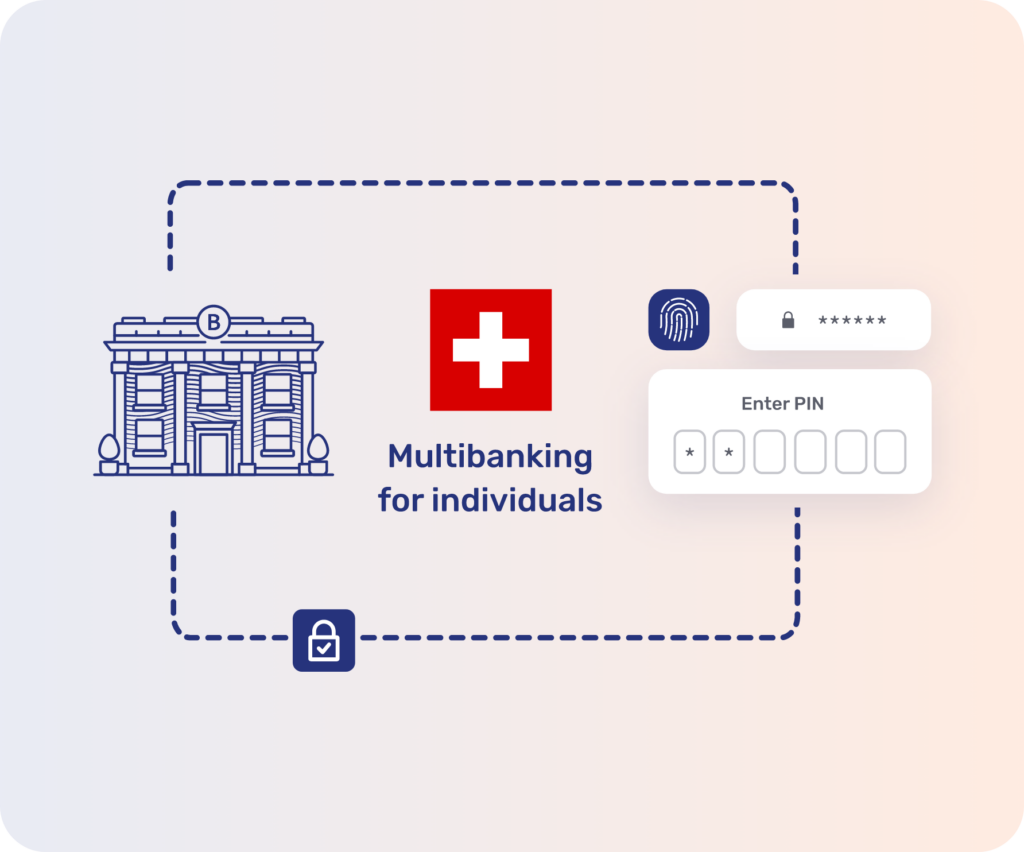
The EU PSD2 directive has been in effect at a Union-wide level since 2018 and Switzerland is poised to follow suit. The Swiss Bankers Association (SBA) signed a “Memorandum of Understanding,” aiming to implement multibanking by the year 2025.
Despite these changes, it doesn’t necessarily imply negative implications for banks. Collaborating with fintech companies allows them to integrate financial services into their touchpoints and products, enhancing the overall customer experience as a result. In 2024, the primary focus of all initiatives should be customer-centricity. Changes that might seem to relinquish traditional power should be viewed as positive steps as long as they contribute to improving the customer experience.
Customer-centricity is the goal in 2024
This year, business leaders in the banking industry should focus on providing superior customer experiences through customer-centricity. Customer expectations are continuing to evolve and driving customer loyalty is no easy task.
The banks that will come out on top are those that provide robust digital channels (that avoid poor customer experiences) and a differentiated product offering. By providing a mix of mobile banking apps, physical branches, and niche products that cater to the entire customer journey, financial sector professionals will be better positioned to drive revenue growth while avoiding bad customer experiences.
Want to find out more about the current state of the financial services industry?
Download our 2024 Retail Banking Trends report here.





 Interaction Management Hub
Interaction Management Hub Secure Messenger
Secure Messenger Video & Voice
Video & Voice



